In this tutorial, you will learn:
- Why you should extend Ollama models with tools from Bright Data’s Web MCP.
- Which tools you need to make that possible.
- What you need to do to get started.
- How to integrate Web MCP into Ollama models using MCPHost.
- How to achieve the same result with
ollmcp. - The new features your local Ollama models will gain, demonstrated in a complete example.
Let’s dive in!
Why Extend Ollama Models with Bright Data’s Web MCP
Ollama offers a wide range of AI models that can run locally. However, no matter which LLM you choose, they all share the same limitation: their knowledge is static, limited to the data they were trained on.
How can you overcome that roadblock? By giving the LLM access to fresh, real-time data from the largest and richest source available, i.e., the Web. That is where Bright Data’s Web MCP comes into play!
The Web MCP server extends Ollama models with the ability to retrieve up-to-date web data and interact with web pages like a human. This allows your AI models to overcome their built-in knowledge limitations.
Web MCP provides over 60 AI-ready tools, all powered by Bright Data’s infrastructure for web interaction and data collection. Even on the free tier, you get access to two highly useful tools:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
search_engine |
Retrieve search results from Google, Bing, or Yandex in JSON or Markdown. |
scrape_as_markdown |
Scrape any webpage into clean Markdown format, bypassing bot detection and CAPTCHA. |
Beyond these, Web MCP includes tools for cloud browser interaction and dozens of specialized tools for structured data feeds across platforms such as YouTube, Amazon, LinkedIn, TikTok, Google Maps, and more.
Add MCP Tools to Ollama Models
As of this writing, the Ollama desktop application does not support MCP integration directly (see updates on the official GitHub issue). This means that if you want to integrate Ollama models with MCP tools, you must rely on third-party solutions.
The most popular solutions for using Ollama with MCP are:
- MCPHost: A CLI host application that allows LLMs to interact with external tools via MCP. It currently supports Claude, OpenAI, Google Gemini, and Ollama models.
- MCP Client for Ollama (
ollmcp): A modern TUI (Text-based User Interface) that connects local Ollama LLMs to one or more MCP servers, enabling advanced tool usage and workflow automation.
Other possible solutions include Dolphin MCP, ollama-mcp-bridge, and others. In this guide, we will focus on the first two, as they are the most widely used and supported.
Prerequisites
In this section, you will set up all the prerequisites required to integrate Bright Data Web MCP with Ollama, using both MCPHost and MCP Client for Ollama (ollmcp), all within a local environment.
Before getting started, make sure you have:
- Node.js installed locally (we recommend downloading the latest LTS version) to run the Bright Data Web MCP server locally.
- At least 16 GB of RAM and a modern CPU to run Ollama smoothly on your machine.
Having a basic understanding of how MCP works and the tools exposed by Web MCP will also be helpful.
At the end of this section, you will have:
- Ollama installed and configured locally, running and ready to be integrated with Bright Data Web MCP.
- A Bright Data account with an API key for Web MCP authentication.
- Confirmation that your machine can successfully run the Web MCP server locally.
Follow the sections below!
Set Up Ollama
If you have not done so yet, download Ollama for your operating system and install it. Then, make sure to pull a few models, such as gpt-oss, qwen3, deepseek-r1, llama3.2, or any others you prefer.
Pull models using the following command:
ollama pull <model_name>Replace <model_name> with the name of one of the available Ollama LLM models.
Both MCPHost and ollmcp require Ollama to be running locally. So, start Ollama with:
ollama serveThis command launches Ollama in server mode without opening the desktop application.
Important: By default, Ollama starts with a context length limited to 4096 tokens, which is generally too low for larger tasks. You can increase it to 40,000 tokens (or the maximum supported by your chosen model) using the following commands:
On macOS/Linux, run:
OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH=40000 ollama serveOr, on Windows (PowerShell), execute:
$Env:OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH=40000; ollama serveThis ensures your Ollama model can handle longer contexts without truncation.
Great! Ollama is now configured and ready to be integrated with the Bright Data Web MCP server.
Retrieve Your Bright Data API Key
The Web MCP server is authenticated using your Bright Data API key. To obtain one, start by creating a Bright Data account. Otherwise, if you already have an account, simply log in.
Then, follow the steps in the official guide to generate your Bright Data API key. Store it in a safe place, as you will need it shortly.
Note: It is recommended to set up an API key with Admin permissions, as that makes the Web MCP integration process much smoother.
Test the Web MCP Locally
Before integrating Ollama models with the Bright Data Web MCP, you must verify that your machine can actually run the server.
