In this article, you will learn:
- What the new Claude Skills mechanism is and how it works.
- Why it does not replace MCP tools but instead works perfectly together with them.
- How to integrate Claude Desktop, API, and Code with Bright Data’s Web MCP and Skills for an improved AI experience.
Let’s dive in!
What Are Claude’s Skills?
On October 16, 2025, Anthropic announced the introduction of Agent Skills in Claude.
In the context of Claude, “Skills” are modular folders that contain instructions, scripts, and resources defined to enhance the model’s performance on specific tasks. More in detail, each Skill acts like a mini knowledge package, teaching Claude how to perform specialized workflows (e.g., data analysis, document creation, applying brand guidelines, and more).
Instead of relying solely on general reasoning, Claude dynamically loads only the relevant Skills when needed—keeping responses both fast and focused.
From a technical perspective, every Skill consists of a directory containing at least a SKILL.md file. That serves as the core of the Skill and must begin with YAML front matter that defines the required metadata, such as the name and description. Also, the file may include additional metadata, task instructions, reference files, executable scripts, or tools.
Currently, there are two main types of Skills:
- Anthropic Skills: Prebuilt by Anthropic for common tasks (e.g., PowerPoint creation, GIF creation, etc.).
- Custom Skills: Created by users or organizations to capture their own workflows and best practices.
Skills are composable and portable. That means they can be combined, reused across Claude apps and the API, and load only the necessary components when required.
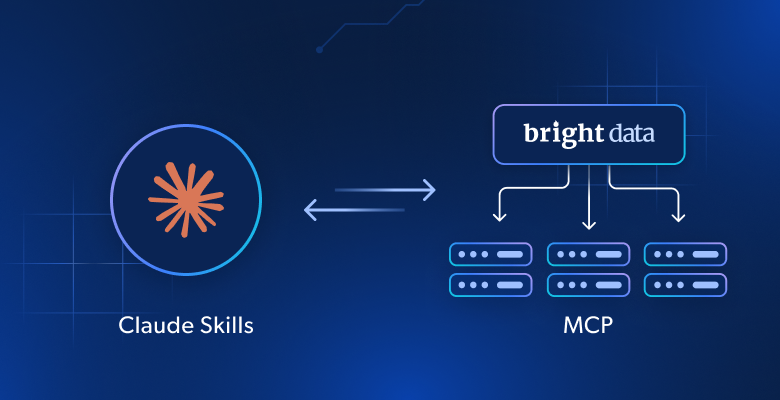
Why Utilize MCP Together with Claude Agent Skills
Now, you might think that Skills are just a new version of the tools exposed by an MCP server, but that is not quite right…
MCP connects Claude (or any other AI model) to external systems such as APIs, databases, or cloud apps. It acts as a bridge that lets the model fetch real-time data or trigger external actions.
For instance, Bright Data’s Web MCP server gives AI models access to over 60 tools for web data retrieval and integration. Those capabilities are powered by API calls to Bright Data servers, which deliver a range of cloud-based solutions.
The main limitation of the MCP technology, however, is that it is token-heavy. It requires detailed context about available endpoints, parameters, and responses. That is also why Bright Data offers two modes for its Web MCP:
- Free tier mode: Includes only a few simple tools, reducing token usage since Claude does not need to process large lists of available tools. Learn more about the Web MCP free tier.
- Pro mode: Provides full access to all 60+ tools but consumes more tokens as the AI must understand and reason across all available options.
On the other hand, Skills are self-contained knowledge modules. They are essentially folders that include instructions, scripts, and resources that teach Claude something. Thus, unlike MCP, Skills do not rely on external connections. They just give Claude procedural know-how it can load whenever needed.
The key takeaway is that Claude Skills and Web MCP tools serve different yet complementary purposes. When used together, they are incredibly cooperative. MCP provides access to external data and tools, while Skills can provide expertise to the AI on how to use them.
In short, Skills do not replace MCP tools. Quite the opposite, they can make Claude smarter in how it uses them.
How to Build an AI Agent with Access to Web MCP and Skills in Claude Desktop
In this guided tutorial, you will learn how to equip a Claude model with tools from Bright Data Web MCP and Skills. In particular, you will see that enhanced AI agent in action through a news + video retrieval scenario.
Note: What follows is just an example. You can easily adapt it to other use cases by modifying the final prompt. Also, the same procedure also works in the web version of Claude (also knwon as Claude.ai). The only thing you need to change is the Web MCP integration, which must pass through the remote version of Web MCP.
Follow the instructions below!
Prerequisites
To follow along with this article, make sure you have:
- Claude Desktop installed locally.
- A Claude account on one of the following plans: Pro, Max, Team, or Enterprise.
- A Bright Data account with an API key ready.
After installing Claude Desktop locally, click on your account icon and verify that you are on one of the required plans:
Next, we will assume that your Claude Desktop instance is already integrated with Bright Data’s Web MCP. For detailed guidance, refer to the official Claude Desktop integration guide.
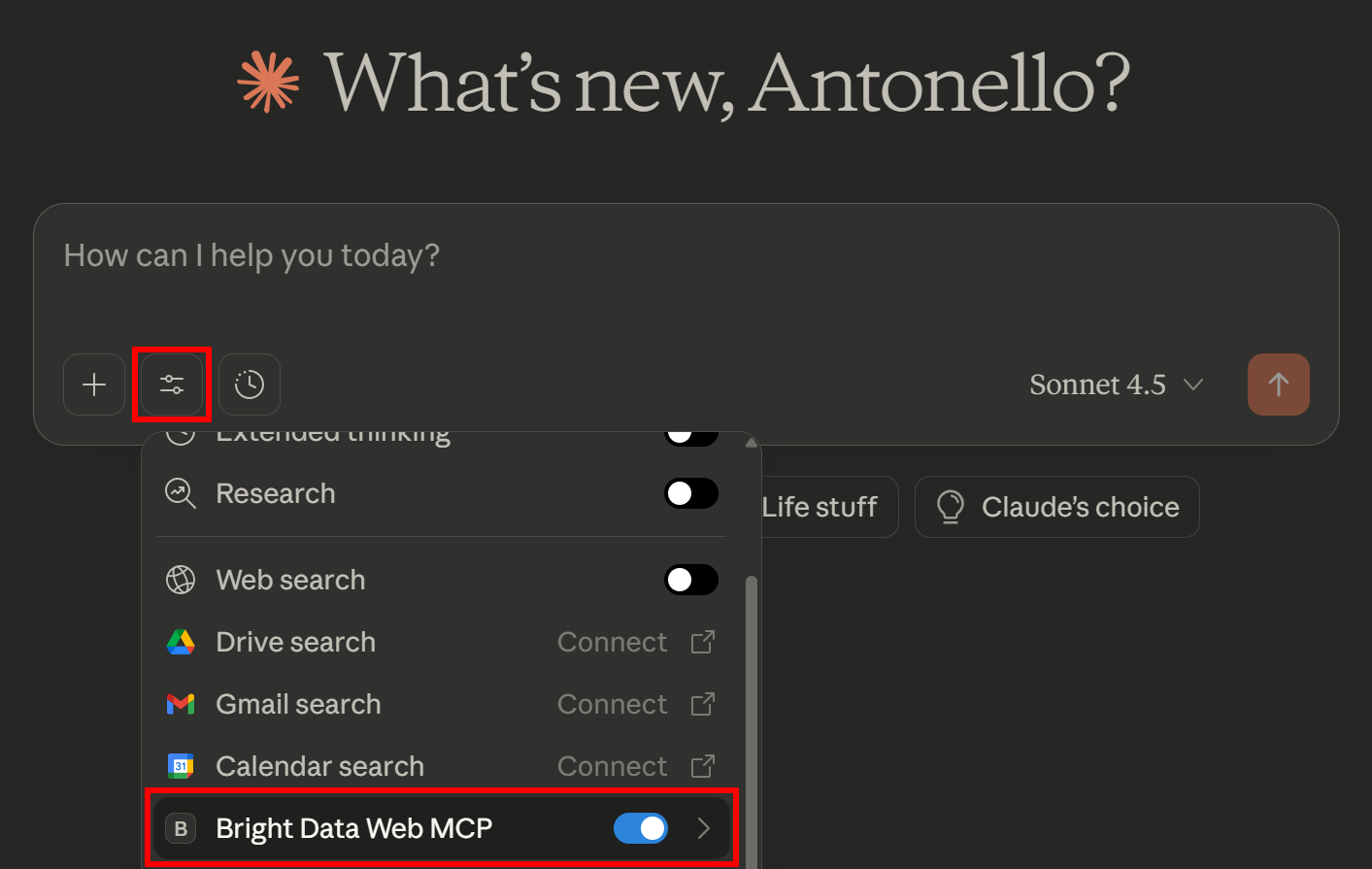
We will also suppose that the Bright Data Web MCP integration is enabled (free tier mode is enough):
Remember: Bright Data’s Web MCP acts as a Claude MCP server.
Great! You now have everything you need to test MCP + Skills integration in Claude.
Step #1: Enable Agent Skills in Claude
As of this writing, Agent Skills is still a beta feature and is disabled by default. Thus, to harness it, you must first enable it.
