In this article, you’ll learn:
- What multimodal AI is and why it matters for modern applications.
- How Bright Data enables practical multimodal AI implementations through web data collection.
- How to build a working multimodal AI application using Bright Data’s tools through a step-by-step guided section.
Let’s dive in!
What Is Multimodal AI?
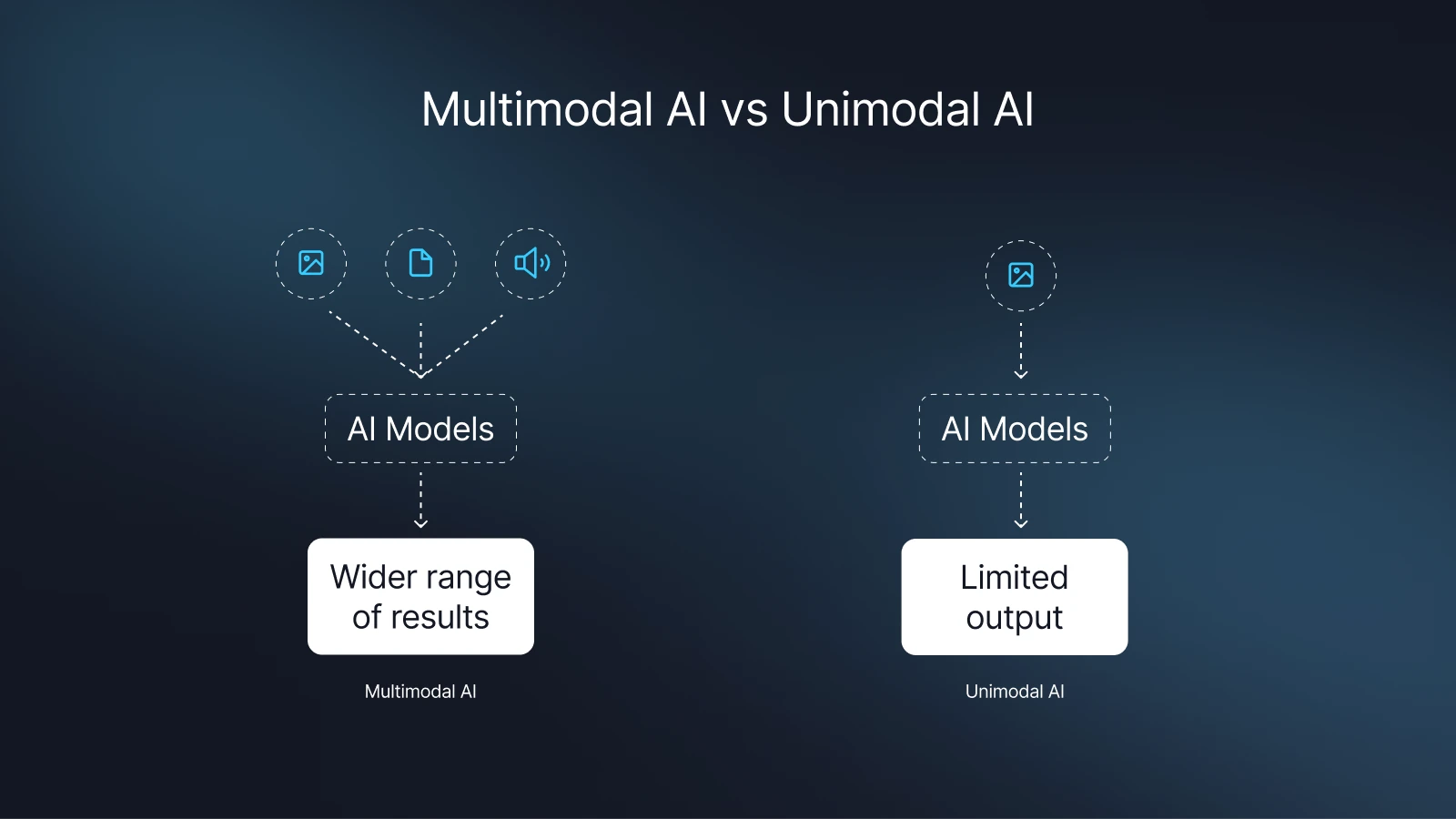
Multimodal AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can process, interpret, and generate insights from more than one type (or “mode”) of data at the same time. This includes text, images, video, audio, and structured data.
For example, it can receive a photo of a plate of cookies and generate a written recipe as a response and vice versa.
This convergence enables far more powerful and nuanced applications, such as:
- Advanced Content Analysis: Understanding the context of a meme by analyzing both the image and its caption.
- Intelligent E-commerce: Recommending products by analyzing visual style from images and textual preferences from reviews.