For a quick setup, log in to our Bright Data account, and refer to the instructions in the “MCP” page:
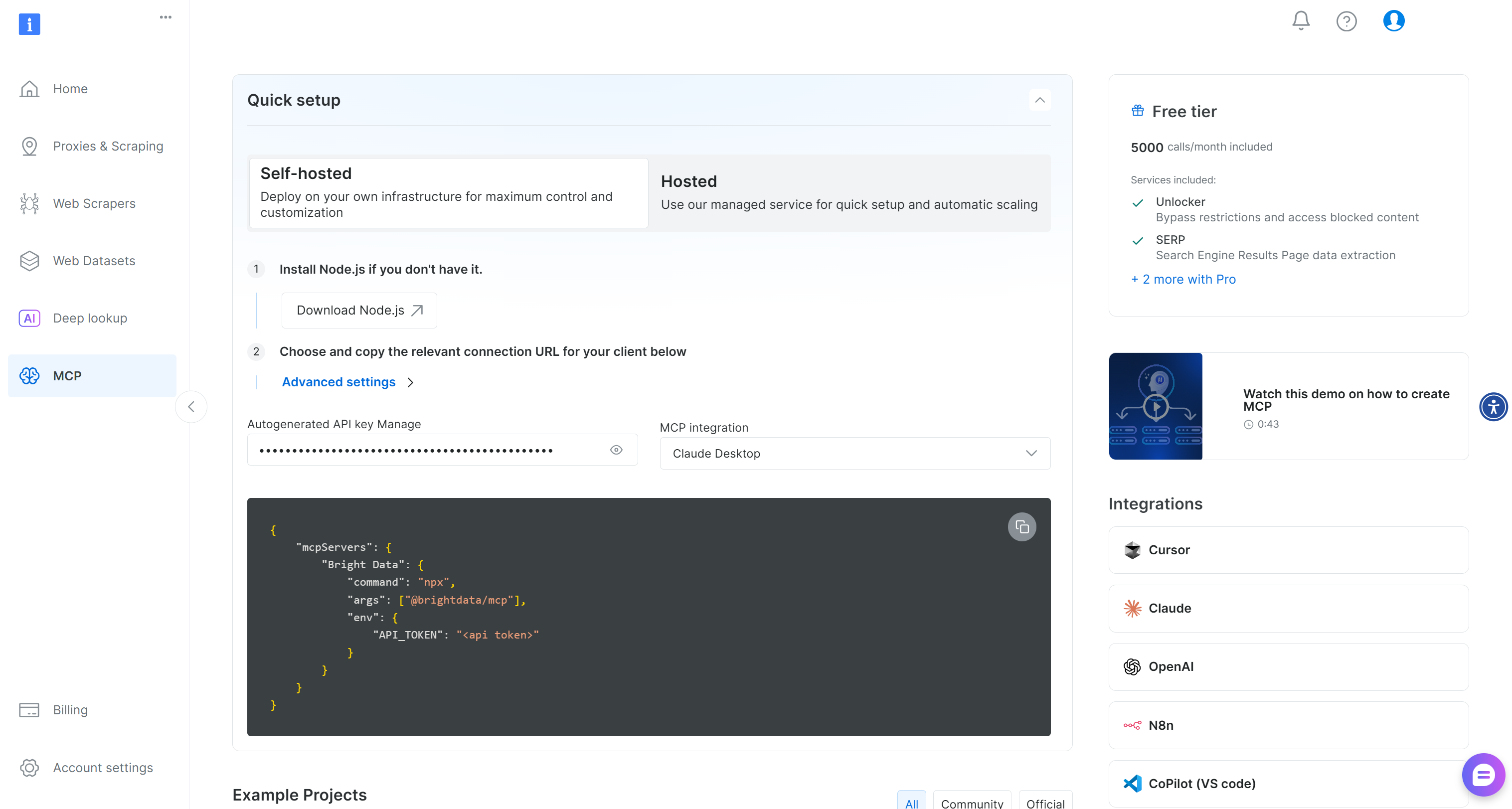
Otherwise, for more guidance, follow the instructions below.
Install the Web MCP globally on your machine via this npm command:
npm install -g @brightdata/mcpCheck that the MCP server works by executing it:
API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>" npx -y @brightdata/mcpOr, equivalently, in PowerShell:
$Env:API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"; npx -y @brightdata/mcpReplace the <YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API> placeholder with the Bright Data API token you retrieved earlier. Those commands set the required API_TOKEN environment variable and launch the Web MCP locally by running the @brightdata/mcp package.
If successful, you should see an output similar to this:
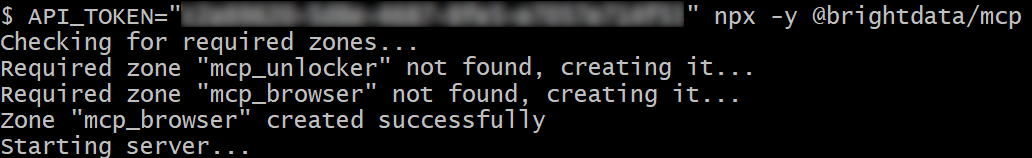
On the first launch, the Web MCP automatically creates two default zones in your Bright Data account:
mcp_unlocker: A zone for Web Unlocker.mcp_browser: A zone for Browser API.
Web MCP relies on those two Bright Data products to power its 60+ tools.