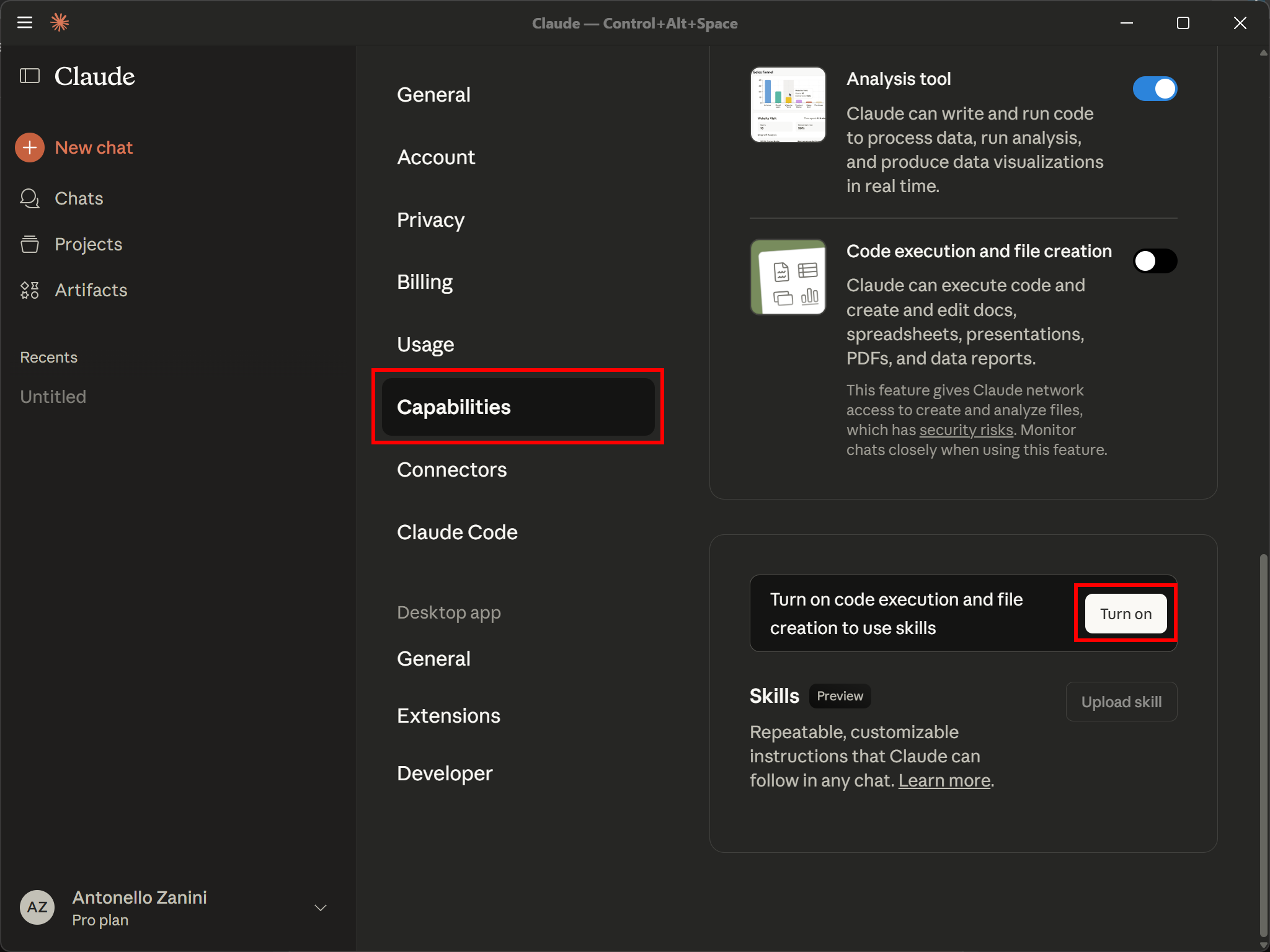
To do so, click on your user profile in the bottom-left corner and select the “Settings” option:
In the “Settings” section, open the “Capabilities” panel, and in the “Skills” section, press the “Turn on” button:
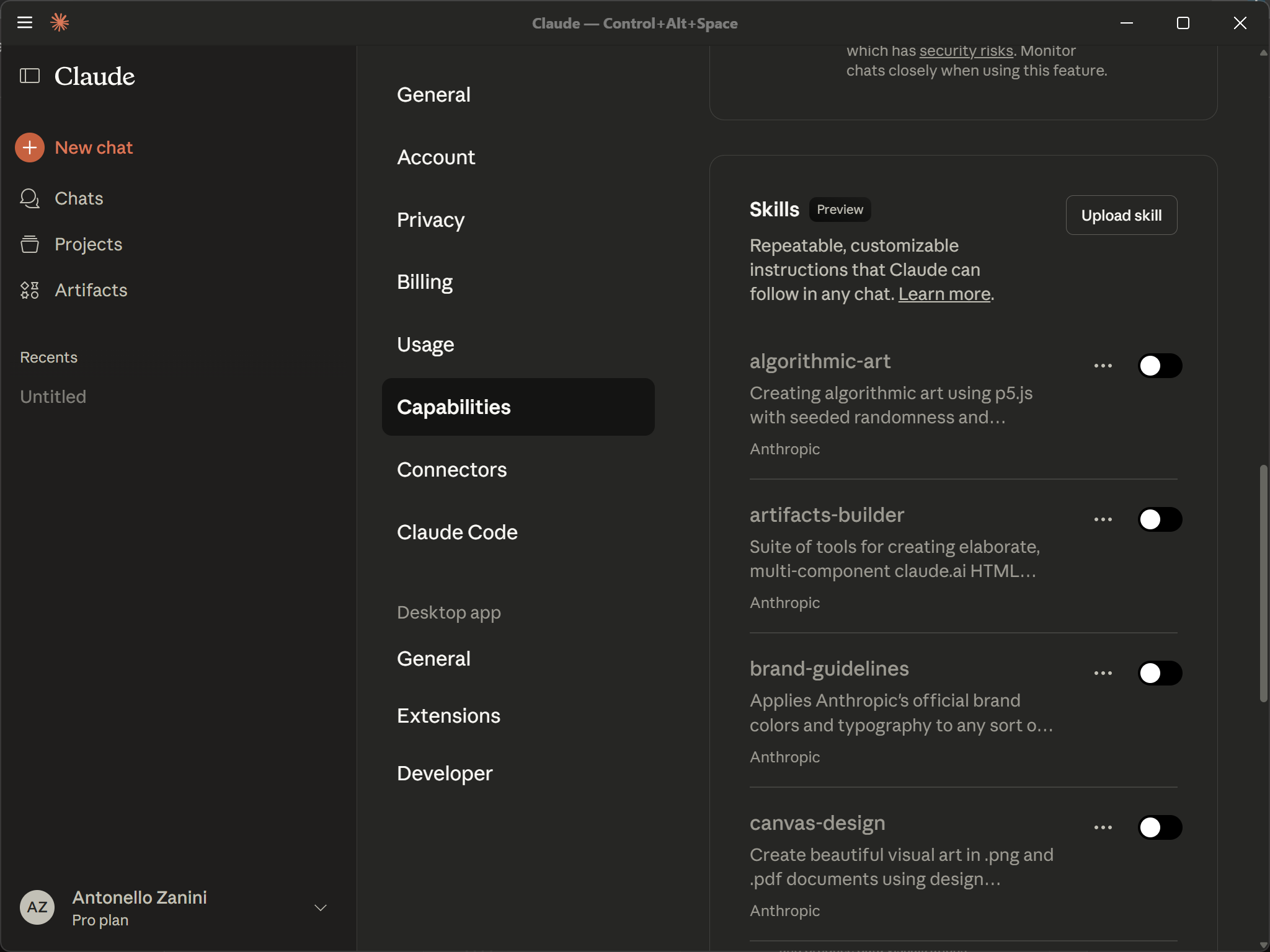
This will automatically check the “Code execution and file creation” option and allow you to activate the pre-configured Claude Skills, as shown below:
You will now be able to activate single Skills by toggling them.
Awesome! Skills are now ready to be used in your Claude integration.
Step #2: Add Custom Skills
By default, Claude offers you a set of Skills. If you are wondering where those Skills come from, take a look at the official anthropics/Skills repository.
In summary, the default Skill are:
algorithmic-art: Create generative art using p5.js with seeded randomness, flow fields, and particle systems.artifacts-builder: Build complex Claude.ai HTML artifacts using React, Tailwind CSS, and shadcn/ui components.brand-guidelines: Apply Anthropic’s official brand colors and typography to artifacts.canvas-design: Design beautiful visual art in .png and .pdf formats using design philosophies.internal-comms: Write internal communications such as status reports, newsletters, and FAQs.mcp-server: Guide for creating high-quality MCP servers to integrate external APIs and services.slack-gif-creator: Create animated GIFs optimized for Slack’s size constraints.Skill-creator: Guide for creating effective Skills that extend Claude’s capabilities.template-Skill: A basic template to use as a starting point for new Skills.theme-factory: Style artifacts with 10 pre-set professional themes or generate custom themes on-the-fly.webapp-testing: Test local web applications using Playwright for UI verification and debugging.
Now, suppose you want to add new Skills to your Claude integration. This is what makes Skills special, as you can easily upload more Skills and let the AI model use them. To discover interesting Skills, take a look at the the ComposioHQ/awesome-claude Skills repository. Also, check out Bright Data’s awesome Claude skills.
