In this blog post, you will learn:
- What robotics AI is and why it is becoming the hottest trend in the market.
- Why high-quality data and dedicated SDKs are the two pillars of the industry.
- The key aspects to consider when comparing robotics AI solutions.
- The top 10 robotics AI libraries, selected and compared according to these criteria.
Let’s dive in!
TL;DR: Summary Table of the Best Robotics AI Libraries, SDKs, and Solutions
Compare the top Robotics AI libraries at a glance in the summary table below:
| Robotics AI Library | Use Cases | Backed By | Nature | License | Main Programming Language | GitHub Stars |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA Isaac | AMRs, manipulators, humanoids, perception, motion planning, SLAM, robot learning, simulation, deployment | NVIDIA | Open robotics platform (open-source components + some NVIDIA-managed resources) | Depends on the specific library | Python | Up to 6k+ |
| LeRobot | Imitation learning, reinforcement learning, vision-language-action (VLA), teleoperation, data collection, training, deployment | Hugging Face | Open-source | Apache-2.0 | Python | 21.4k |
| Intel Open Edge Robotics AI Suite | Humanoid imitation learning, AMRs, stationary robot vision & control, perception, motion planning, VLA tasks | Intel | Open-source SDKs and libraries | Depends on the specific library | Python | 84 |
| Bullet Physics SDK | Collision detection, multi-physics simulation, reinforcement learning, kinematics, VR, robotics | Erwin Coumans + community | Open-source | zlib | C++ (with Python bindings) | 14.2k |
| MoveIt Pro | Motion planning, collision avoidance, manipulation, multi-arm systems, vision-guided robotics | PickNik Robotics | Hybrid (commercial platform + open-source SDK) | BSD-3-Clause | Python | 10 |
| Gymnasium-Robotics | Reinforcement learning, multi-goal tasks, manipulation, navigation, multi-agent setups | Farama Foundation | Open-source | MIT | Python/TypeScript | 18 |
Important: No matter which library, SDK, or solution you choose for robotics AI development, you need a trusted provider of high-quality multimodal data. Bright Data supports you with:
- Multimodal AI data packages: Curated datasets for training and fine-tuning AI models.
- Endless video data: Massive volumes of video content ready for robotics AI scenarios.
- Annotation and labeling services: Scalable, accurate labeling for text, images, video, and audio to enhance your models.
What Is Robotics AI? And Why It Is the Next Big Trend!
Robotics AI refers to the integration of artificial intelligence into robotic systems. The idea behind it is to empower machines to perceive, adapt, reason, and act autonomously in dynamic environments rather than just follow pre-programmed instructions.
It merges physical robotics hardware with cognitive AI aspects such as machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing. The robotics AI field is gaining significant attention, with established companies and startups entering the market. Known products include:
- Optimus (Tesla): AI-powered humanoid for industrial and household tasks
- NEO (1X): Home assistant robot with AI autonomy and safe human interaction
- Electric Atlas (Boston Dynamics): Agile industrial robot for inspection, research, and dynamic tasks
- Figure 03 (Figure AI): AI-driven robot for industrial automation and logistics
- G1 (Unitree Robotics): Compact, efficient robot for logistics and service industries
Market projections highlight the growth potential. Goldman Sachs expects the robotics AI market to reach $28 billion by 2035, while Morgan Stanley predicts a $5 trillion market by 2050. These trends indicate that robotics AI is a fundamental driver of the next wave of industrial and human innovation.
Data and SDKs: The Two Core Pillars of Successful Robotics AI Projects
Training AI models—or fine-tuning them for specific tasks—is never simple. When these models need to control robots or interact with the physical world, complexity grows exponentially. To tackle this, you need access to:
- Robotics AI libraries and SDKs specifically built to train and deploy AI for robotic applications, including perception, navigation, and manipulation.
- Multimodal data (images, video, audio) optimized to streamline robotics AI model training and enhance real-world performance and interactivity.
Explore these two pillars as the foundation for effective robotics AI systems!
The Need for Dedicated Robotics AI Libraries
Robotics AI libraries are specialized frameworks engineered to develop intelligent systems that synchronize perception, decision-making, and motion control in real time.
Unlike general AI or ML libraries, they combine physics simulation, sensor models, kinematics, motion planning, and robot-specific learning workflows into cohesive toolkits. Robotics AI tools bridge the gap between sensory input and physical execution, helping robots navigate and interact with their environments dynamically.
