In this tutorial, you will see:
- What Semantic Kernel is, the core features it provides, and how it works.
- Why extending it with MCP makes it even more powerful.
- How to build an AI agent with Bright Data Web MCP integration using Semantic Kernel.
Let’s dive in!
What is Semantic Kernel?
Semantic Kernel is an open-source SDK developed by Microsoft that helps you integrate AI models and LLMs into applications to build AI agents and advanced GenAI solutions. It acts as production-ready middleware, providing connectors to multiple AI services and enabling both semantic (prompt-based) and native (code-based) function execution.
The SDK is available in C#, Python, and Java. It is a flexible solution to generate text, perform chat completions, or connect to external data sources and services. As of this writing, the GitHub repository of the project has more than 26k stars.
Main Capabilities
The main features offered by Semantic Kernel are:
- AI model integration: Connects to services like OpenAI and Azure OpenAI with a unified interface for chat completion, text generation, and more.
- Plugin system: Supports plugins with semantic functions (prompts) and native functions (C#, Python, or Java) to extend AI functionality.
- AI agents: Lets you build agents that interpret user requests and coordinate multiple plugins and services to solve complex tasks.
- Planning and function calling: Helps agents break down and execute multi-step tasks by selecting the right plugins or functions.
- Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG): Integrates real data into prompts using search and data connectors for more accurate, up-to-date responses.
How Semantic Kernel Works
To understand how the library operates, it helps to know its main components:
- Core kernel: Orchestrates AI services and plugins.
- AI service connectors: Link application code to different AI models and services through a common interface.
- Plugins: Contain semantic and native functions that extend the agent’s capabilities.
- AI agents: Built on top of the kernel, using plugins to process requests and run workflows.
Why Extend Semantic Kernel with MCP Integration
Semantic Kernel is a model-agnostic SDK that allows you to build, orchestrate, and deploy complex AI agents, workflows, and even multi-agent systems. No matter how sophisticated your architecture becomes, these workflows and agents still require an underlying AI model to function.
Whether it is OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, or another LLM, all models share the same fundamental limitation: their knowledge is static…
LLMs are trained on data that represents a snapshot in time, which means their knowledge can quickly become outdated. More importantly, they cannot natively interact with live websites or external data sources.
This is where Semantic Kernel’s extensibility through plugins makes all the difference. By integrating it with Bright Data’s Web MCP, you can extend your AI agents beyond static knowledge, enabling them to retrieve fresh, high-quality data directly from the web.
The open-source Web MCP server provides access to more than 60 AI-ready tools, all powered by Bright Data’s infrastructure for web interaction and data collection.
Even on the free tier, your AI agent can already use two powerful tools:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
search_engine |
Retrieve search results from Google, Bing, or Yandex in JSON or Markdown. |
scrape_as_markdown |
Scrape any webpage into clean Markdown format, bypassing bot detection and CAPTCHA. |
Beyond that, Web MCP unlocks dozens of specialized tools for structured data collection across platforms like Amazon, LinkedIn, Yahoo Finance, TikTok, and more. Learn more on the official GitHub page.
In short, combining Semantic Kernel with Web MCP transforms static workflows into dynamic AI agents that can interact with live websites and access web data to generate insights grounded in the real world.
How to Build an AI Agent in Semantic Kernel That Connects to Bright Data’s Web MCP
In this guided section, you will learn how to connect Bright Data’s Web MCP to a Semantic Kernel AI agent written in C#. In particular, you will use this integration to build a Reddit analyzer AI agent that:
- Utilizes Bright Data Web MCP tools to retrieve information from Reddit posts.
- Processes the retrieved data using an OpenAI GPT-5 model.
- Returns the results to you in a Markdown report.
Note: The code below is written in C# using .NET 9. However, you can easily convert it to Python or Java, the other two supported programming languages.
Follow the steps below to get started!
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have:
- .NET 8.0 or higher installed locally (this tutorial will refer to .NET 9)
- An OpenAI API key
- A Bright Data account with an API key ready
Do not worry about setting up the Bright Data account, as you will be guided through that process in a later step.
Step #1: Set Up Your .NET C# Project
Initialize a new .NET console project called SK_MCP_Agent with:
dotnet new console -n SK_MCP_AgentNext, enter the project folder:
cd SK_MCP_AgentYou should now see the following file structure:
SK_MCP_Agent/
├── Program.cs
├── SK_MCP_Agent.csproj
└── obj/
├── project.assets.json
├── project.nuget.cache
├── SK_MCP_Agent.csproj.nuget.dgspec.json
├── SK_MCP_Agent.csproj.nuget.g.props
└── SK_MCP_Agent.csproj.nuget.g.targetsIn detail, Program.cs currently contains a default “Hello, World” program. This file is where you will place your Semantic Kernel AI agent logic.