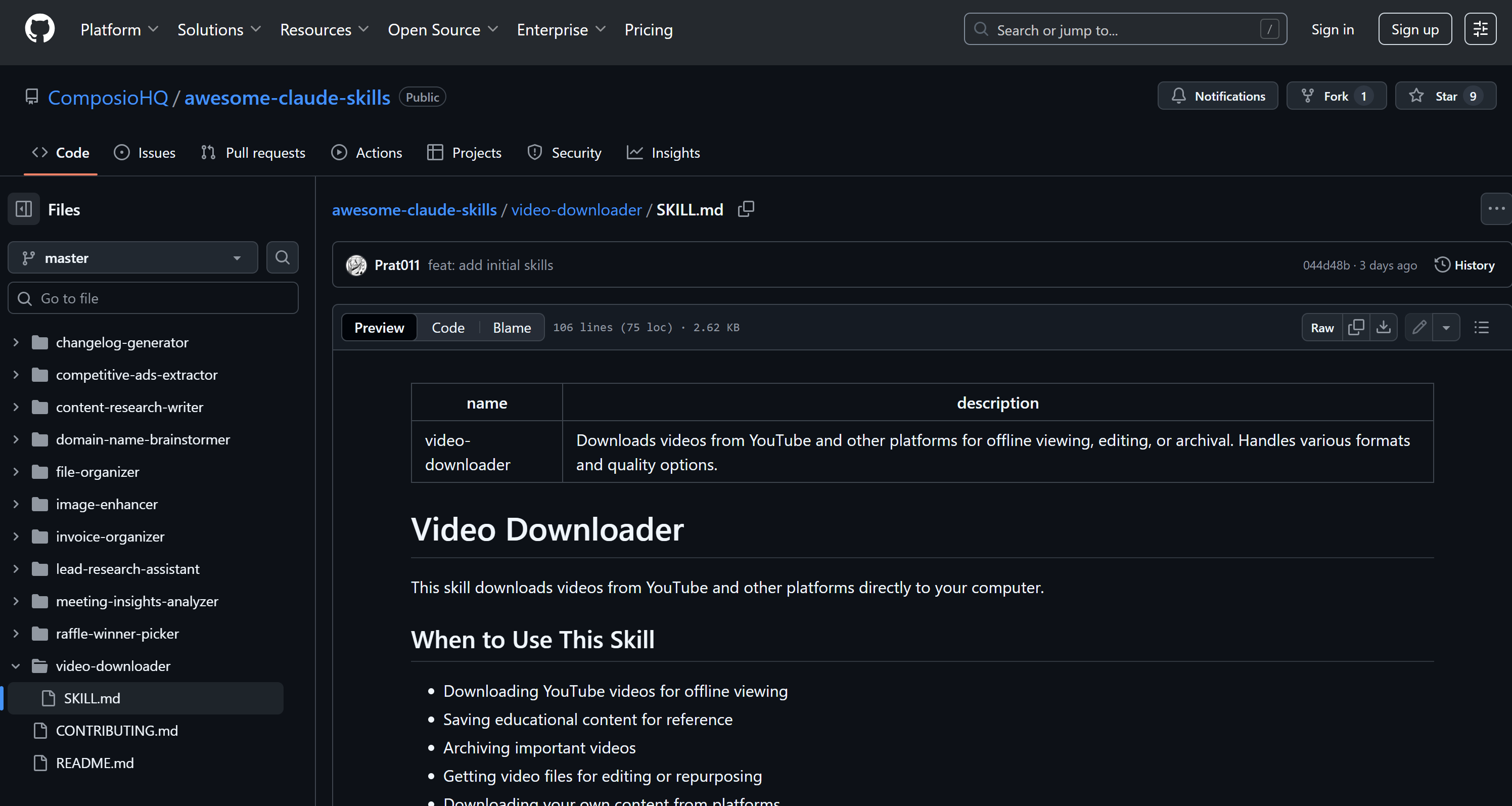
For example, consider the “Video Downloader” Skill, which allows Claude models to download videos from YouTube and similar platforms:
Close the ComposioHQ/awesome-claude-Skills repository, navigate to the “Video Downloader” (i.e., video-downloader/) Skill folder, and turn it into a ZIP file:
git clone https://github.com/ComposioHQ/awesome-claude-Skills/
cd awesome-claude-Skills/video-downloader
zip -r video-downloader-Skill.zip .Note: You can also do this without the CLI. The goal is to create a .zip file containing the SKILL.md file in the awesome-claude-Skills/video-downloader folder. This is the required format for Claude Skill import.
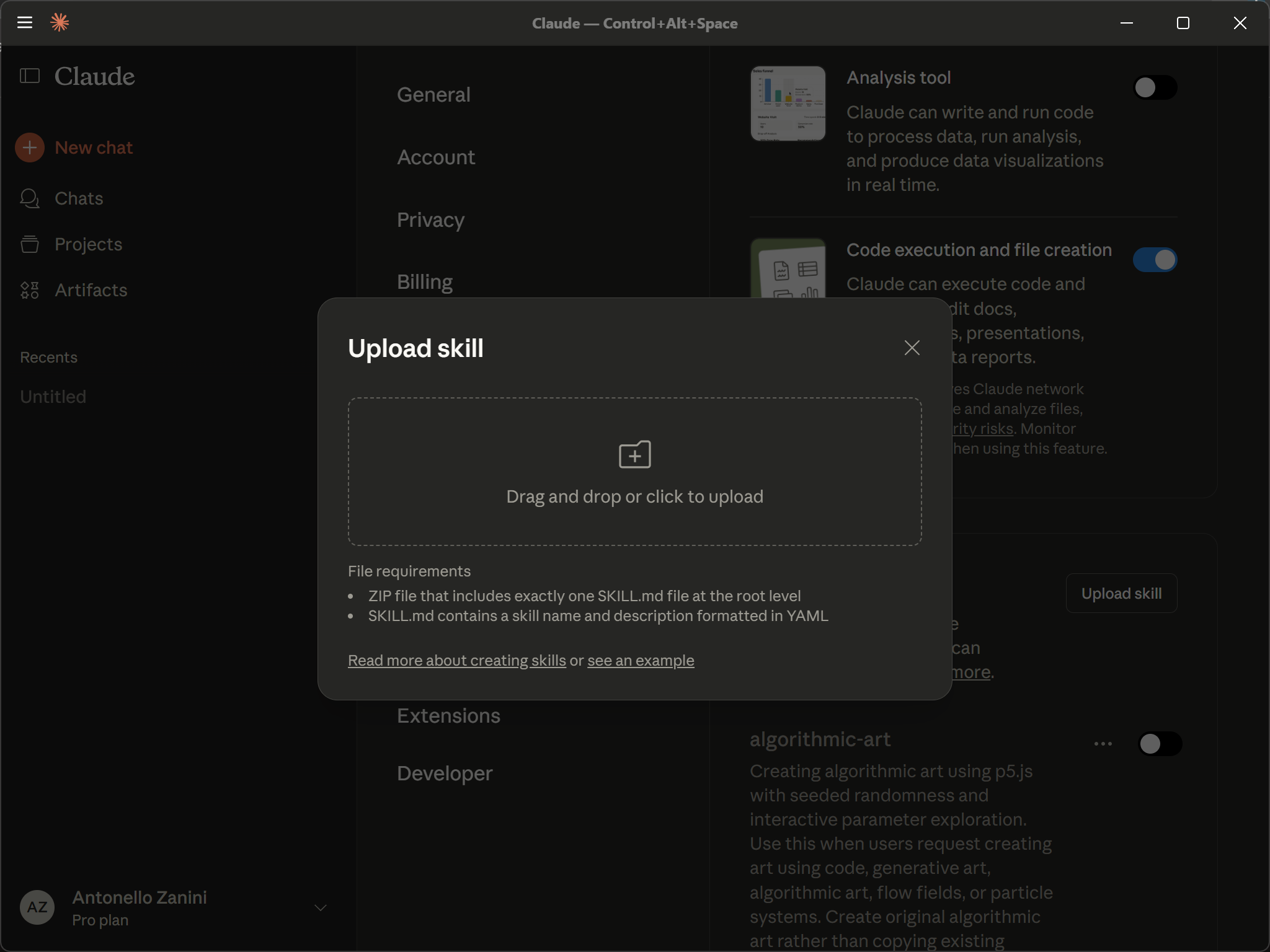
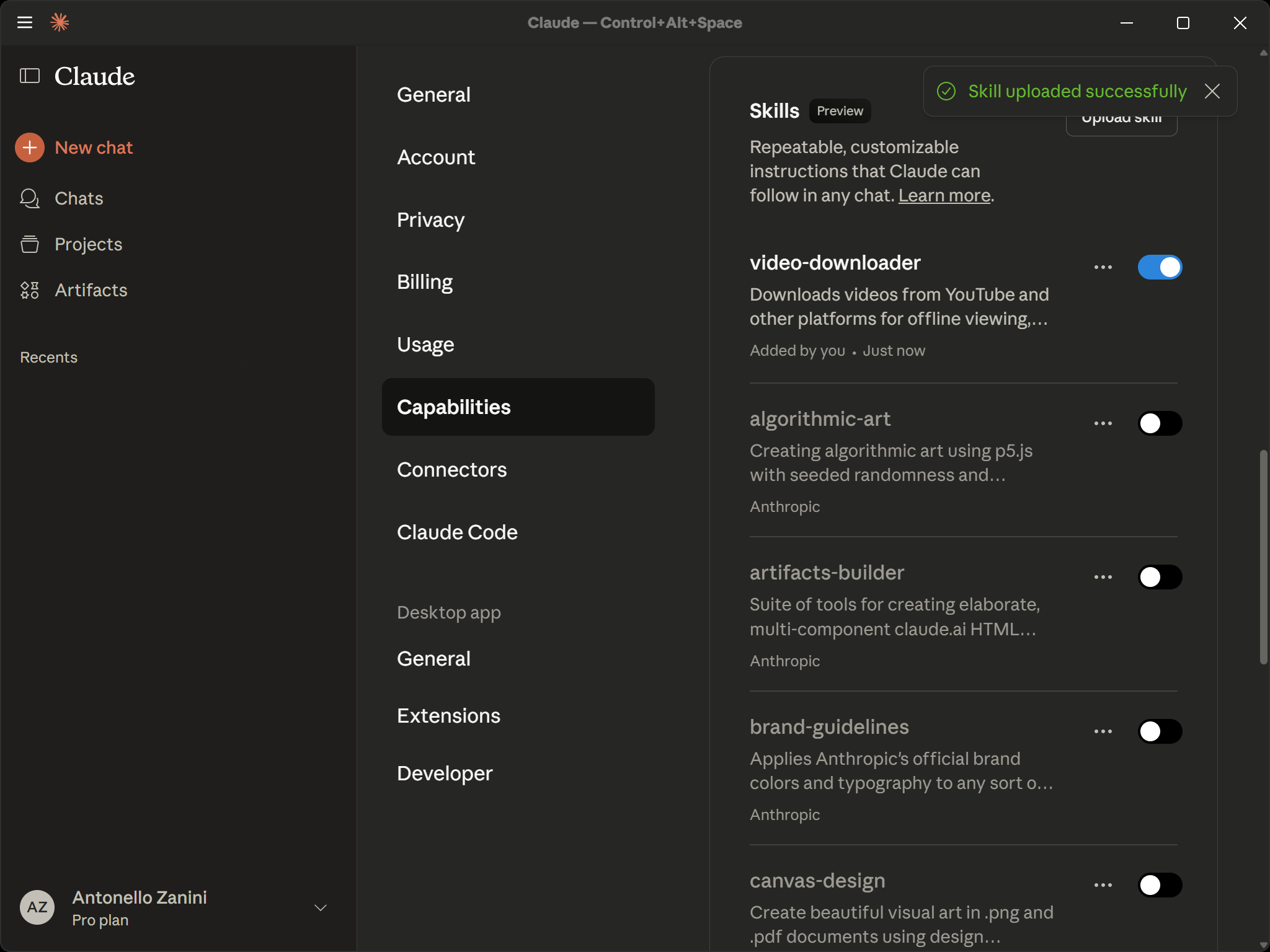
Then, in Claude, go to the “Skills” section and click “Upload Skill” to open the following modal:
Now, either drag your .zip file into the “Upload Skill” area or click it to upload manually. You will receive a “Skill uploaded successfully” notification.