They are indispensable because robotics operates in the physical world, where errors are costly and constraints are non-negotiable. By standardizing pipelines and integrating tightly with hardware and simulators, they drastically reduce development time and make advanced robotics AI practical to build, test, and deploy at scale.
Bright Data: The Best Data Provider for Robotics AI
No matter how powerful a robotics AI library or toolkit is, model performance and system reliability ultimately depend on the quality of the data used to train and ground it. Robots operate in the physical world, where perception errors, incomplete context, or biased training data can directly lead to failed actions, safety risks, or brittle behavior.
Modern robotics artificial intelligence systems rely on up-to-date, diverse multimodal data for training vision-language-action models on real environments, edge cases, and long-tail scenarios. Without this foundation, even the most advanced simulation, planning, or control stack will underperform when deployed in the real world.
This is where Bright Data becomes a critical enabler for robotics AI!
Bright Data provides enterprise-ready services for discovering, extracting, and delivering massive volumes of high-quality, multimodal web data at scale. Key services include:
- Multimodal AI data packages: Access hundreds of curated datasets or set up real-time extraction pipelines to power AI development and deployment.
- Endless video data: Over 2.3B videos extracted and available for AI training, including robotics scenarios.
- Annotation and labeling services: Scalable, accurate data annotation for text, images, video, and audio—via automated, hybrid, or human-supervised workflows.
All of Bright Data’s solutions are backed by enterprise-grade infrastructure with 99.99% uptime, 24/7 expert support, and unlimited scalability, ensuring continuous access to the data your robotics AI systems need.
Main Factors to Consider When Evaluating Robotics AI Libraries
Robotics artificial intelligence is still a growing field, so there are not yet universally established SDKs or providers. However, many robotics AI libraries exist, and the best way to compare them is using common criteria like:
- Scope: Defines the library’s focus and which aspects of robotics AI it supports.
- Origin: The organization or community behind the library.
- Nature: Whether it is open source, proprietary, or a hybrid model.
- Programming languages: Languages supported for developing with the library and integrating its API.
- GitHub stars: Popularity and community adoption based on GitHub metrics.
Top 10 Robotics AI Solutions
Explore the list of top robotics AI libraries, SDKs, and solutions, carefully selected and ranked based on the criteria outlined above.
1. NVIDIA Isaac
NVIDIA Isaac is an open, end-to-end robotics AI platform for developing, simulating, and deploying autonomous robots such as AMRs, manipulators, and humanoids. It combines CUDA-accelerated libraries, Isaac ROS, and Isaac Sim with pretrained AI models and reference workflows to enable high-performance perception, motion planning, SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), and robot learning across simulation and deployment.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Robotics teams needing full-stack, large-scale, high-performance simulation, learning, and deployment in one ecosystem.
Scope:
- Open robotics development platform for building AI-powered robots.
- Supports simulation, robot learning, training, deployment, operation, and optimization.
- Covers manipulation, mobility, perception, SLAM, motion planning, and humanoid robotics.
- Includes simulation (Isaac Sim), robot learning (Isaac Lab), ROS 2 acceleration (Isaac ROS), and foundation models (Isaac GR00T).
Origin:
- NVIDIA + community.
Nature:
- Open robotics development platform, with open-source components (e.g., Isaac ROS, Newton) alongside NVIDIA-managed libraries and models.
Programming languages:
- Generally, in Python (e.g., pycuVSLAM, Isaac Lab, Isaac Sim workflows), but this depends on the specific sub-library.
- CUDA (for accelerated libraries and models).
- ROS 2–based APIs (language bindings not explicitly specified).
GitHub stars:
- Some specific libraries exceed 6k stars.
2. LeRobot
LeRobot by Hugging Face is an open-source PyTorch library designed to democratize robotics AI. It provides tools, datasets, and pre-trained models for real-world robotics use cases. The library supports hardware-agnostic control across low-cost arms and humanoids, standardized LeRobotDataset formats, and state-of-the-art imitation and reinforcement learning policies. It equips you with tools for training, teleoperation, and deployment of autonomous robotic tasks.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Researchers and hobbyists collecting, training, and deploying real-robot datasets.
Scope:
- Provides models, datasets, and tools for real-world robotics in PyTorch.
- Focuses on imitation learning, reinforcement learning, and vision-language-action (VLA) policies.
- Supports hardware control, data collection, training, simulation, and evaluation.