Now, open your project folder in a .NET C# IDE, such as Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code. In the IDE’s terminal, install the required dependencies with these commands:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.EnvironmentVariables
dotnet add package Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.UserSecrets
dotnet add package Microsoft.SemanticKernel --prerelease
dotnet add package Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Agents.Core --prerelease
dotnet add package ModelContextProtocol --prerelease
dotnet add package System.Linq.AsyncEnumerable --prereleaseThe required NuGet packages are:
Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.*: Provides key-value-based configuration to read settings from environment variables and .NET user secrets.Microsoft.SemanticKernel.*: A lightweight SDK for integrating AI LLMs with conventional programming languages, with tools for agent development.ModelContextProtocol: The official MCP C# client, which will be used to connect to Bright Data Web MCP.System.Linq.AsyncEnumerable: Exposes a full set of LINQ extension methods forIAsyncEnumerable<T>.
Note: The --prerelease flag in dotnet add package tells the .NET CLI to install the latest (pre-release) versions of a NuGet package. This is required for some packages because they are still in development or experimental stages.
Done! Your .NET development environment is set up to build an AI agent in C# using Semantic Kernel, with Bright Data Web MCP integration.
Step #2: Configure Secret Loading
Your AI agent will rely on third-party components such as OpenAI models and the Bright Data Web MCP server. Both of these integrations require authentication via API key tokens. To avoid exposing these keys directly in your code, store them securely using the .NET user secrets storage system or environment variables.
To configure that, first import the configuration package:
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;Then, load the secrets into a config object with:
var config = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.AddUserSecrets<Program>()
.AddEnvironmentVariables()
.Build();You can now access your secrets in code like this:
config["<secret_name>"]Initialize the user secrets storage by running the following command in your project folder:
dotnet user-secrets initThis will create a safe local storage for your secrets (i.e., the API keys).
Well done! Your C# program can now securely handle sensitive credentials without exposing them in your source code.
Step #3: Test Bright Data’s Web MCP
Before connecting to Bright Data’s Web MCP in your agent, first verify that your machine can run the MCP server.
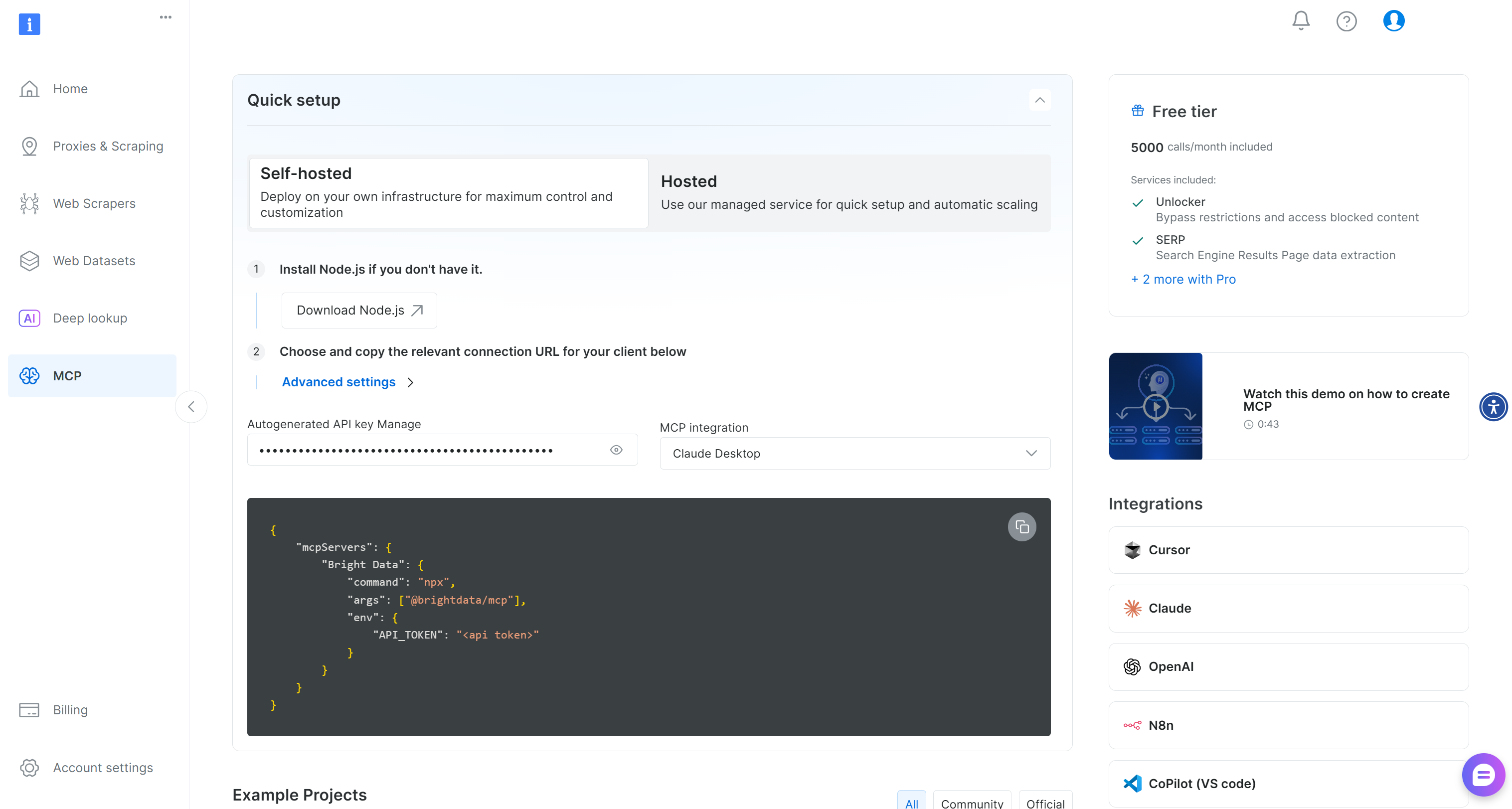
If you do not already have a Bright Data account, create a new one. If you do, simply log in. For a quick setup, navigate to the “MCP” section in the dashboard and follow the instructions:
Otherwise, start by generating a Bright Data API key. Then, store it in a safe place, as you will need it soon. In this section, we will assume the API key has Admin permissions because that simplifies the Web MCP integration process.
Run the following command to install the Web MCP globally in your system:
npm install -g @brightdata/mcpNext, check that the local MCP server works by executing:
$Env:API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>"; npx -y @brightdata/mcpOr, equivalently, on Linux/macOS:
API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>" npx -y @brightdata/mcpReplace <YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API> with your actual Bright Data API token. The command sets the required API_TOKEN environment variable and launches the Web MCP through the @brightdata/mcp package.
If successful, you should see logs similar to this:
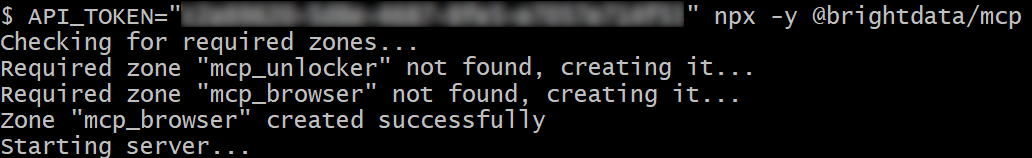
On the first launch, the Web MCP automatically creates two default zones in your Bright Data account:
mcp_unlocker: A zone for Web Unlocker.mcp_browser: A zone for Browser API.
The MCP server relies on those two zones to power all 60+ tools.