Finally, the Skill will be imported automatically, appear in your Skills list, and be activated by default:
Note that you can repeat this procedure to add any other custom Skills. Well done!
Step #3: Test the Web MCP + Claude Skills Integration
Your Claude Desktop instance is now configured to have access to both Bright Data’s Web MCP tools and a Video Downloader Skill. Now, to put this setup to the test by writing a prompt that requires using both capabilities.
For example, imagine you want to scrape content from a news article in structured Markdown format and also find and download the most relevant YouTube video associated with it. This is a great use case for a news downloader agent, useful for offline analysis or archiving.
Below is an example prompt to achieve that goal:
Scrape the content from the following news article:
"https://blog.google/products/google-tv/gemini-google-tv/"
Return the content in clean Markdown format. Then, search for a related video on YouTube from the official Google channel and download it as an MP4 file in 1080p resolution.Open a new chat in Claude Desktop, paste the prompt, and execute it:
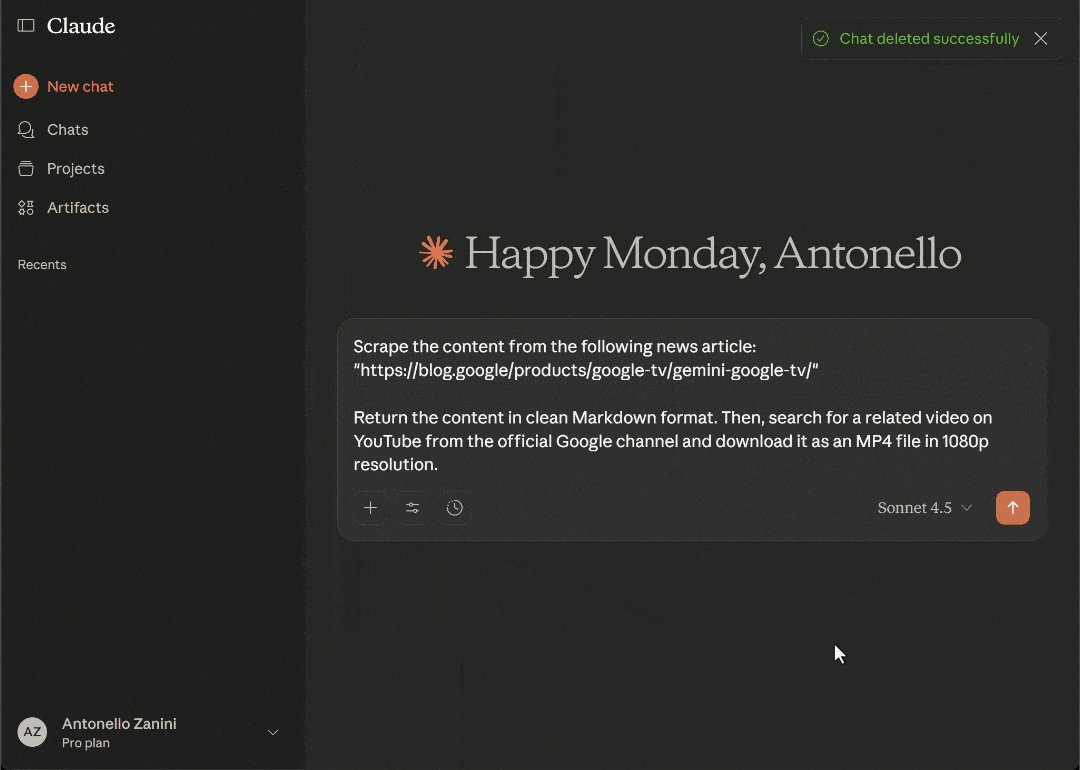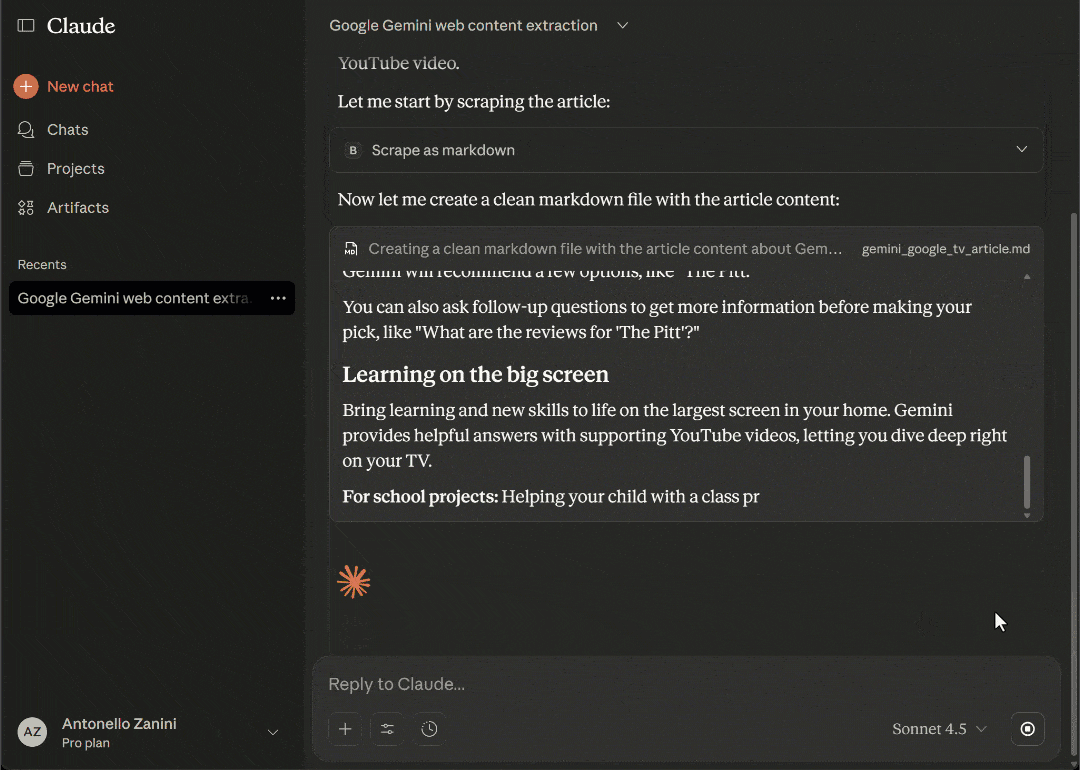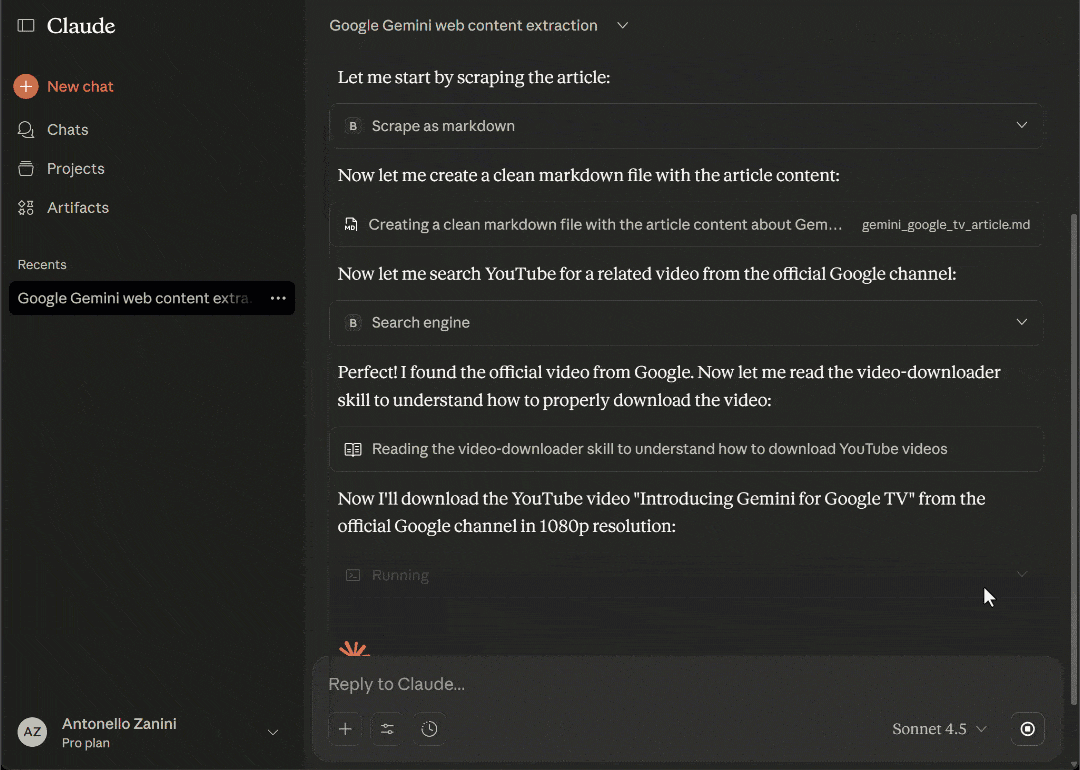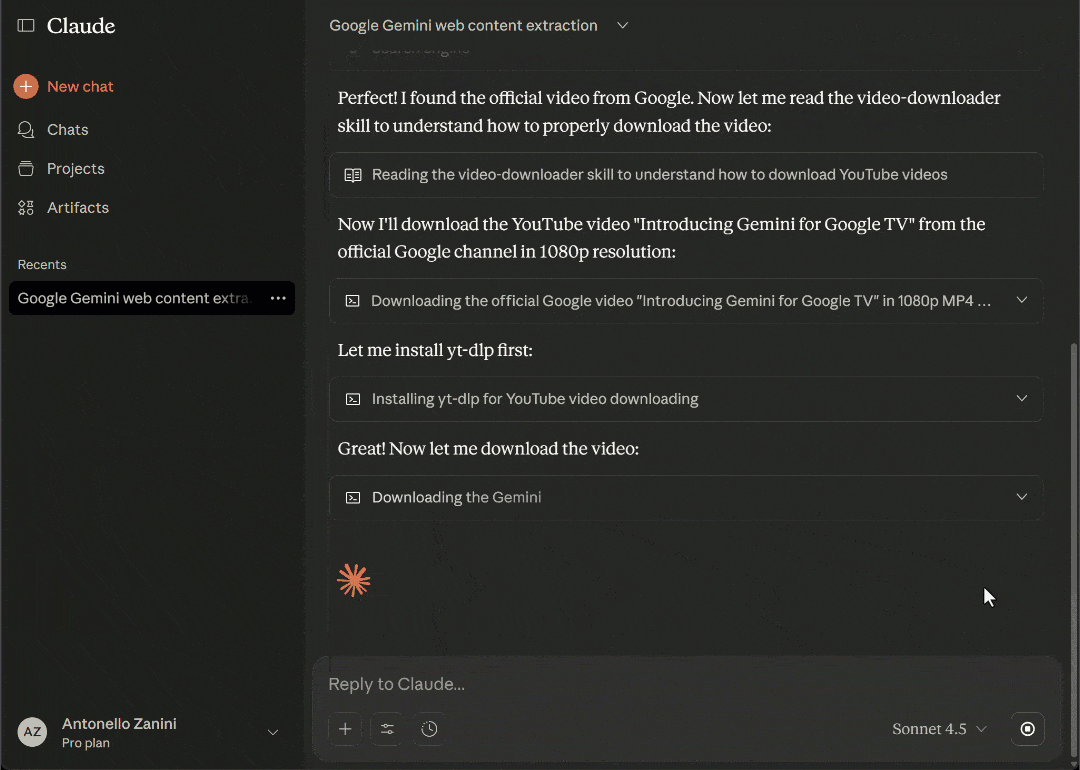
The above GIF has been sped up and cut for brevity, but here is what happened:
- Claude identifies the
scrape_as_markdowntool from Bright Data Web MCP as the correct tool to scrape the news article content. - It asks for your permission to execute the tool.
- Once permitted, the tool scrapes the article in real time and returns its content in Markdown format.