Origin:
- Hugging Face + community.
Nature:
- Open-source (community contributions welcomed).
- Apache-2.0 license.
Programming languages:
- Python.
GitHub stars:
- 21.4k stars.
3. Intel’s Open Edge Robotics AI Suite
Robotics AI Suite is an open-source collection of SDKs, microservices, and reference applications for stationary, autonomous mobile (AMR), and humanoid robots. Built on Intel’s Open Edge platform with ROS 2 integration, OpenVINO optimization, and hardware acceleration. It helps robots see, move, and make decisions at the edge, supporting vision AI, motion control, and imitation learning workflows.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Vision-heavy industrial and stationary robots running on constrained edge devices.
Scope:
- Provides AI models, libraries, pipelines, and benchmarking tools for robotics applications.
- Supports humanoid imitation learning, stationary robot vision and control, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs).
- Focuses on perception, motion planning, control, and vision-language-action (VLA) tasks.
- Includes OpenVINO-optimized models for computer vision, LLMs, and hardware acceleration on Intel CPUs, GPUs, and NPUs.
Origin:
- Intel.
Nature:
- Open-source SDKs and libraries for development and deployment.
Programming languages:
- Primarily Python, with ROS 2 integration and compatible pipelines.
- Depends on the specific sub-library or SDK being used.
GitHub stars:
- 84 stars.
4. Bullet Physics SDK
The Bullet Physics SDK is an open-source C++ library for real-time collision detection and multi-physics simulation. It is widely used in robotics, VR, games, and machine learning. The library supports both rigid and soft body dynamics, enabling realistic physical interactions. Python bindings are available via PyBullet, making it suitable for AI training and reinforcement learning research.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Learning and testing control, kinematics, and contact dynamics.
Scope:
- Collision detection and multi-physics simulation for VR, games, robotics, machine learning, and visual effects.
- Provides PyBullet Python bindings for robotics, reinforcement learning, and VR research.
- Supports physics-based object interactions, kinematics, and simulation across platforms.
Origin:
- Erwin Coumans + Bullet Physics community.
Nature:
- Open-source.
- Licensed under the permissive zlib license.
Programming languages:
- Developed in C++, C, Python, Lua, CMake, Batchfile.
- Binding available in Python via PyBullet, the recommended way to use the library.
GitHub stars:
- 14.2k stars.
5. MoveIt Pro
MoveIt Pro is a commercial, hardware-agnostic robotics AI platform by PickNik Robotics for building, simulating, and deploying advanced manipulation applications. Built on ROS 2, it combines behavior trees, AI-driven motion planning, and collision avoidance with a Python API. Supported by an open-source SDK, it underpins rapid development of robust robotic arm and mobile manipulation systems in complex environments.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Complex multi-arm or mobile manipulation with collision-aware planning.
Scope:
- Robotics application platform focused on manipulation and mobile manipulation.
- Supports motion planning, collision avoidance, computer vision, and real-time control.
- Enables simulation, deployment, teleoperation, and production-grade runtime execution.
- Engineered for complex, multi-arm, vision-guided, and AI-enabled robotic applications.
Origin:
- PickNik Robotics.
Nature:
- Hybrid model: Commercial platform (MoveIt Pro) with an open-source SDK.
- SDK licensed under BSD-3-Clause.
Programming languages:
- Python (primary SDK and APIs).
- ROS 2–based integration.
- CMake and Docker used for build and deployment workflows.
GitHub stars:
- 10 stars (on the public mirror).
6. Gymnasium-Robotics
Gymnasium-Robotics is an open-source Python library providing high-fidelity robotics simulation environments for reinforcement learning (RL). Built on the MuJoCo physics engine, it includes environments like Fetch, Shadow Dexterous Hand, and Franka Kitchen, supporting manipulation, navigation, and multi-goal tasks. Its Gymnasium-compatible API and goal-conditioned observations facilitate research, benchmarking, and reproducible RL experiments.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Benchmarking reinforcement learning algorithms in robotics.
Scope:
- Collection of reinforcement learning robotics simulation environments.
- Supports multi-goal tasks, object manipulation, and multi-agent setups.
- Uses MuJoCo physics engine and Gymnasium API for environment creation and interaction.
- Includes environments like Fetch, Shadow Dexterous Hand, Adroit Arm, Franka Kitchen, Maze, and MaMuJoCo.
- Compatible with D4RL datasets and supports Hindsight Experience Replay (HER) for RL research.