To confirm the zones were created, log in to your Bright Data dashboard. Go to the “Proxies & Scraping Infrastructure” page, and you should see them in the zone table:
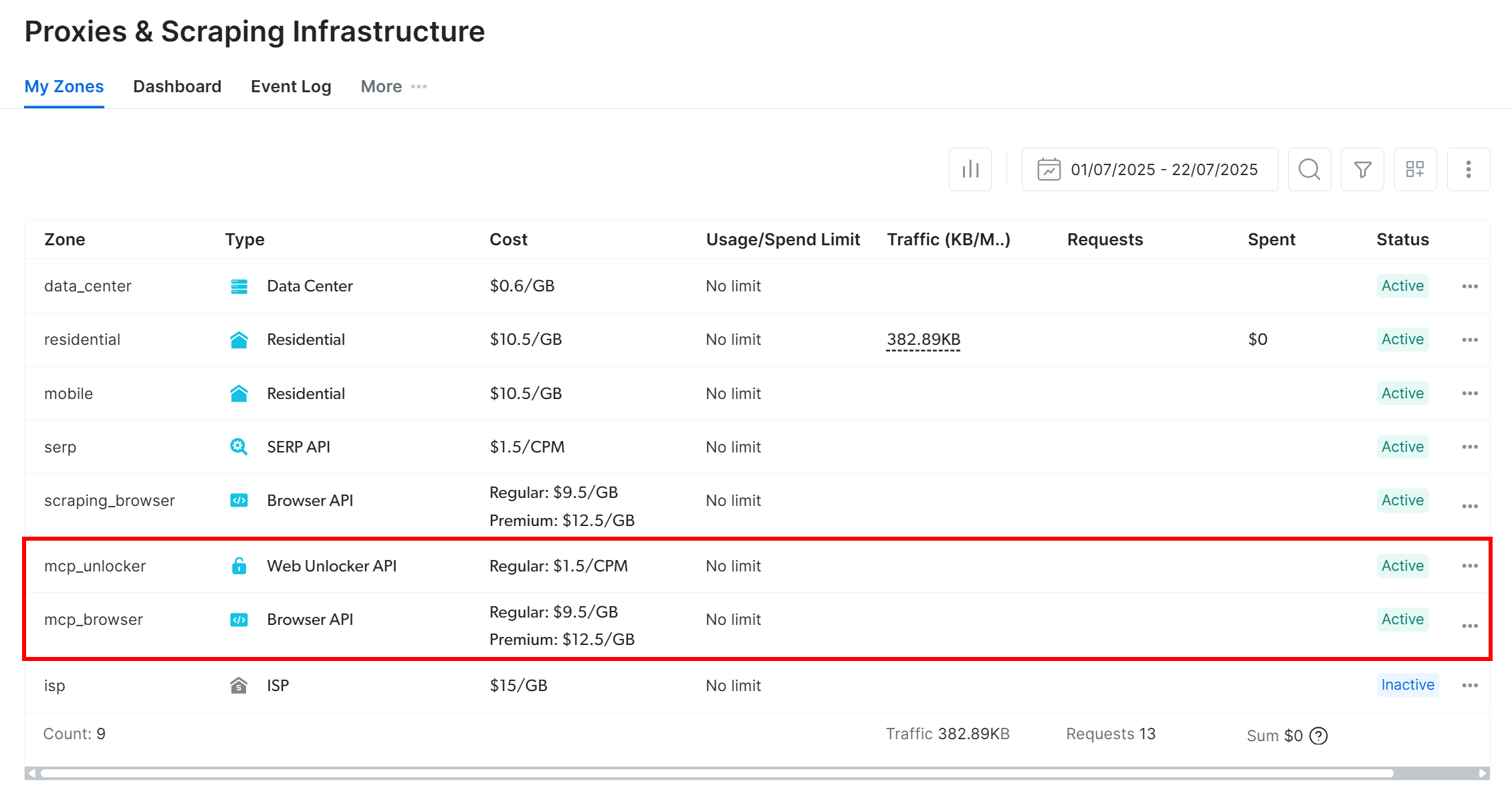
If your API token does not have Admin permissions, these zones will not be created for you. In that case, you must create them manually in the dashboard and configure their names via environment variables (check out the GitHub page for details).
Important: By default, the MCP server only exposes the search_engine and scrape_as_markdown tools (and their batch versions). These tools are included in the Web MCP free tier.
To unlock advanced tools, such as browser automation and structured data feeds, you need to enable Pro mode. To do so, set the PRO_MODE="true" environment variable before launching the Web MCP:
$Env:API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>"; $Env:PRO_MODE="true"; npx -y @brightdata/mcpOr, on Linux/macOS:
API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>" PRO_MODE="true" npx -y @brightdata/mcpPro mode unlocks all 60+ tools, but it is not included in the free tier and will incur additional charges.
Success! You just verified that the Web MCP server runs on your machine. Kill the MCP process, as you are about to configure your Semantic Kernel agent to launch the server and connect to it in the next steps.
Step #4: Configure the Web MCP Integration
Now that your machine can execute the Web MCP, start by adding the Bright Data API key you retrieved earlier to the user secrets:
dotnet user-secrets set "BrightData:ApiKey" "<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"Replace the <YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY> placeholder with your actual API key. That command securely stores the key in your project’s secrets storage.