If you want to verify that the zones were set up, reach the “Proxies & Scraping Infrastructure” page in your Bright Data dashboard. You should see the two zones in the table:
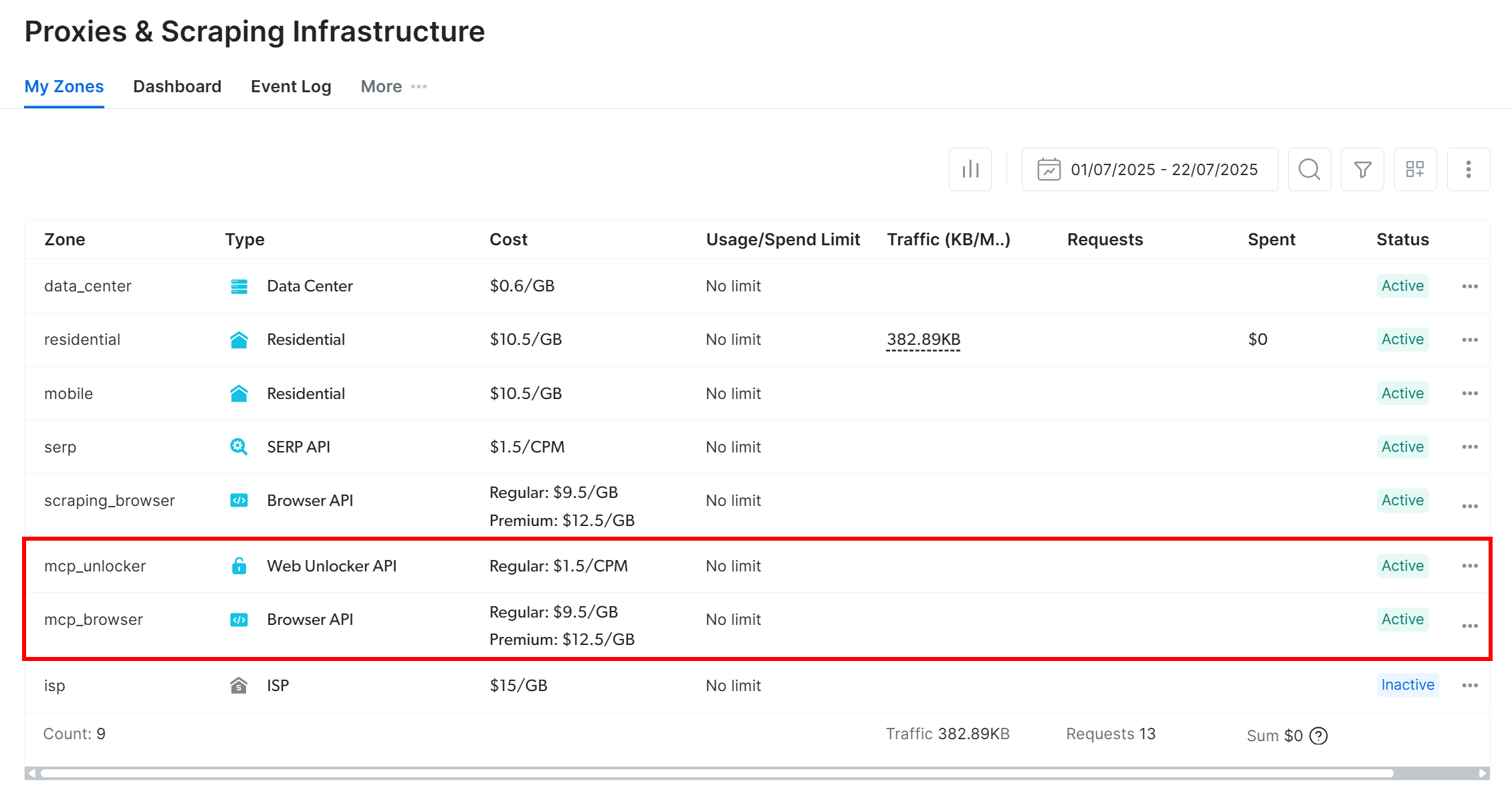
Note: If your API token does not have Admin permissions, the two zones will not be created. In this case, you must define them manually and set them via environment variables as shown on GitHub.
On the Web MCP free tier, the MCP server only exposes the search_engine and scrape_as_markdown tools (and their batch versions). To unlock all other tools, you need to enable Pro mode **by setting the PRO_MODE="true" environment variable:
API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>" PRO_MODE="true" npx -y @brightdata/mcpOr, on Windows:
$Env:API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>"; $Env:PRO_MODE="true"; npx -y @brightdata/mcpPro mode unlocks all 60+ tools, but it is not included in the free tier. So, it will incur additional charges.
Perfect! You just verified that the Web MCP server is running on your machine. Now, stop the MCP process, as you will configure the MCP clients to launch and connect to it next.
How to Integrate Bright Data Web MCP into Ollama with MCPHost
In this step-by-step section, you will learn how to integrate an Ollama model with a local instance of Bright Data Web MCP using MCPHost.
Prerequisites
Along with the previous prerequisites, you need Go 1.23+ installed on your system. It is necessary to set up and run MCPHost.
Step #1: Install MCPHost
Install MCPHost using the command below:
go install github.com/mark3labs/mcphost@latestYou can now launch MCPHost using the mcphost command-line tool.