Origin:
- Farama Foundation + community.
Nature:
- Open-source.
- MIT license.
Programming languages:
- Python.
GitHub stars:
- 846 stars.
7. AI2-THOR
AI2-THOR is an open-source robotics AI platform that provides near photo-realistic 3D environments for embodied AI research. It supports multi-agent types, interactive object manipulation, physics-based simulations, and Sim2Real studies. With over 2000 objects, 200+ scenes, and rich sensory data, it gives you what you need for training and evaluating AI agents for navigation, manipulation, and perception tasks.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Training agents for visual navigation and object interaction.
Scope:
- Provides a high-level platform for embodied AI research, including visual interaction, navigation, and object manipulation.
- Supports multiple agent types, including humanoids, drones, and robotic arms (e.g., LoCoBot, Kinova-inspired).
- Offers physically realistic simulation with interactive object states, multi-agent support, and domain-randomized environments.
- Facilitates Sim2Real research with RoboTHOR and supports diverse image modalities for perception tasks.
Origin:
- PRIOR team at Allen Institute for AI (AI2) + community.
Nature:
- Open-source.
- Apache-2.0 license.
Programming languages:
- Developed in C#, Python, ShaderLab, JavaScript, HLSL, and HTML.
- Available as a Python library.
GitHub stars:
- 1.7k stars.
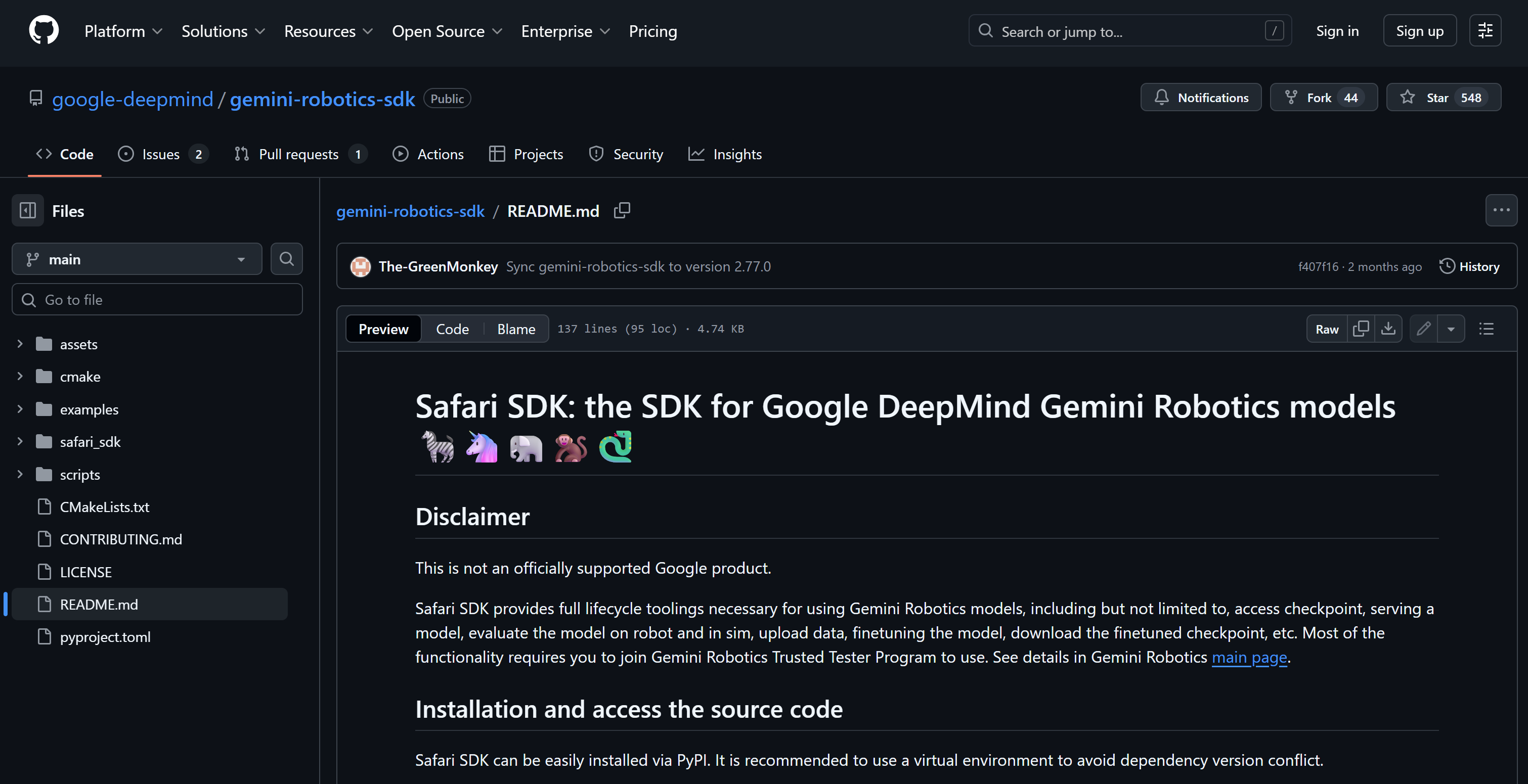
8. Safari SDK
Safari SDK, formerly known as the Gemini Robotics SDK, is an open-source Python toolkit. It helps you build and evaluate AI agents on physical and simulated robots. Developed by the Google DeepMind team, it supports full model lifecycle management and modular agent frameworks. It includes hardware-specific embodiments like Aloha and Apollo, as well as a Flywheel CLI for training, data management, and deployment.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best For: Research on interactive, reasoning-driven embodied robotics AI agents.