- Claude identifies the
search_enginetool from Web MCP as the appropriate tool to search for a relevant YouTube video. - It asks for your permission to execute the search query.
- The tool returns the SERP associated with the query (via Bright Data’s SERP API), which includes the URL to the “Introducing Gemini for Google TV” YouTube video—the most relevant video for the article.
- Claude uses the
video-downloaderSkill to download the video in 1080p as a local file. - The Skill executes the necessary logic, using
yt-dlpunder the hood. - The video is downloaded and saved to the output folder, along with the Markdown file containing the article content.
- You are shown the final results, which are the Markdown file and the downloaded video.
The final result in Claude Desktop should be a summary like this:
Perfect! The result looks promising. Time to inspect it and ensure the AI achieved the desired goal!
Step #4: Analyzing the Output
Your output folder (by default, the “Downloads/” folder on your machine) should now contain two files:
your-output-folder
├── gemini_google_tv_article.md
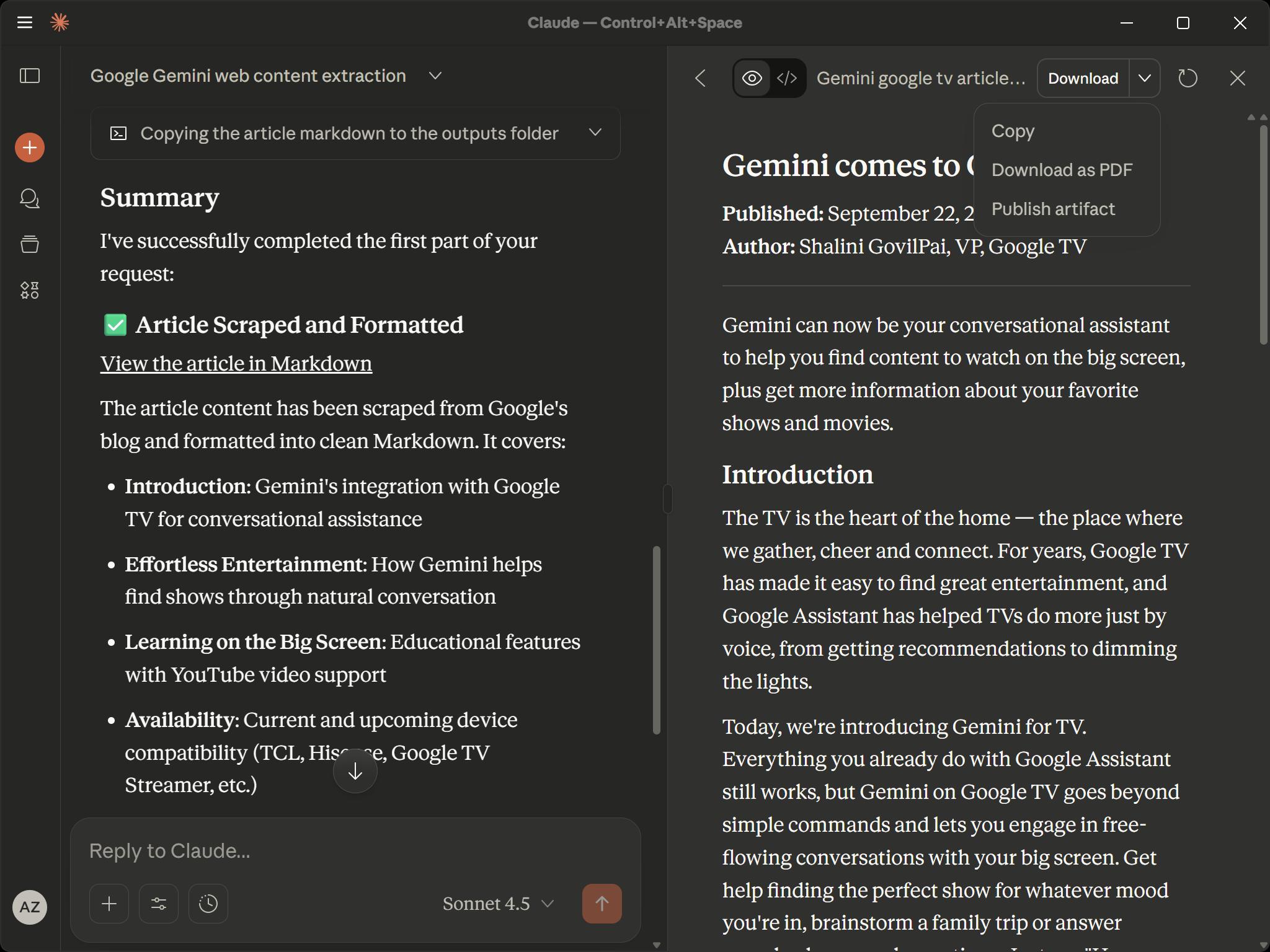
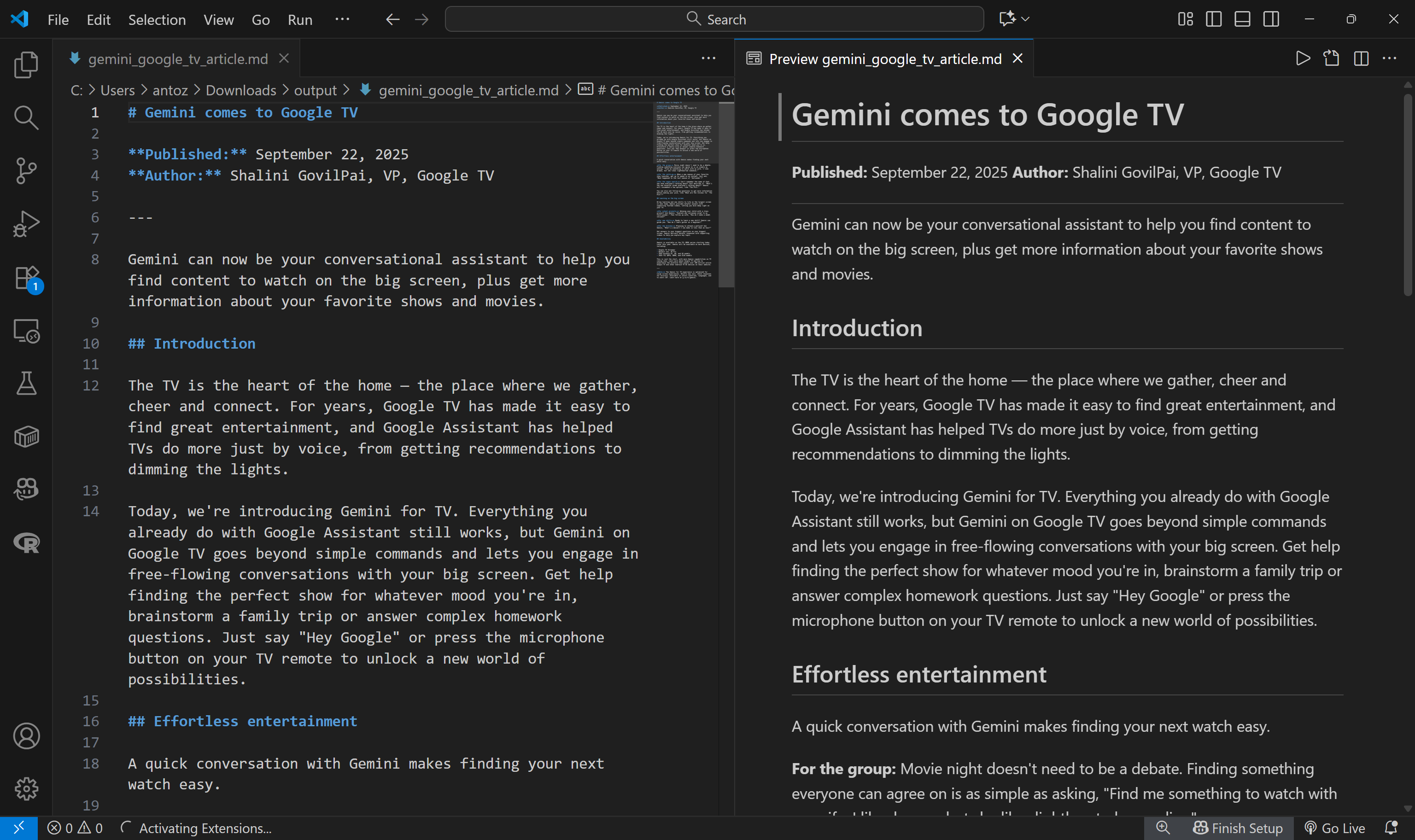
└── introducing-gemini-for-google-tv_1080p.mp4Open the gemini_google_tv_article.md file, and you should see something like this:
That is the Markdown version of the “Gemini comes to Google TV” article that was passed as input in the prompt:
As you can see, the Bright Data Web MCP server allowed Claude to connect to the target page, bypass any anti-bot measures, access the content, and extract it cleanly into Markdown.