Note: MCPHost can also be used programmatically in Go scripts via its SDK.
Step #2: Configure the Tool and Get Familiar With It
To start MCPHost with a specific Ollama model, run the following command:
mcphost -m ollama:<model_name>Replace <model_name> with the name of the Ollama model you want MCPHost to use.
If the specified model is not available locally, it will be automatically pulled for you. Once loaded, this is the UI you will see in the CLI:
Refer to the documentation for a full list of available commands. For example, running the /tools command will display:

You will see no tools, as you still need to specify an MCP integration.
Step #3: Create the Web MCP Connection Configuration File
By default, MCPHost looks for global-level configuration in ~/.mcphost.yml or~/.mcphost.json on macOS and Linux, and in %USERPROFILE%\.mcphost.yml or %USERPROFILE%\.mcphost.json on Windows.
Here, we will define a configuration to connect to Web MCP using a local YAML file. If you prefer a global configuration, you can update the files mentioned above.
In your project folder, create a file named bd-web-mcp.yml with the following content:
mcpServers:
bright-data-web-mcp:
type: "local"
command: ["npx", "-y", "@brightdata/mcp"]
environment:
API_TOKEN: "<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"
PRO_MODE: "true"The setup above reflects the npx command used earlier, utilizing the following environment variables:
API_TOKENis required. Set it to your Bright Data API key.PRO_MODEis optional. You can remove it if you prefer not to enable Pro Mode.
In other words, this configuration file instructs MCPHost on how to launch the Web MCP server locally and connect to it.
Step #4: Connect the Ollama Model to Web MCP**
You can now start MCPHost for Web MCP integration in Ollama using the following command:
mcphost -m ollama:<model_name> --config "./bd-web-mcp.yml"For example, to launch MCPHost with the qwen2.5:0.5b model:
mcphost -m ollama:qwen2.5:0.5b --config "./bd-web-mcp.ymlThe result will look like this:
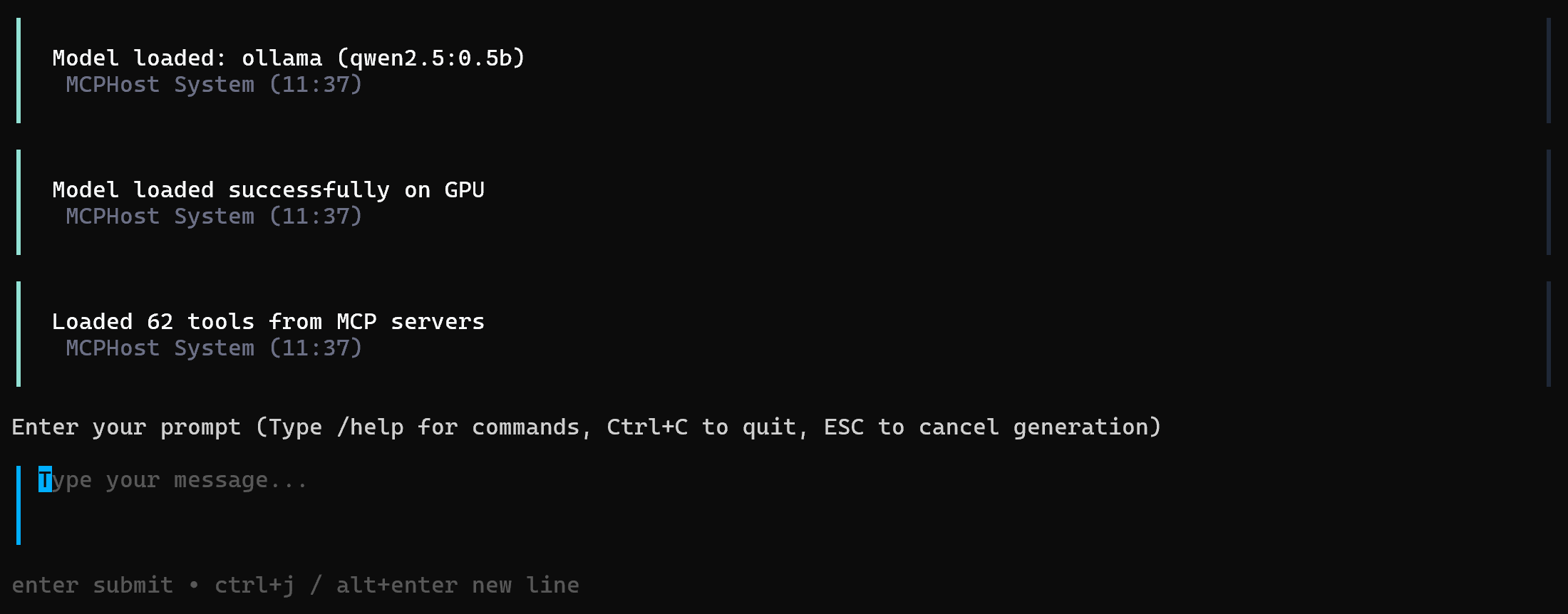
Notice that the Ollama model now has access to 60+ tools exposed by your local Web MCP instance. You can verify that by running the /tools command in the CLI, which will display a list like this:
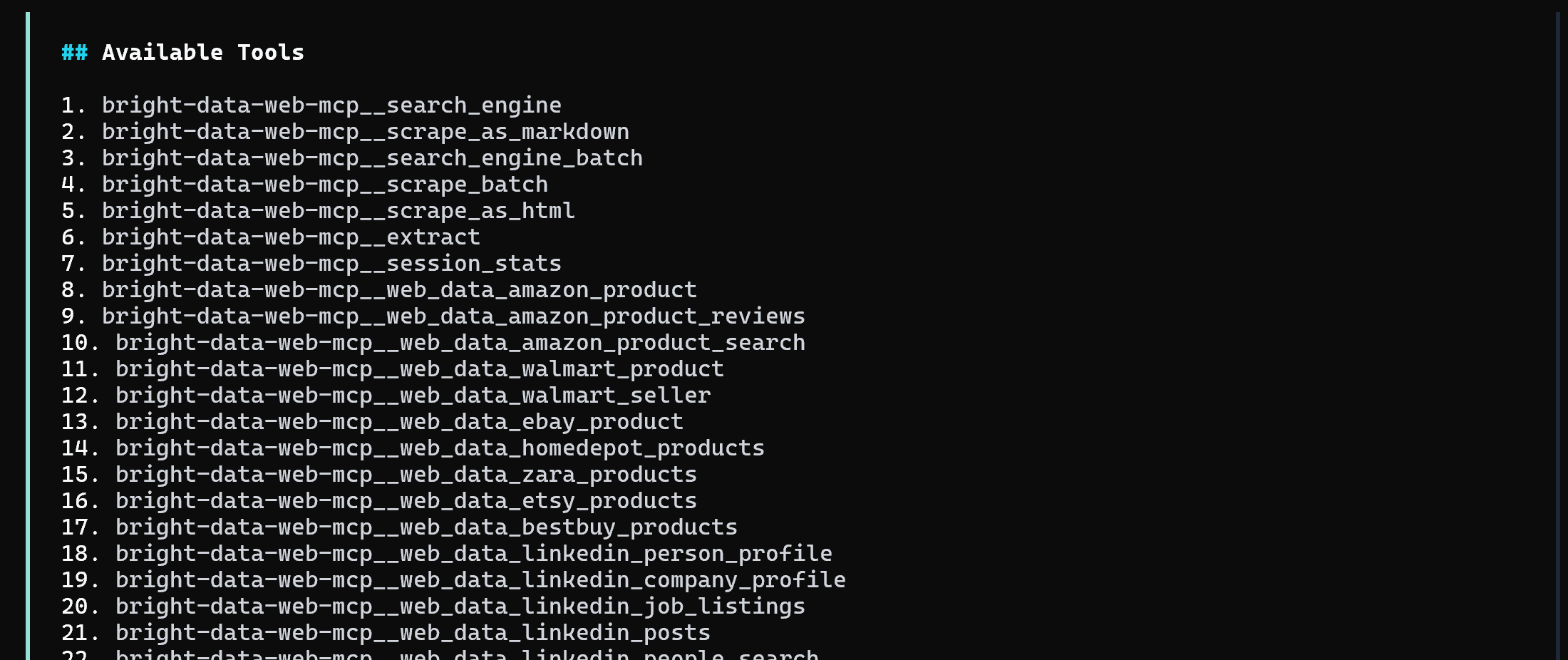
If the MCP server was configured in Pro Mode, you will see 60+ tools. Otherwise, only the 4 tools available in the free tier (search_engine, scrape_as_markdown, and their batch versions) will be accessible.
Done! Your Ollama model is now configured to work with Bright Data’s Web MCP tools.
Set Up Bright Data’s Web MCP in Ollama via ollmcp
In this section, you will be guided through connecting local Ollama models to a local Bright Data Web MCP server instance using ollmcp—the MCP Client for Ollama.
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial section, in addition to the previous prerequisites, you must have Python 3.10+ installed locally. This is required to install and run ollmcp.
Step #1: Get Started with ollmcp
Install ollmcp locally using the following command:
pip install --upgrade ollmcpNote: You can also run this command inside a virtual environment, if preferred.
Verify that the MCP Client for Ollama is installed correctly by launching it:
ollmcpYou should see the view below:
By default, ollmcp uses qwen2.5:7b as the initial model. Also, notice that the client will not detect any MCP tools yet, which is expected.
Step #2: Configure an LLM
Launch ollmcp with a specific Ollama model via the --model (or -m) flag. So, the launch command would become:
ollmcp --model <model_name>Or, equivalently:
ollmcp -m <model_name>Where <model_name> is the name of your desired Ollama model.