Scope:
- Provides full lifecycle tooling for Gemini Robotics models, including training, serving, evaluation, and fine-tuning.
- Supports building interactive agents capable of perceiving environments, reasoning, and controlling robot hardware.
- Includes modular agent framework, hardware-specific embodiments, and tools for instruction execution, scene description, and success detection.
- Enables integration with simulation and real-world robots, exemplified with the Aloha robot platform.
Origin:
- Google DeepMind (even if it is not considered an official Google product).
Nature:
- Open-source.
- Apache-2.0 license.
Programming languages:
- Python.
GitHub stars:
- 548 stars.
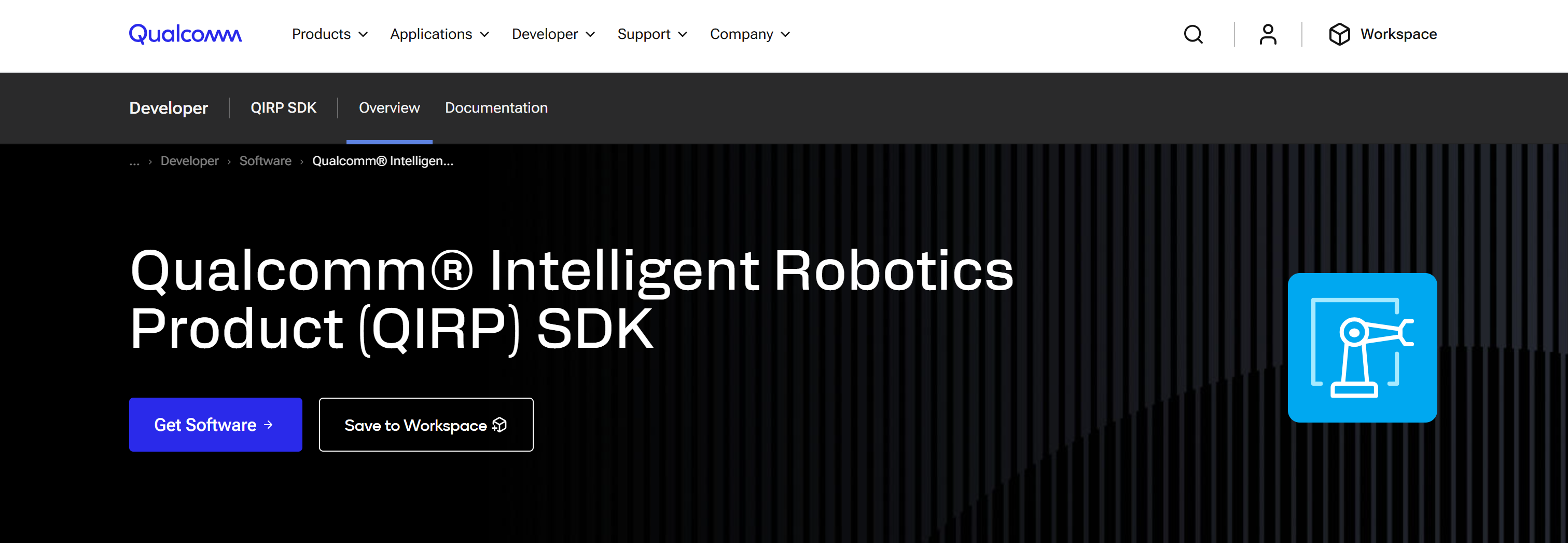
9. Qualcomm Intelligent Robotics Product (QIRP) SDK
The Intelligent Robotics Product SDK (QIRP SDK) is a developer-focused toolkit for building advanced robotics on Qualcomm platforms. It exposes ROS packages, reference applications, hardware-accelerated sensor integration, and cross-compile tools. With end-to-end samples, Gazebo simulations, and comprehensive documentation, QIRP SDK accelerates AI, motion control, and vision-based development for intelligent robotic systems on Qualcomm Linux releases.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Hardware-accelerated SLAM, vision, and sensor fusion on embedded devices.