Keep in mind that you can achieve the same result by setting the API key as an environment variable:
$Env:BrightData__ApiKey="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"Or, on macOS/Linux:
export BrightData__ApiKey="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"Note: Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration will convert BrightData__ApiKey to BrightData:ApiKey for you.
Next, use the McpClientFactory from the ModelContextProtocol package to define an MCP client and connect to the Web MCP:
await using var mcpClient = await McpClientFactory.CreateAsync(new StdioClientTransport(new()
{
Name = "BrightDataWebMCP",
Command = "npx",
Arguments = ["-y", "@brightdata/mcp"],
EnvironmentVariables = new Dictionary<string, string?>
{
{ "API_TOKEN", config["BrightData:ApiKey"] },
// { "PRO_MODE", "true" }, // <-- Optional: enable Pro Mode
}
}));The above configuration results in the same npx command seen in the previous setup steps, with the required environment variable. Note that PRO_MODE is optional, while API_TOKEN is read from the BrightData:ApiKey secret defined earlier.
Next, load the list of all available tools:
var tools = await mcpClient.ListToolsAsync().ConfigureAwait(false);The script will execute the npx command to launch the Web MCP as a local process and connect to it, accessing the tools it exposes.
You can verify that the connection to the Web MCP works and that you have access to its tools by logging them all:
foreach (var tool in tools)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{tool.Name}: {tool.Description}");
}If you run your script now, you should see output similar to this:
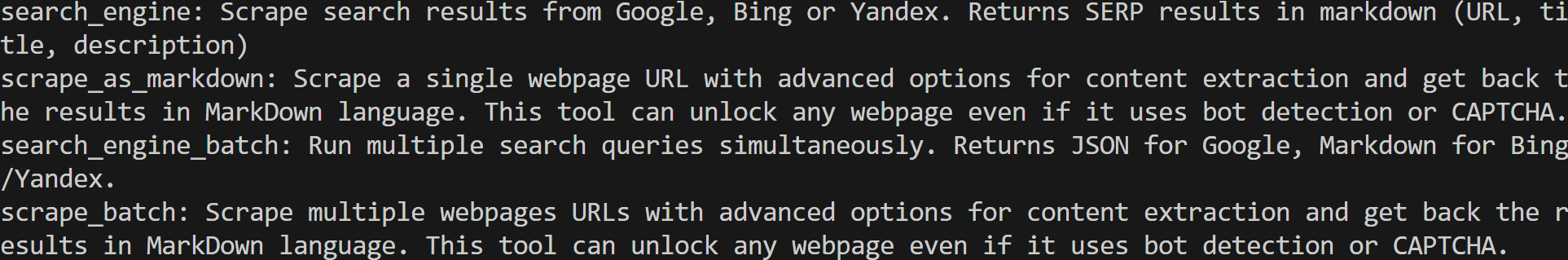
These are the 2 default tools (+ 2 batch versions) exposed by the Web MCP in the free tier. In Pro mode, you would have access to all 60+ tools.
Wonderful! The above output confirms that the Web MCP integration is working perfectly!
Step #5: Build a Kernel with Access to MCP Tools
In Semantic Kernel, a kernel acts as a Dependency Injection container that manages all the services and plugins required to run your AI application. Once you provide your services and plugins to the kernel, these can be used by the AI whenever needed.
Now, it is time to create a kernel for OpenAI integration with support for tool calling via MCP. Start by adding your OpenAI API key to the user secrets:
dotnet user-secrets set "OpenAI:ApiKey" "<YOUR_OPENAI_KEY>"As mentioned earlier, you can also set this as an environment variable called OpenAI__ApiKey.
Next, define a new kernel that connects to OpenAI:
var builder = Kernel.CreateBuilder();
builder.Services
.AddOpenAIChatCompletion(
modelId: "gpt-5-mini",
apiKey: config["OpenAI:ApiKey"]
);
Kernel kernel = builder.Build();In this example, the kernel connects to the gpt-5-mini model (but you can configure any other OpenAI model) using the API key stored in your user secrets.
Then, add a plugin to the kernel for tool usage:
kernel.Plugins.AddFromFunctions("BrightData", tools.Select(aiFunction => aiFunction.AsKernelFunction()));This line of code converts your MCP tools into kernel-ready functions that can be called by the specified AI model.
The required imports for this section are:
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.OpenAI;Perfect! You now have a fully configured kernel, which is the core of your Semantic Kernel AI application.