Alternatively, you can configure the model from within the CLI using the model command:
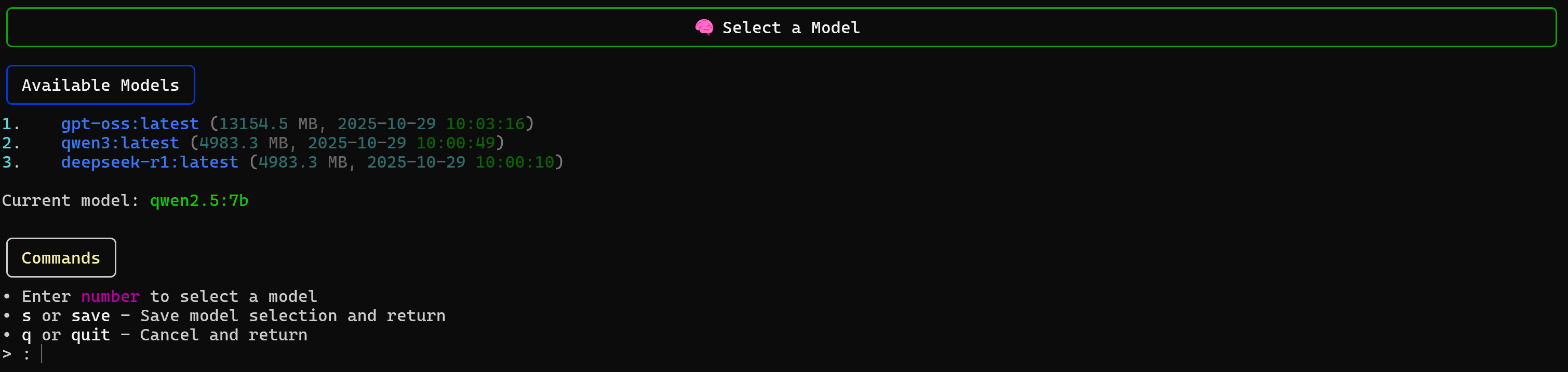
Then select the model you want to use. For more information about available flags and options, refer to the official documentation.
Step #3: Add the Web MCP Configuration File
ollmcp supports several options for MCP server integration:
--mcp-server,-s: Path to one or more MCP server scripts (.pyor.js). It can be specified multiple times.--mcp-server-url,-u: URL to one or more SSE or streamable HTTP MCP servers. You can specify it multiple times.--servers-json,-j: Path to a JSON file containing server configurations with a specific format.--auto-discovery,-a: Automatically discover servers from Claude’s default config file (default behavior if no other options are provided).
In this guide, we are going to use a custom JSON file, which is Claude-like and one of the simplest options.
In your project folder, create a file named bd-web-mcp.json. Populate it as follows:
{
"mcpServers": {
"bright-data-web-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@brightdata/mcp"],
"env": {
"API_TOKEN": "<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>",