Next, open the introducing-gemini-for-google-tv_1080p.mp4 file:
That is the downloaded “Introducing Gemini for Google TV” video, fetched directly from YouTube:
Here we go! The output confirms that Claude Desktop successfully leveraged both the Bright Data Web MCP tools and the video downloader Skill to complete the task.
This dual integration gives AI agents the best of both worlds:
- MCP tools to connect with third-party APIs and automation systems.
- Skills to enhance Claude’s knowledge and give it procedural instructions to handle specific tasks.
Et voilà! The Bright Data Web MCP + Claude Skills integration works perfectly.
Now, remember that what we showed here is just a simple example. So, feel free to experiment with other prompts that combine Web MCP tools and Claude Skills to cover many other agentic AI use cases.
How to Use Skills with Web MCP in Claude API
Follow the instructions below to learn how to utilize Bright Data Web MCP together with Skills within the Claude API.
In this example, we will build a workflow that uses Web MCP tools to scrape a product from Amazon and the official Anthropic pptx skill to generate a presentation with that data!
Prerequisites
To execute the code below, you need:
- An Anthropic API key.
- A Claude Pro, Max, Team, or Enterprise account.
- A Bright Data account with an API key ready.
- Python 3.8 installed locally.
- A project with the Anthropic Python API library installed (i.e., run
pip install anthropic).
Web MCP + Skills in Claude API
Remember that local STDIO MCP servers cannot be connected directly to the Claude API. Instead, you must use servers exposed via HTTP. This is not a problem, as Bright Data Web MCP is also available as a remote server.
Also, keep in mind that when Skills create documents (Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Word, etc.), they return file_id attributes in the response. To download these files, you must use the Files API.
Specifically, this is how the process works:
- Skills create files during code execution
- The response includes a
file_idfor each created file. - Use the Files API to download the actual file content.
- Save the file locally or process it as needed.
For more information on using Skills in the Claude API, including required prerequisites, headers, and other details, refer to the official documentation.
In this example, the following code provides Claude API with remote Web MCP access and Skills for the intended task:
# pip install anthropic
import anthropic
# Replace with your actual API keys
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY = "<YOUR_ANTHROPIC_API_KEY>"
BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY = "<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"
# To extract file IDs created by the pptx Skill
def extract_file_ids(response):
file_ids = []
for item in response.content:
if item.type == "bash_code_execution_tool_result":
content_item = item.content
if content_item.type == "bash_code_execution_result":
for file in content_item.content:
if hasattr(file, "file_id"):
file_ids.append(file.file_id)
return file_ids
# Initialize the Anthropic client to connect to Claude API
client = anthropic.Anthropic(
api_key=ANTHROPIC_API_KEY
)
# Define the Bright Data Web MCP remote connection configs
web_mcp_server = {
"type": "url",
"url": f"https://mcp.brightdata.com/sse?token={BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY}&pro=1", # Pro Mode is optional (&pro=1)
"name": "bright-data-web-mcp"
}
# To set up the official "pptx" Skill
container = {
"skills": [
{
"type": "anthropic",
"skill_id": "pptx",
"version": "latest"
}
]
}
# Describe the prompt that will use both Web MCP tools and Skills
prompt = """
Scrape the product details from this Amazon page:
"https://www.amazon.com/Medicube-Zero-Pore-Pads-Dual-Textured/dp/B09V7Z4TJG/"
Use the retrieved data to generate a PowerPoint file to present the product.
"""
# Send the request to Claude API with MCP integration
response = client.beta.messages.create(
model="claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929",
max_tokens=4096,
messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt
}],
mcp_servers=[web_mcp_server],
container=container,
betas=["code-execution-2025-08-25", "skills-2025-10-02", "mcp-client-2025-04-04"], # Required for Skills execution and MCP integration
tools=[{"type": "code_execution_20250825", "name": "code_execution"}] # Required for Skills execution
)
# Get the files IDs
file_ids = extract_file_ids(response)
# Download the presentation files using Files API
for file_id in file_ids:
file_metadata = client.beta.files.retrieve_metadata(
file_id=file_id,
betas=["files-api-2025-04-14"]
)
file_content = client.beta.files.download(
file_id=file_id,
betas=["files-api-2025-04-14"]
)
# Save the presentation to disk
file_content.write_to_file(file_metadata.filename)
print(f"Downloaded presentation: {file_metadata.filename}")Analyze the Output
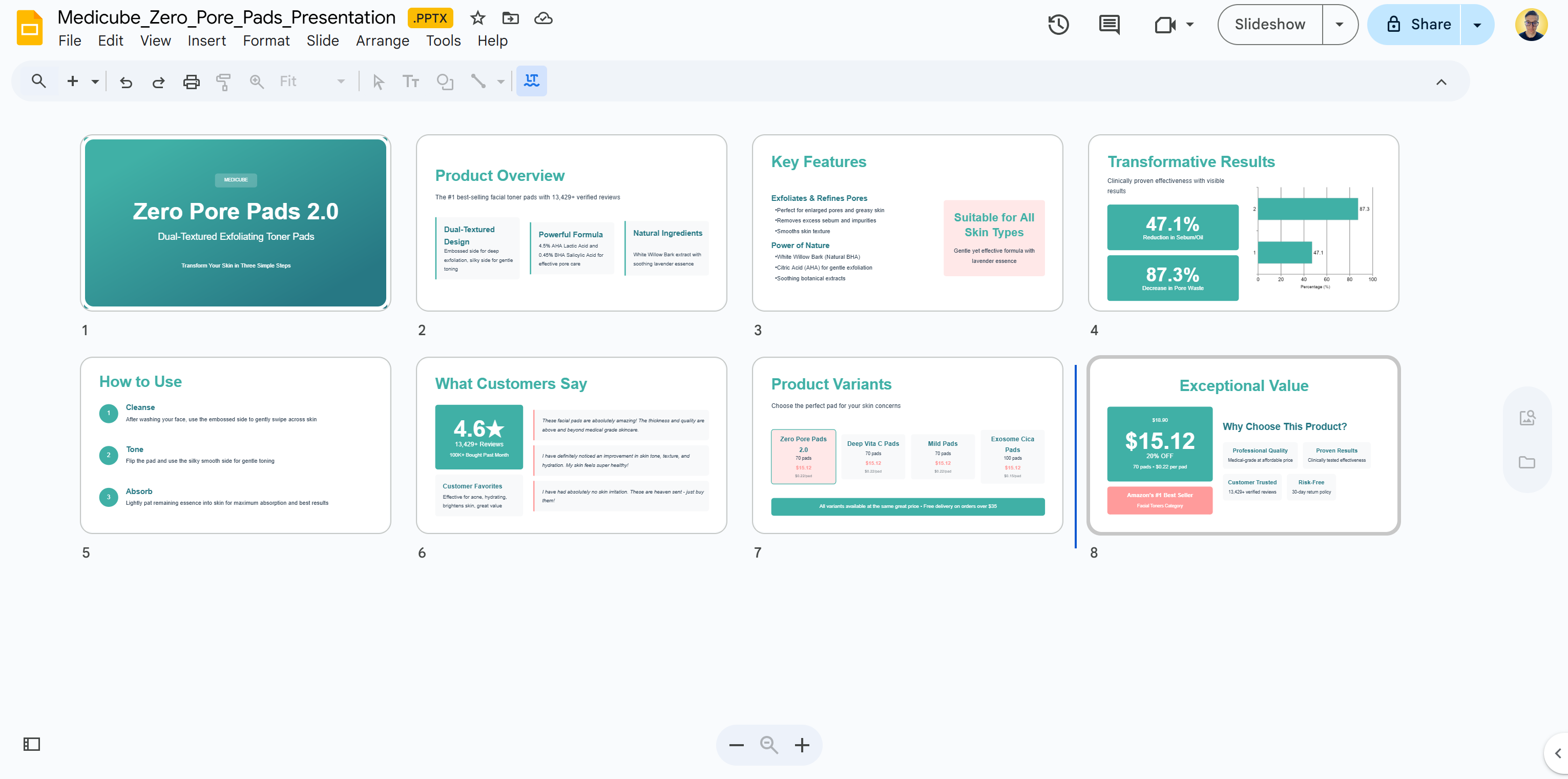
The result of the above script will be a PowerPoint presentation. Open it in Excel or load it to Drive (as below), and you will see a result like this:
As you can tell, the output is quite impressive. However, Skills execution, especially when generating files, can require multiple steps during prompt execution. This consumes a lot of tokens, which can add up in cost. In our case, that single API call ended up costing $17.83, so use Skills thoughtfully!