Step #6: Define the AI Agent
Start by importing the Agents class from SemanticKernel:
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Agents;Next, use the kernel to initialize a new AI agent that is configured to automatically call tools:
var executionSettings = new OpenAIPromptExecutionSettings()
{
FunctionChoiceBehavior = FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto() // Enable automatic function calling for the LLM
};
var agent = new ChatCompletionAgent()
{
Name = "RedditAgent",
Kernel = kernel,
Arguments = new KernelArguments(executionSettings),
};Essentially, the agent created here can execute the tools exposed by the Bright Data Web MCP. That occurs whenever the AI model determines that one or more tools are required to achieve what is described in the input prompt.
Note that the agent has been named “RedditAgent” because this tutorial focuses on building a Reddit-focused agent. Adapt the name to fit your own project if you are creating a Semantic Kernel AI agent for a different purpose.
Cool! The next step is simply to execute a prompt using the agent.
Step #7: Execute a Task in the Agent
To test the web data retrieval capabilities of your AI agent enhanced with the tools provided by the Bright Data Web MCP, you need a proper prompt. For example, you could ask the AI agent to retrieve information from a particular subreddit, as follows:
var prompt = @"
Scrape pages from the following subreddit:
https://www.reddit.com/r/webscraping/
From the scraped content, generate a Markdown report that includes:
- The official description of the subreddit and key stats (community type, creation date)
- A list of URLs for the ~10 most recent posts
"; This is an ideal task to test web retrieval capabilities. Standard OpenAI models fail when asked such a prompt because they cannot programmatically access the Reddit page to retrieve real-time data:

Note: The output above is unreliable, as the majority of the content is either false or completely fabricated. OpenAI models cannot reliably fetch fresh web data from the web without external tools like those provided by Bright Data.
Thanks to the tools available through the Web MCP, your agent will be able to retrieve the required Reddit data and present an accurate result. Execute the task and print the result in the terminal with:
ChatMessageContent response = await agent.InvokeAsync(prompt).FirstAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"\n\nResponse:\n{response.Content}");This is sufficient to test a single prompt. In real-world scenarios, you generally want to keep your agent running and context-aware by implementing a REPL loop with memory to track previous interactions.
And there you have it! Your Reddit-expert AI agent, built with Semantic Kernel and integrated with Bright Data Web MCP, is now fully functional.
Step #8: Put It All Together
The final code in Program.cs is:
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using ModelContextProtocol.Client;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.OpenAI;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Agents;
// Load user secrets and environment variables for API keys
var config = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.AddUserSecrets<Program>()
.AddEnvironmentVariables()
.Build();
// Create an MCP client for the Bright Data Web MCP server
await using var mcpClient = await McpClientFactory.CreateAsync(new StdioClientTransport(new()
{
Name = "BrightDataWebMCP",
Command = "npx",
Arguments = ["-y", "@brightdata/mcp"],
EnvironmentVariables = new Dictionary<string, string?>
{
{ "API_TOKEN", config["BrightData:ApiKey"] },
// { "PRO_MODE", "true" }, // <-- Optional: enable Pro Mode
}
}));
// Retrieve the list of tools available on the Bright Data Web MCP server
var tools = await mcpClient.ListToolsAsync().ConfigureAwait(false);
// Build a Semantic Kernel and register the MCP tools as kernel functions
var builder = Kernel.CreateBuilder();
builder.Services
.AddOpenAIChatCompletion(
modelId: "gpt-5-mini",
apiKey: config["OpenAI:ApiKey"]
);
Kernel kernel = builder.Build();
// Create a plugin from the MCP tools and add it to the kernel's plugin collection
kernel.Plugins.AddFromFunctions("BrightData", tools.Select(aiFunction => aiFunction.AsKernelFunction()));
// Enable automatic function calling for the LLM
var executionSettings = new OpenAIPromptExecutionSettings()
{
FunctionChoiceBehavior = FunctionChoiceBehavior.Auto()
};
// Define the AI agent with MCP integration
var agent = new ChatCompletionAgent()
{
Name = "RedditAgent",
Kernel = kernel,
Arguments = new KernelArguments(executionSettings), // Pass settings for MCP tool calls
};
// Test the AI agent with a subreddit scraping prompt
var prompt = @"
Scrape pages from the following subreddit:
https://www.reddit.com/r/webscraping/
From the scraped content, generate a Markdown report that includes:
- The official description of the subreddit and key stats (community type, creation date)
- A list of URLs for the ~10 most recent posts
";
ChatMessageContent response = await agent.InvokeAsync(prompt).FirstAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"\n\nResponse:\n{response.Content}");Wow! In just around 65 lines of C#, you built a Semantic Kernel AI agent with Bright Data Web MCP integration.