- Enhanced Research: Extracting data from scientific papers that include charts, diagrams, and text.
Think of multimodal AI as giving your computer both eyes and ears, it can read text and view images.
Why Bright Data Is Key to Building Multimodal AI Applications
Building a multimodal AI application starts with one critical component: diverse, high-quality, and scalable data. This is where Bright Data becomes an indispensable partner.
Access to Diverse Data Sources
Multimodal AI requires a rich diet of different data types. Bright Data provides seamless access to text, images, videos, and structured data from across the entire public web. Whether you need to collect product images and descriptions from e-commerce sites, analyze social media posts with their visuals, or gather news articles with embedded media, Bright Data’s infrastructure and tools (like the Web Scraper API and Datasets) make it possible to gather all these modalities in one cohesive workflow.
Enterprise-Grade Data Quality
AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on or given. Bright Data ensures the data you collect is clean, reliable, and accurate. Through features like automatic IP rotation, CAPTCHA handling, and JavaScript rendering, Bright Data fetches complete, unblocked data exactly as a human user would see it. This quality is non-negotiable for building production AI applications that deliver consistent, trustworthy results.
Scalability for Production Use Cases
A proof-of-concept is one thing; a full-scale application is another. Bright Data’s global proxy network and robust infrastructure are built for scale. You can collect multimodal data from thousands of sources simultaneously without worrying about blocks, bans, or rate limits, ensuring your AI application can grow to meet user demand.
How to Build a Multimodal AI Application with Bright Data
Let’s build a practical application. This tool will use Bright Data to scrape a product page, collect the image and text data, and then send it to a multimodal AI model (like GPT-4 Vision) to generate a structured analysis
Prerequisites
- A Bright Data account.
- An OpenAI API key with access to the gpt-4-vision-preview model or an Anthropic API key.
- Node.js (v18+) or Python environment installed.
- Basic knowledge of API integration.
Step 1: Set Up Bright Data for Multimodal Data Collection
We’ll use Bright Data’s Web Scraper API for its ease of use and JavaScript rendering capabilities, which are crucial for capturing modern, dynamic product pages.
- Log into Bright Data Web Scraper
- Create a new scraper. For this example, let’s target a sample product page.
- Enter your target URL
- In the “Parsing Instructions,” copy and paste the JSON below.
Scraper Configuration Example (Bright Data UI):
{
"title": ".product-title",
"image_url": ".main-product-image img | attr:src",
"description": ".product-description",
"price": ".price",
"specs": ".specifications-table"
}Step 2: Configure the Multimodal AI Model
Now that your data pipeline is ready, let’s hook up the AI brain of our project — OpenAI’s gpt-4-vision model.
This model can understand both text and images, which makes it perfect for our multimodal use case.
1. Get Your API Key
Head over to your OpenAI Dashboard and create a new API key.
Keep this key safe, you’ll need it in your code shortly.
2. Set Up Your Development Environment
We’ll be running this project in either Node.js or Python, depending on your preference.
Open your terminal inside your project folder, then install the official OpenAI SDK:
For Node.js:
npm init
npm install openaiFor Python:
pip install openaiOnce the installation finishes, you’re ready to send your first request to the model in the next step.
Step 3: Collect Web Data with Bright Data
Now that our model is ready, let’s gather real-world data using Bright Data.
This is the part where your project starts feeling alive. We’re going to fetch text and image data from an actual product page.
1. Connect to the Bright Data API
Open your project’s main script (for example, index.js or main.py), and add the following code to connect to Bright Data’s Web Scraper API.
Node.js Example:
import fetch from "node-fetch";
const BRIGHTDATA_API_KEY = "YOUR_BRIGHTDATA_API_KEY";
const SCRAPER_ID = "YOUR_SCRAPER_ID";
const response = await fetch(
`https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/run?dataset_id=${SCRAPER_ID}`,
{
method: "POST",
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${BRIGHTDATA_API_KEY}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
url: "https://example.com/product-page", // Replace with an actual product URL
}),
}
);
const scrapedData = await response.json();
console.log("Collected Multimodal Data:", scrapedData);2. Verify Your Data
Once you run this script, you should see structured product data printed in your console.
It might look something like this (values will differ based on your target URL):
{
"title": "Wireless Noise-Cancelling Headphones",
"image_url": "https://examplecdn.com/headphones.jpg",
"description": "Premium over-ear headphones with active noise cancellation and 30-hour battery life.",
"price": "$199.99",
"specs": {
"battery_life": "30 hours",
"connectivity": "Bluetooth 5.2",
"color": "Black"
}
}This output confirms that your Bright Data setup is working correctly and returning both text and image inputs, the perfect foundation for our multimodal AI analysis.