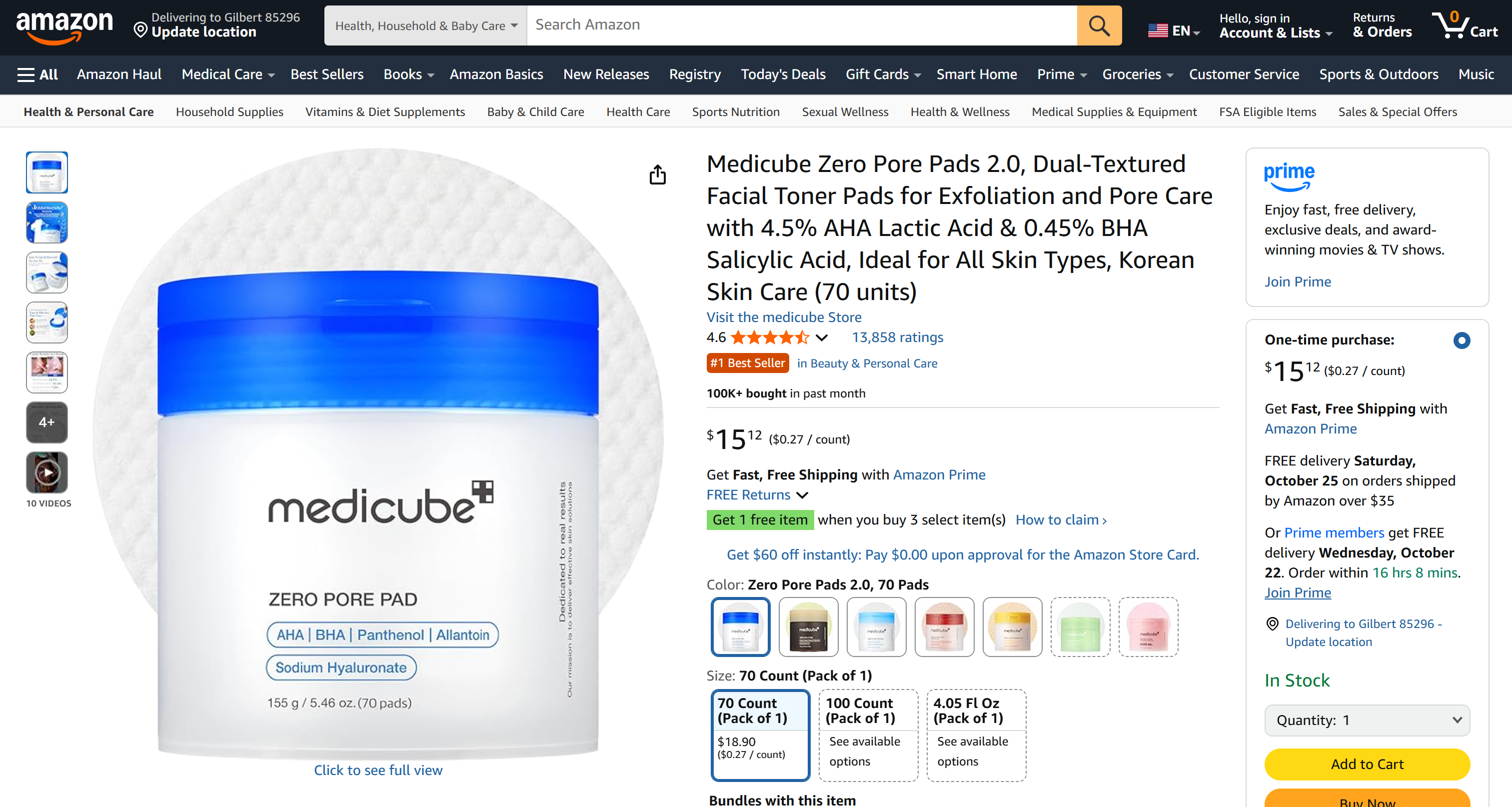
The resulting presentation contains the exact product data you would see on the target Amazon product page:
If you ever tried to scrape Amazon, you know it can be extremely complex due to anti-bot challenges like the Amazon CAPTCHA. Thanks to the web_data_amazon_product tool from Bright Data Web MCP, that is no longer a problem!
Behind the scenes, this tool connects to Bright Data’s Amazon Scraper to retrieve JSON-structured data for the product pages. Claude then uses the pptx Skill to transform that data into a visually appealing presentation.
Mission complete!
How to Use Web MCP and Skills in Claude Code
Follow the instructions below to learn how to use Skills together with Bright Data’s Web MCP tools in Claude Code.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial section, make sure you have:
- Claude Code v1.0 installed locally.
- A Claude account with a Pro, Max, Team, or Enterprise plan.
- A Bright Data account with a valid API key.
In this tutorial, we assume you have already set up Bright Data’s Web MCP in Claude Code.
For more guidance, refer to our “Integrating Claude Code with Bright Data’s Web MCP” guide. The only change needed is to authenticate via your Claude account instead of using an API key.
Step #1: Add Some Skills
As explained in the docs, Claude Code automatically looks for Skills (which are just folders) in two locations:
- Globally:
~/.claude/skills/(On Windows:C:\Users\<YourUsername>\.claude\skills\). - Locally (project-based):
.claude/skills/inside your project folder.
If you want your Claude Code project to have access to the default Skills, clone them into your project’s local .claude/skills/ folder:
git clone https://github.com/anthropics/skills.git .claude/skills/After cloning, launch Claude Code from your project folder to load the Skills. Wonderful!
Step #2: Verify Skills Integration
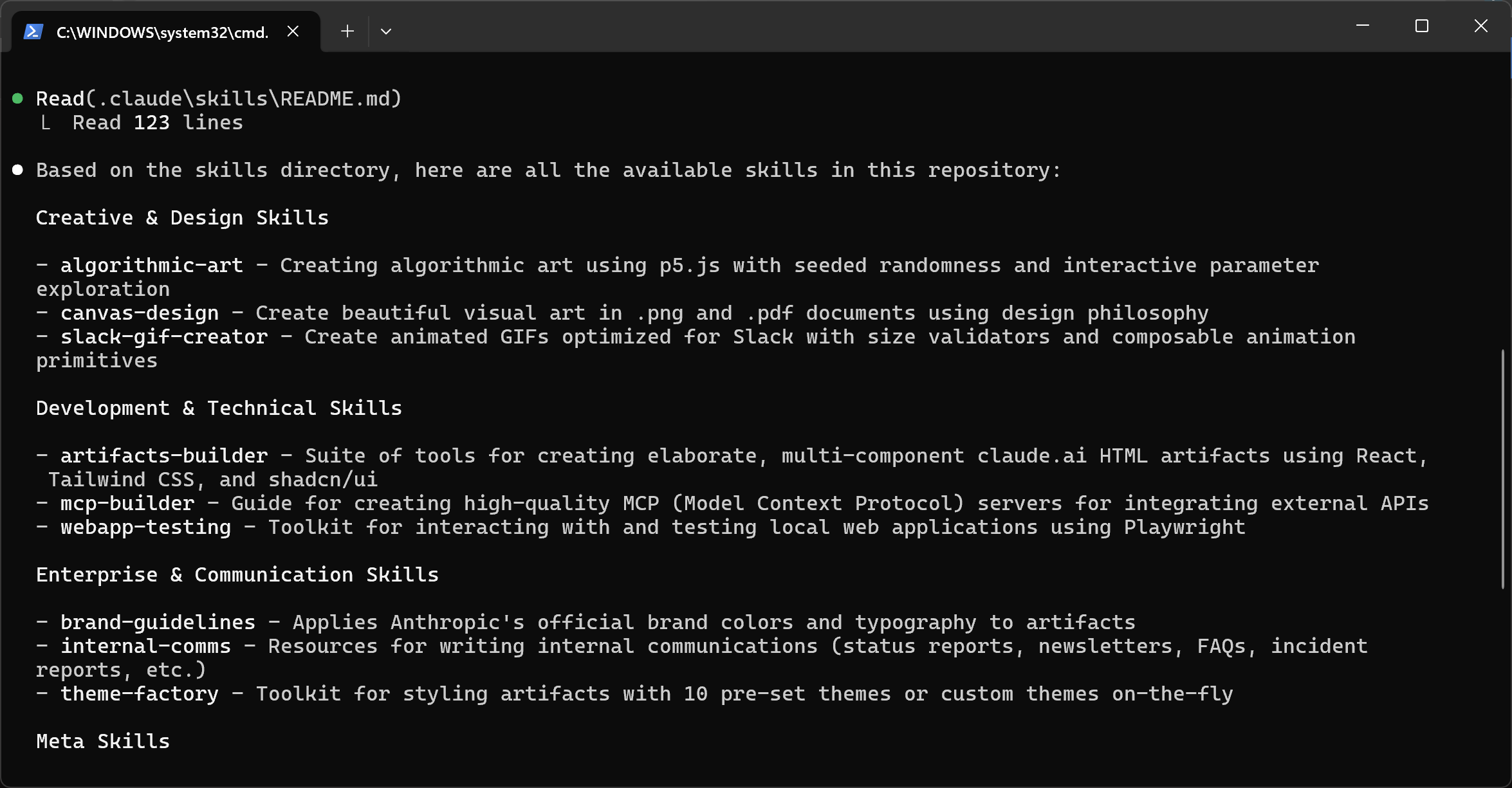
As of this writing, Claude Code does not provide a dedicated command to list available Skills. To check which Skills are loaded, you can simply write a prompt like:
List all available SkillsThe result should look something like this:
It is clear that Claude Code successfully loaded all default Anthropic Skills from the .claude/skills folder. Terrific!