"PRO_MODE": "true"
}
}
}
}The above setup mirrors the npx command tested earlier, using these environment variables:
API_TOKENis required. Replace the<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>placeholder with your Bright Data API key.PRO_MODEis optional. So, you can remove it, if you do not want to enable Pro Mode.
In simpler terms, that JSON file tells the MCP Client for Ollama how to start the Web MCP server locally and connect to it.
Step #4: Connect to the Web MCP
Use the --servers-json flag to specify the bd-web-mcp.json file you created earlier and connect to the Web MCP server:
ollmcp --servers-json .\bd-web-mcp.jsonThis is what you should get:
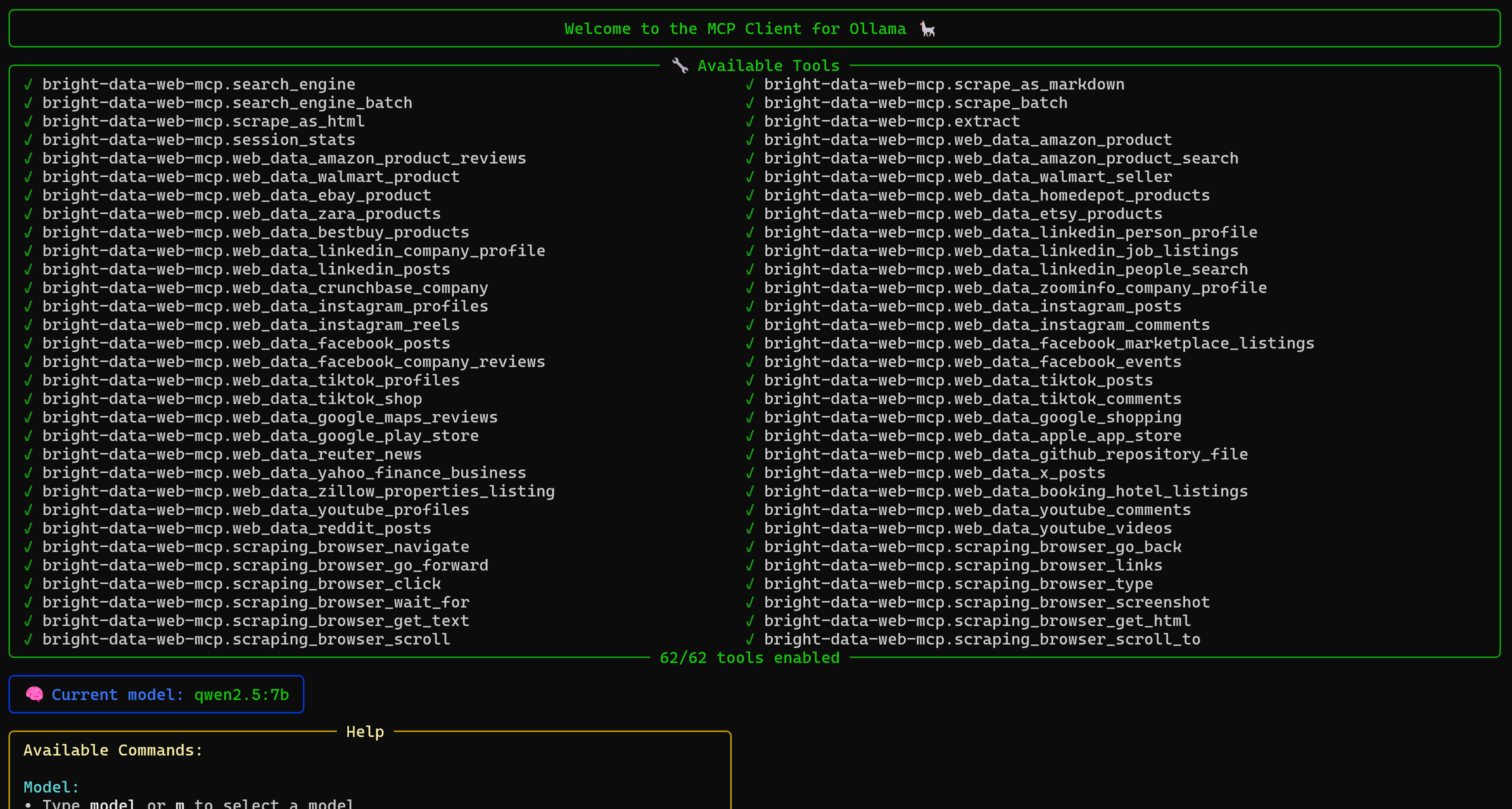
As you can tell, the model in ollmcp now has access to the 60+ tools exposed by your local Web MCP server instance. If you configured the server without Pro Mode enabled, only a few tools (such as search_engine, scrape_as_markdown, and their batch versions) will be available.
You can also list all available tools by running the tools command in the CLI:
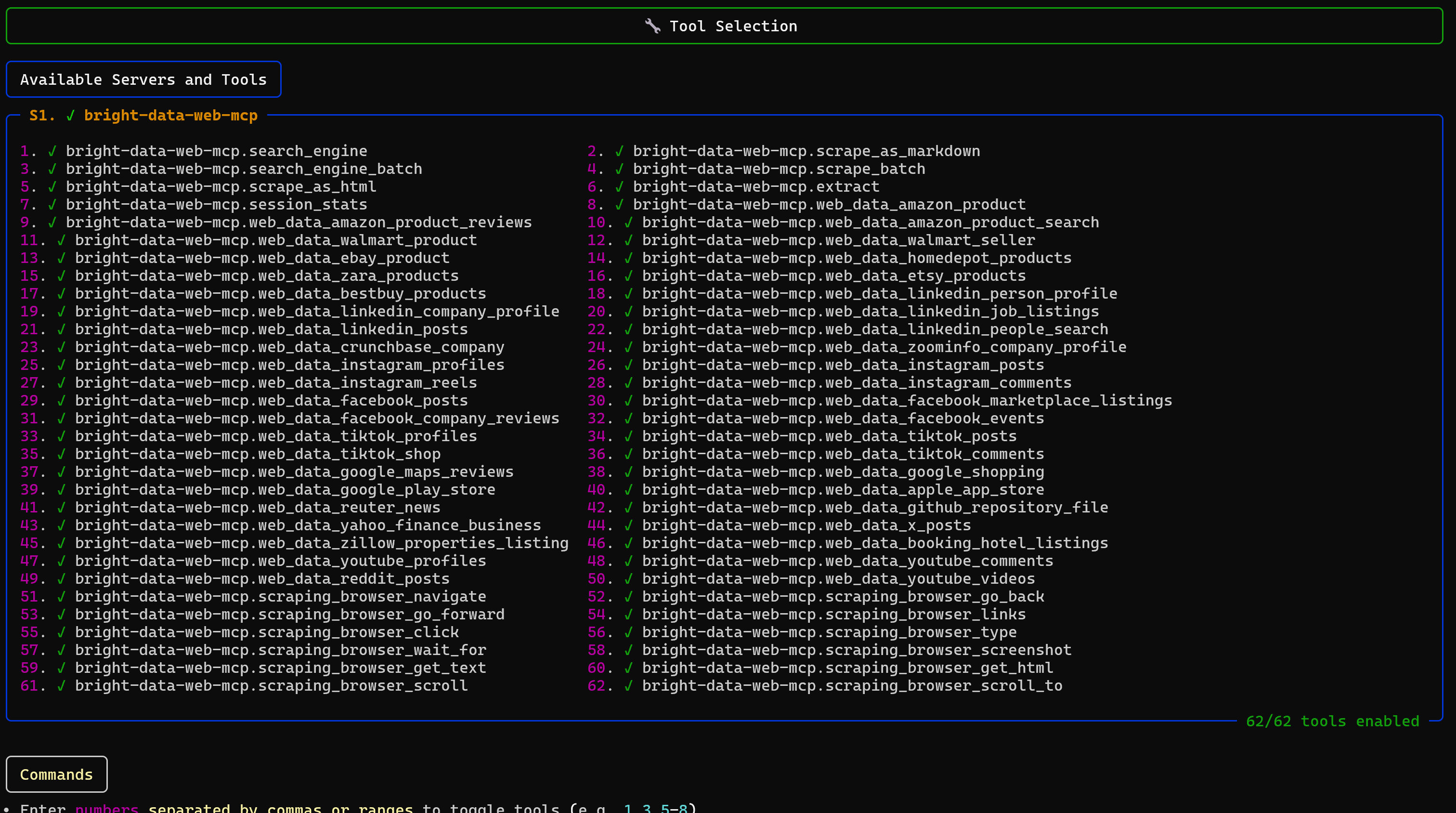
You have successfully integrated your Ollama model with the Web MCP. Mission complete!