Run your agent with:
dotnet runThe output should look similar to this:
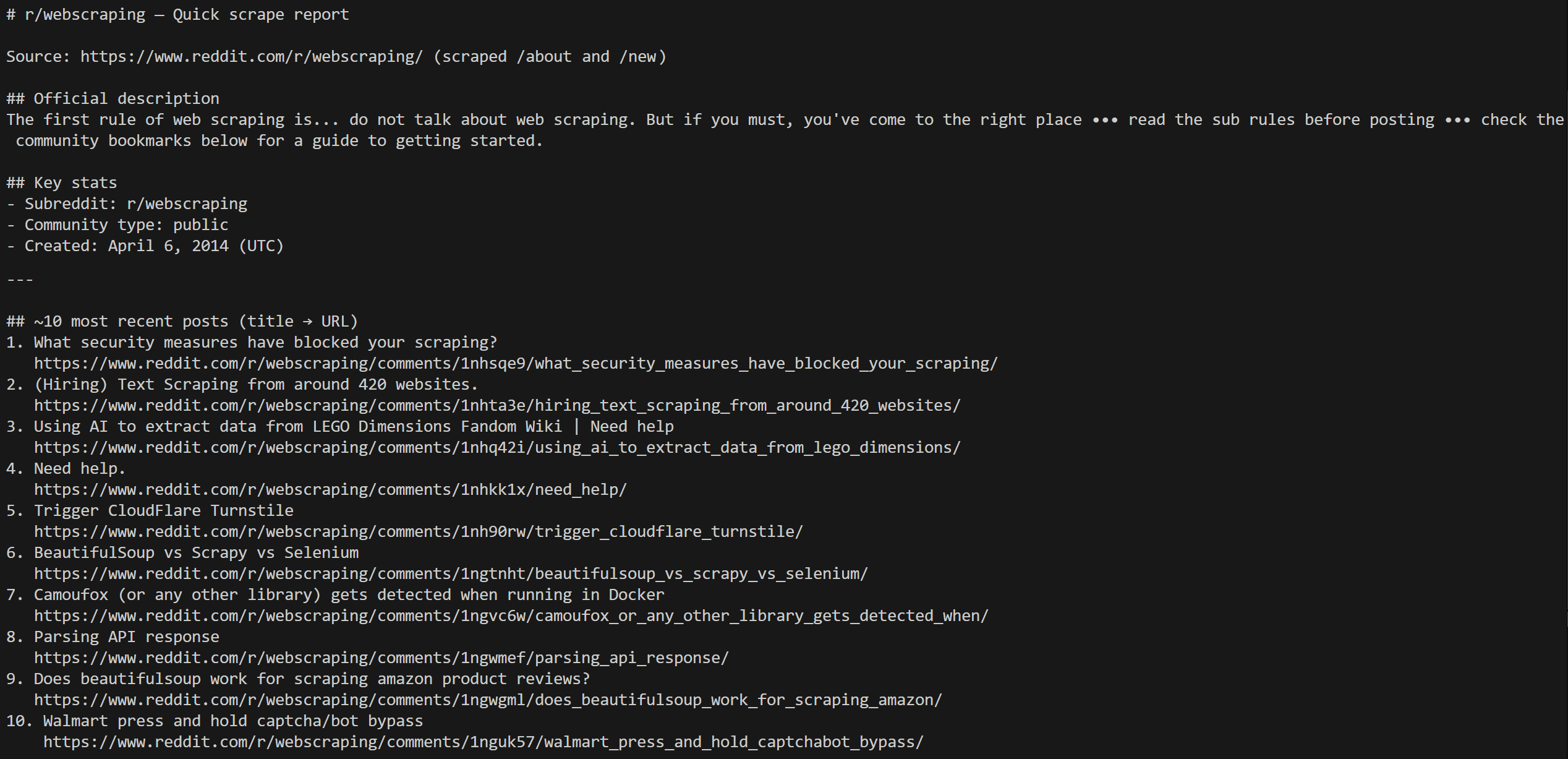
Notice how the agent scraped the /about page to get the subreddit information, and then the /new pages to fetch the most recent posts.