Scope:
- Provides libraries, reference code, and ROS packages for developing robotics applications.
- Supports hardware-accelerated sensor integration (VSLAM, IMU, 2D Lidar) and AI inference on Qualcomm CPUs, GPUs, and Hexagon NPUs.
- Offers tools for vision AI, motion control, navigation, SLAM, and multimedia/AI pipelines.
- Includes cross-compile toolchain, simulation environments, and sample applications for rapid development.
Origin:
- Qualcomm.
Nature:
- Open-source.
- BSD-3-Clause license.
Programming languages:
- Primarily BitBake and Shell for build/configuration.
- Python for robotics modules and ROS integration.
GitHub stars:
- 10 stars.
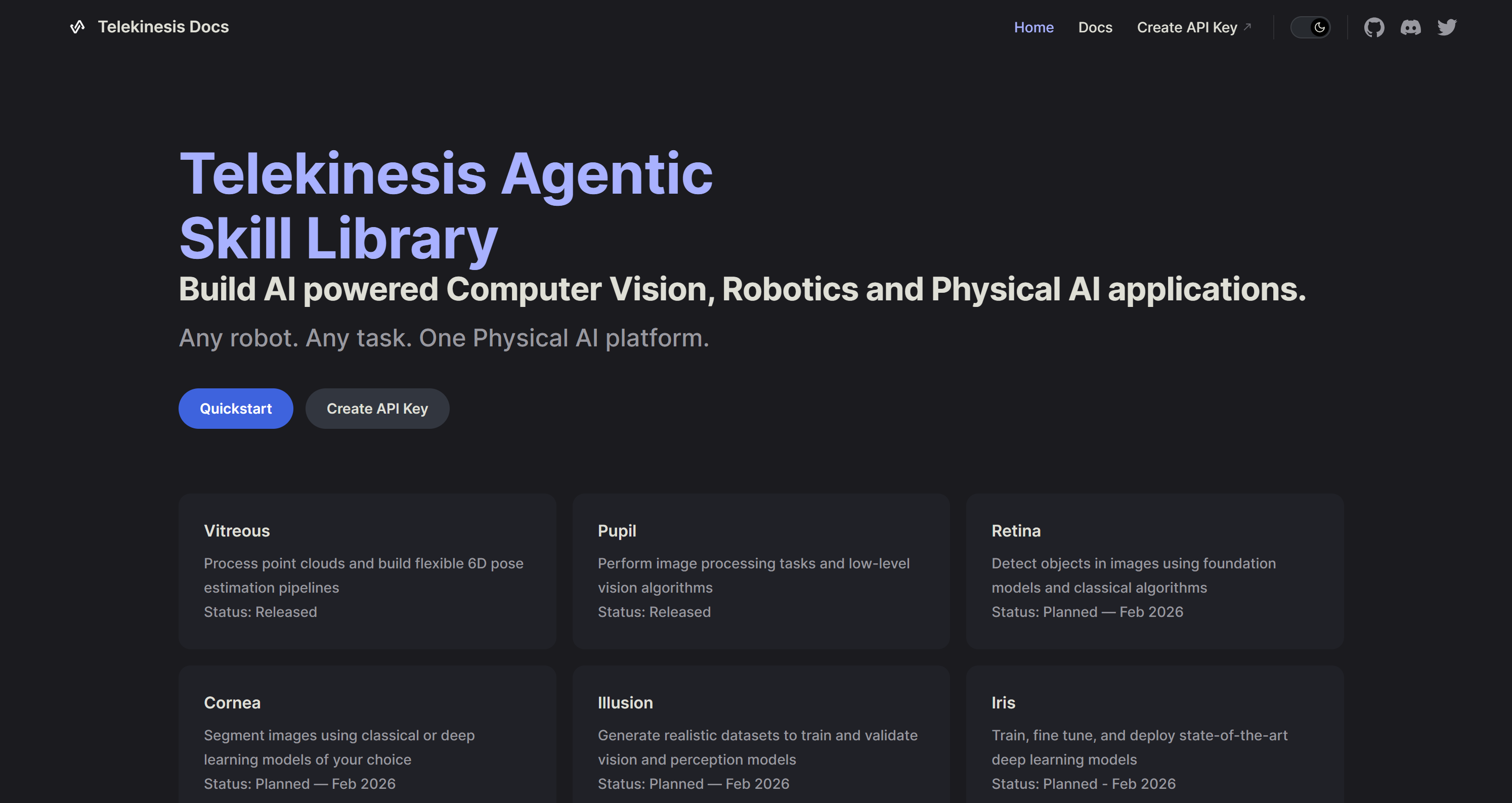
10. Telekinesis SDK
Telekinesis is a unified Python and Node.js library for Physical AI, robotics, and computer vision. It enables secure, simplified interaction with remote objects and functions using “web-pointer” Telekinesis objects. The SDK provides modular, composable skills for perception, motion planning, and control. It helps you build complete agent-based robotics systems efficiently, even in limited-trust or distributed environments.
🔗 Further reading:
1️⃣ Best for: Distributed or remote robot control in low-trust environments.
Scope:
- Supports perception (2D/3D vision, object detection, segmentation, pose estimation), motion planning, and motion control.
- Enables creation and orchestration of Physical AI Agents (LLM/VLM-driven) for task planning and real-world robot execution.
- Facilitates industrial, mobile, and humanoid robot control, simulation-to-real pipelines, and vision-guided manipulation.
- Helps you build agentic robotics, computer vision, and Physical AI systems.
Origin:
- Telekinesis.
Nature:
- Open-source.
- MIT license.
Programming languages:
- Developed in Python, TypeScript, and JavaScript.
- Available as both a Python and Node.js library.
GitHub stars:
- 18 stars.
Conclusion
In this article, you explored the immense potential of robotics AI and the pivotal role of high-quality data and libraries in building effective systems. In detail, you reviewed the top 10 robotics AI libraries and learned that what truly makes the difference is the source of the multimodal data required by these systems.