Take Advantage of Web MCP Tools in Ollama Models
No matter which path you choose for Web MCP integration in Ollama, the result is the same: an Ollama model extended by the Bright Data Web MCP server tools.
This means your Ollama model now has access to tools for web search, web scraping, browser page integration, web data retrieval, and more. This enables your model to cover a wide range of use cases that are normally unavailable to standard LLMs.
For example, you can use your LLM for fact-checking via web search tools, summarizing news articles given a URL using scraping tools, web interaction in an agentic AI system, and many more tasks.
To better showcase the Web MCP server functionality, configure it in Pro mode. Then, use ollmcp with the llama3.2 model (or MCPHost):
ollmcp --model llama3.2 --servers-json .\bd-web-mcp.jsonTry a prompt like this:
Retrieve TikTok profile data from the following TikTok profile URL:
"https://www.tiktok.com/@khaby.lame".
Return the key influencer stats in a report in Markdown, and include a final comment on whether this user could be a good candidate for a collaboration to promote our air conditioner, given their audience.This is a great example of a task requiring web data retrieval capabilities.
The result will look like this:
The Ollama model analyzes your prompt and selects the web_data_tiktok_profiles tool from Web MCP. That tool is defined as “Quickly read structured TikTok profile data. Requires a valid TikTok profile URL. Often faster and more reliable than scraping.” Thus, that was the perfect tool selection.
You will be asked for permission to run the tool. Type y and press Enter to execute the prompt. This launches an asynchronous TikTok Scraper task on Bright Data infrastructure. Once the structured profile data is ready, Ollama processes it.
This time, the resulting report was:
**Profile:**
- **Nickname:** Khabane Lame
- **Verified:** Yes
- **Followers:** 161,100,000
- **Following:** 83
- **Account Created:** August 10, 2016
- **Profile Language:** English
- **Biography:** "Se vuoi ridere sei nel posto giusto. If u wanna laugh u r in the right place"
- **Profile Link:** \[TikTok Profile\](https://www.tiktok.com/@khaby.lame)
**Engagement Rates:**
- **Average Engagement Rate:** 0.61%
- **Like Engagement Rate:** 0.60%
- **Comment Engagement Rate:** 0.009%
**Content Overview:**
- **Total Videos:** 1,293
- **Top Videos Playcount Range:** 1.4M – 209.3M
- **Top Videos Favorites Range:** 1,199 – 287,000
- **Top Videos Comments Range:** 1,035 – 87,000
**Audience Insight:**
- Content is highly comedic and appeals to a global audience seeking light, humorous content.
- Engagement is strong in terms of likes and shares, though comment engagement is comparatively low.
**Collaboration Potential:**
Khabane Lame's massive audience and global appeal make him a strong candidate for brand promotion. However, his niche is humor and viral entertainment. Collaborating on an air conditioner campaign would require a creative, humorous angle that naturally fits his content style. Straight product promotion may not resonate unless tied to comedic or relatable scenarios (e.g., escaping heat in funny ways). As you can see, this report contains all the data for Khaby Lame‘s TikTok profile—including insightful analysis such as engagement rates.
The final comment highlights that the selected influencer may not necessarily be ideal for promoting an air conditioner, which is exactly what you want to determine.
Now, try experimenting with other prompts and explore the Web MCP capabilities in Ollama!
Conclusion
In this blog post, you learned how to leverage MCP tools in Ollama. In particular, you saw how to enhance local Ollama models with tools from Bright Data’s Web MCP, running locally via the @brightdata/mcp package.
This integration empowers your model with capabilities for web search, structured data extraction, live web data feeds, automated web interactions, and much more.
To create even more advanced AI agents, explore the full suite of AI-ready tools and services available within Bright Data’s ecosystem.
Sign up for a free Bright Data account today and get your hands on our web data tools!