All the data shown in the output is correct, as you can verify it by visiting the subreddit’s /about page:
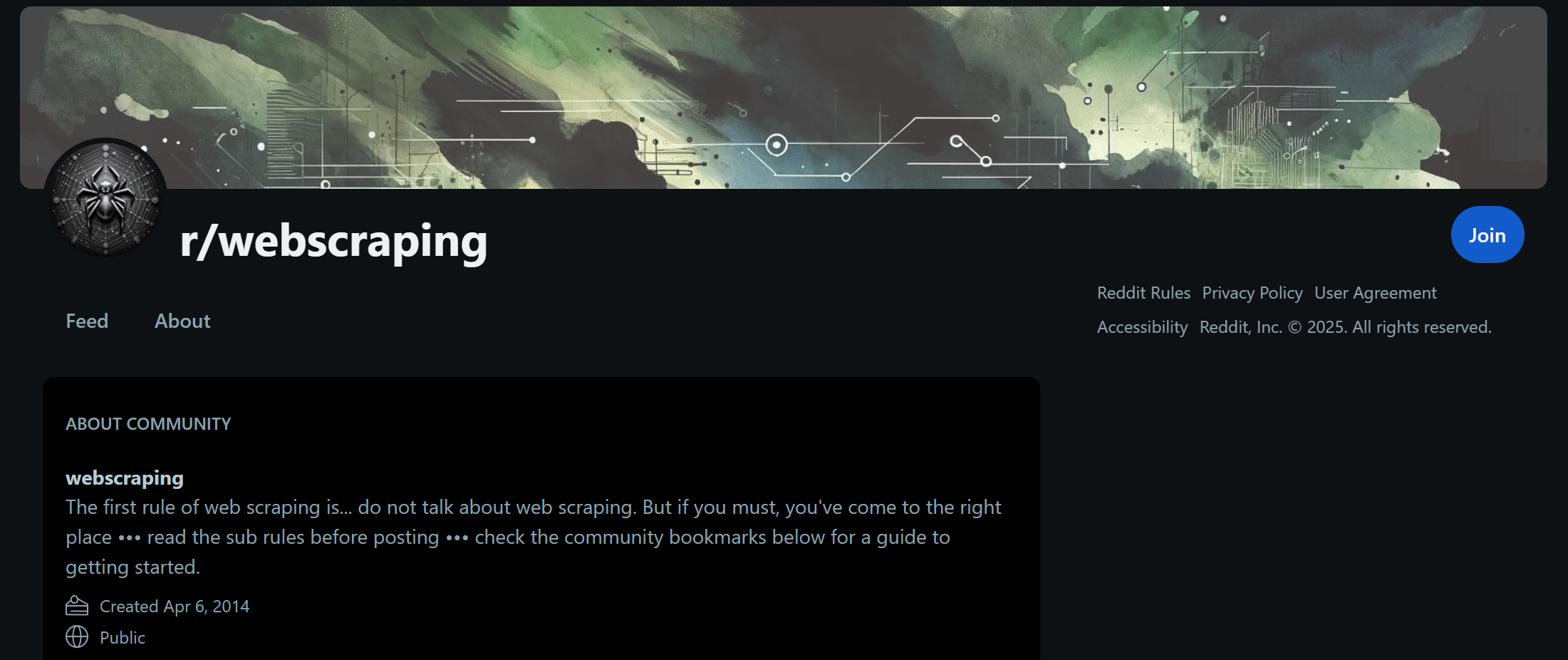
The data in the AI agent’s output matches exactly what is shown on this page. The same applies to the most recent posts, which you can find on the subreddit’s /new page.
The only difference is the order of the posts, which is determined by Reddit’s frontend and is not relevant here.
Scraping Reddit is challenging because it is protected by anti-bot systems that block automated requests. Thanks to the web scraping capabilities with anti-bot bypass provided by the Bright Data Web MCP server, your AI agent has access to a powerful set of tools for web data retrieval, interaction, and search.
This example demonstrates just one of the many possible scenarios. With the wide range of Bright Data tools available through Semantic Kernel, you can build more complex agents that adapt to many other use cases.
Et voilà! You just experienced the power of Bright Data Web MCP integration within a Semantic Kernel AI agent in C#.
Conclusion
In this blog post, you saw how to connect an AI agent built with Semantic Kernel to Bright Data’s Web MCP (which now comes with a free tier!). This integration gives your agent enhanced capabilities, including web search, data extraction, and real-time interaction.
For building more advanced AI agents, explore the broader suite of products and services in Bright Data’s AI infrastructure. These tools are designed to power diverse AI workflows and agentic use cases.
Sign up for a free Bright Data account today and start experimenting with AI-ready web data solutions!