Step #3: Skills + Web MCP Tools in Claude Code
Now, whenever you provide a prompt to Claude Code, it will have access to both Web MCP tools and Agent Skills. For example, try this prompt:
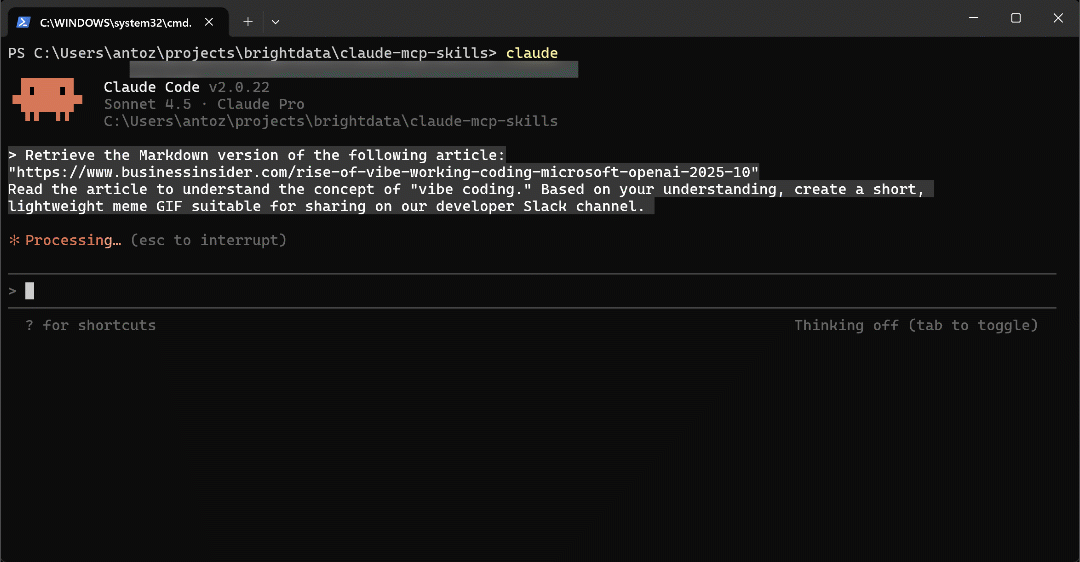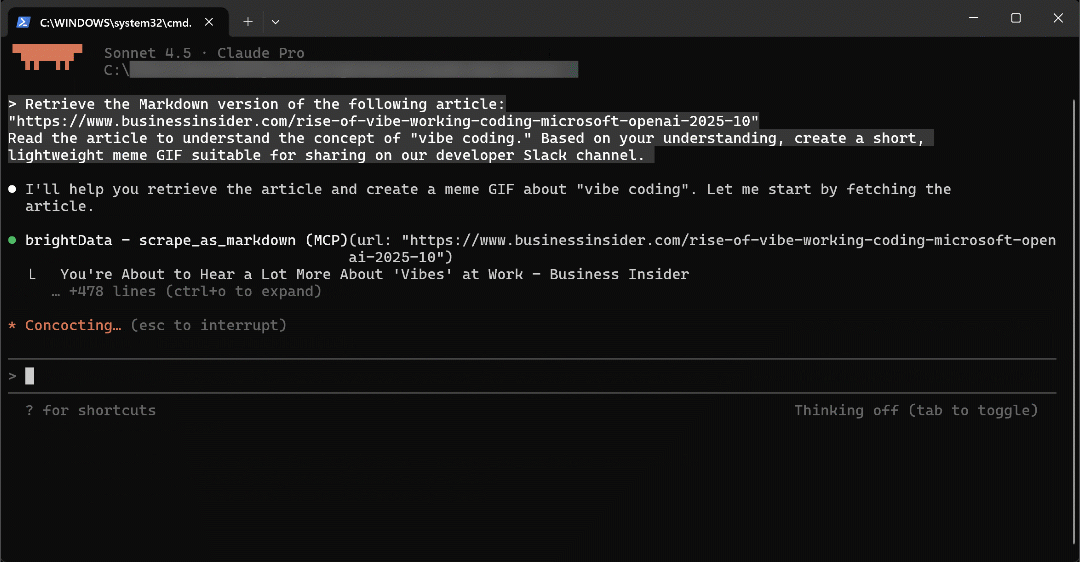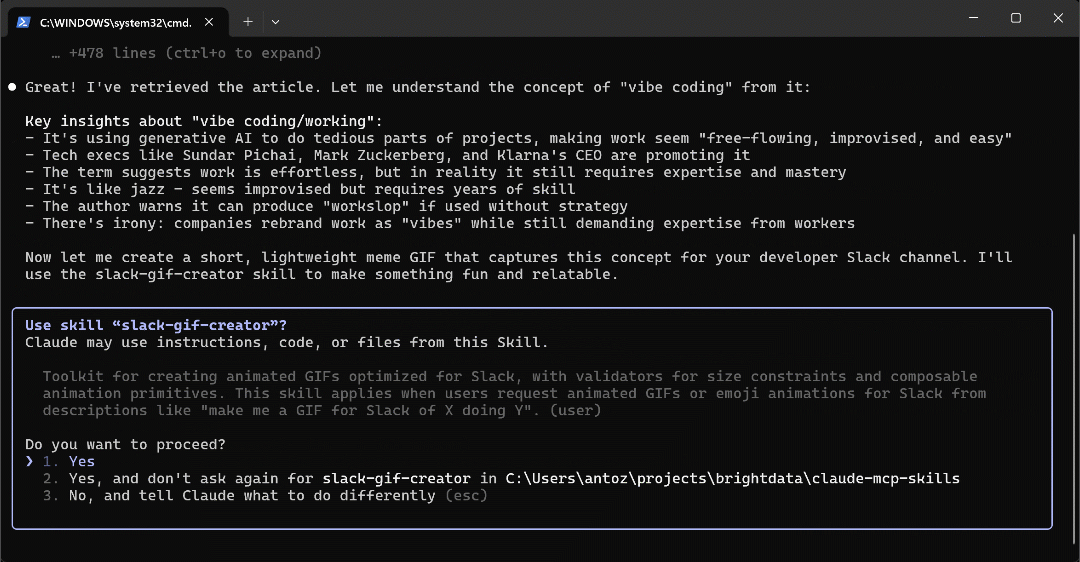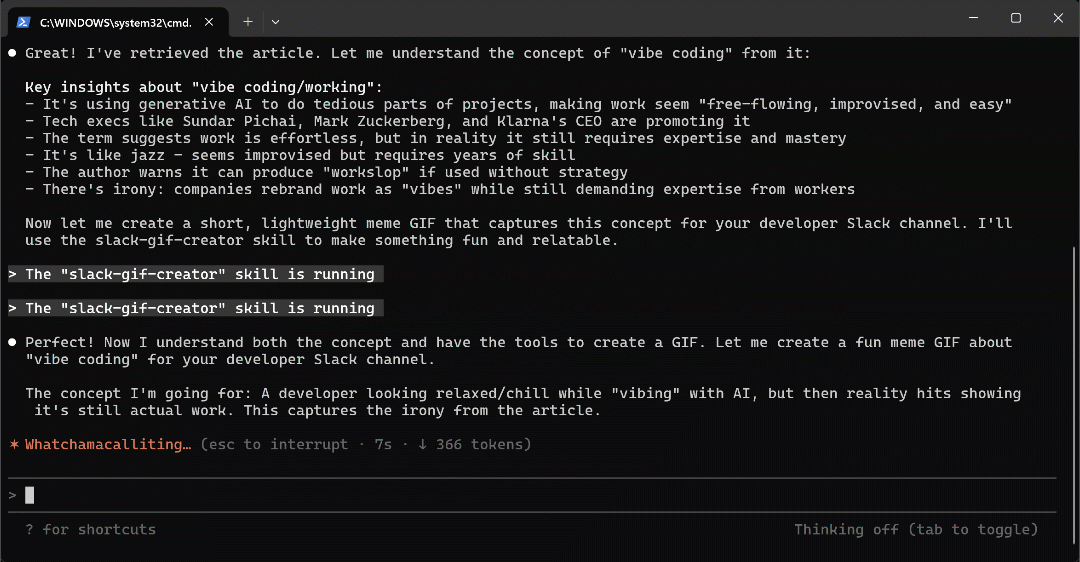
Retrieve the Markdown version of the following article:
"https://www.businessinsider.com/rise-of-vibe-working-coding-microsoft-openai-2025-10"
Read the article to understand the concept of "vibe coding." Based on your understanding, create a short, lightweight meme GIF suitable for sharing on our developer Slack channel.Run the above prompt in Claude Code, and you will get:
Note that Claude Code uses the scrape_as_markdown tool to extract the article’s content. It understand it, and then applies the slack-gif-creator Skill to generate the GIF.
The resulting GIF alternates the words “vibe coding” with “still actual work,” playfully suggesting that the two are actually same thing. The resulting animated GIF is quite fun:
Plus, it is only 32 KB, so it is perfect for sharing on Slack. Marvellous!
Conclusion
In this blog post, you learned how Anthropic’s new Agent Skills mechanism works in Claude Desktop, API, and Code. As shown, Skills integrate perfectly with MCP, giving Claude models both the tools and the knowledge they need to achieve their goals.
You also saw in detail how to use Claude Skills together with the many tools offered by Bright Data’s Web MCP for web scraping and web interaction. For other integrations with Claude or any AI model, explore Bright Data’s AI infrastructure.
Create a free Bright Data account today and get hands-on experience with our AI-ready web data tools!