Step 4: Process and Structure the Data
Now that we’ve collected our raw product data from Bright Data, it’s time to prepare it for our multimodal AI model.
The goal here is to give the model everything it needs, clean text, a clear image reference, and a well-structured prompt that tells it exactly what to do.
1. Format the Product Data
Let’s take our scraped data and turn it into a well-structured message for the AI model.
Node.js Example:
// Assume scrapedData contains the product info returned from Bright Data
const productAnalysisPrompt = `
Analyze this product and provide a structured summary. Use both the product image and text data.
Product Details:
- Title: ${scrapedData.title}
- Description: ${scrapedData.description}
- Price: ${scrapedData.price}
- Specifications: ${JSON.stringify(scrapedData.specs)}
Based on the image and text, please answer:
1. What is the primary use case for this product?
2. List 3 key features visible or described.
3. Evaluate the product’s perceived quality and value.
`;
const imageUrl = scrapedData.image_url;What we did here:
- Combined all our text data into one detailed prompt.
- Stored the image URL separately so the AI can visually process it.
2. Test Your Data Structure
Before moving to the AI call, log your variables to verify they look clean and valid.
console.log("Prompt Preview:", productAnalysisPrompt);
console.log("Image URL:", imageUrl);If everything looks readable and the image URL begins with https://, you’re ready for the next phase, feeding it into the multimodal AI model.
Step 5: Send Data to the Multimodal AI Model
Now comes the exciting part, sending our combined text + image data to the multimodal AI model to get intelligent insights.
We’ll use the gpt-4-vision model from OpenAI, which can “see” the image and “read” the text simultaneously to generate a detailed analysis.
1. Initialize the OpenAI Client
We’ll connect to the API using the official OpenAI SDK.
Node.js Example:
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({ apiKey: "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY" });2. Create a Multimodal Request
Next, we’ll send the formatted product text and image URL together in one API call.
const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4-vision-preview",
messages: [
{
role: "user",
content: [
{ type: "text", text: productAnalysisPrompt },
{ type: "image_url", image_url: { url: imageUrl } },
],
},
],
max_tokens: 1000,
});
const aiResponse = completion.choices[0].message.content;
console.log("AI Analysis Result:", aiResponse);3. Interpret the AI’s Response
After running this, you’ll get a structured analysis similar to this:
The product appears to be premium wireless over-ear headphones designed primarily for travelers and professionals who need noise isolation in noisy environments.
Key features include:
1. Active noise cancellation technology visible from the ear cup design
2. 30-hour battery life mentioned in specifications
3. Premium matte black finish visible in the image
The headphones present as high-quality based on the visible materials and the detailed technical specifications provided. The price point suggests a premium market positioning.Step 6: Handle and Display Results
Now that the AI model has produced its analysis, let’s organize and present the response in a more readable way.
You can keep it simple in the console or render it nicely in a web dashboard later on.
1. Format the AI Response
We’ll take the raw text returned by the model and output it neatly.
Node.js Example:
console.log("=== PRODUCT INTELLIGENCE ANALYSIS ===");
console.log(aiResponse);
// (Optional) Save the output to a file
import fs from "fs";
fs.writeFileSync("analysis_output.txt", aiResponse);
console.log("Analysis saved to analysis_output.txt");If you want to store results centrally for later use, you could also save them in a database or display them on a simple React frontend.
2. (Optional) Create a Basic Web Preview
For a more visual experience, you can serve the results through a local web page.
Mini Node.js Server Example:
import express from "express";
import fs from "fs";
const app = express();
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
const result = fs.readFileSync("analysis_output.txt", "utf8");
res.send(`
<h2>Product Intelligence Analysis</h2>
<pre>${result}</pre>
`);
});
app.listen(3000, () =>
console.log("Server running at http://localhost")
);Open your browser and visit http://localhost, you’ll see the model’s analysis nicely formatted in plain text.
Conclusion
Multimodal AI represents a significant leap forward, enabling applications that understand the world in a richer, more human-like way. As we’ve demonstrated, the key to unlocking this potential is access to high-quality, diverse, and scalable real-world data.
Expand and Experiment
You can take this project even further:
- Add more data sources: Pull reviews or videos from e-commerce websites for deeper analysis.
- Integrate a frontend: Display the AI’s output in a clean React or Next.js dashboard.
- Automate reports: Schedule daily scrapes and analyses for competitive product monitoring.
Each extension you create pushes your project closer to a production-level AI data intelligence tool.
Ready to power your AI projects with the world’s best web data?
- Sign up for Bright Data today and get started with free credits.
- Experiment with the code example, try it on different websites, and explore other tools in Bright Data’s arsenal, like the Data Collector or ready-made Datasets.
Start building the next generation of intelligent applications.