Bright Data supports all robotics AI libraries, SDKs, and solutions with enterprise-level infrastructure for AI. This includes massive multimodal datasets, unlimited access to video data, and scalable annotation services.
Sign up for a Bright Data account today for free to explore our rich web data services for AI!
FAQ
What is the difference between robotics and artificial intelligence?
Robotics focuses on designing and building physical machines that interact with the real world using sensors and actuators. By contrast, artificial intelligence technology enables learning, reasoning, and decision-making. Although they are distinct fields, robotics and AI overlap when AI is used to control or enhance robotic behavior.
What are artificially intelligent robots?
Artificially intelligent robots sit at the intersection of robotics and AI. They are physical robots whose behavior is partially controlled by AI algorithms, allowing perception, navigation, environmental understanding, and task optimization. Most rely on AI for specific functions like vision processing or path planning, rather than for controlling the entire robotic system.
What are some real-world applications of AI in robotics?
Some of the most relevant use cases for AI in robotics are:
- Manufacturing: AI-powered robots automate assembly, quality control, and predictive maintenance in smart factories.
- Service industries: Robots assist in food service, retail, and customer interaction.
- Transportation: Self-driving cars and drones use AI for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
- Healthcare: Surgical robots, rehabilitation exoskeletons, and care assistants improve precision and patient outcomes.
- Agriculture: Autonomous robots handle precision weeding, harvesting, and crop monitoring.
- Logistics: Robots enable automated sorting, warehouse automation, and last-mile delivery.
What are the primary data requirements for training robotics AI?
Training robotics AI requires diverse multimodal data, such as images and videos, to connect digital logic with physical interaction. This input allows algorithms to recognize objects so that AI-powered robots can navigate complex environments and carry out tasks accurately. Discover how Bright Data supplies video and multimedia data for AI.
Where can I find other awesome robotics AI resources?
For a list of community-curated robotics resources, see: