Google AI Mode represents a fundamental shift in how search results are presented, offering conversational AI-powered responses that synthesize information from multiple sources. For businesses tracking their digital presence, competitive intelligence teams, and SEO professionals, this new search format creates both opportunities and challenges for data extraction.
This comprehensive guide covers what Google AI Mode is, why scraping this data delivers strategic business value, the technical challenges you’ll face, and both manual and automated approaches to extract this information efficiently at scale.
What is Google AI Mode?
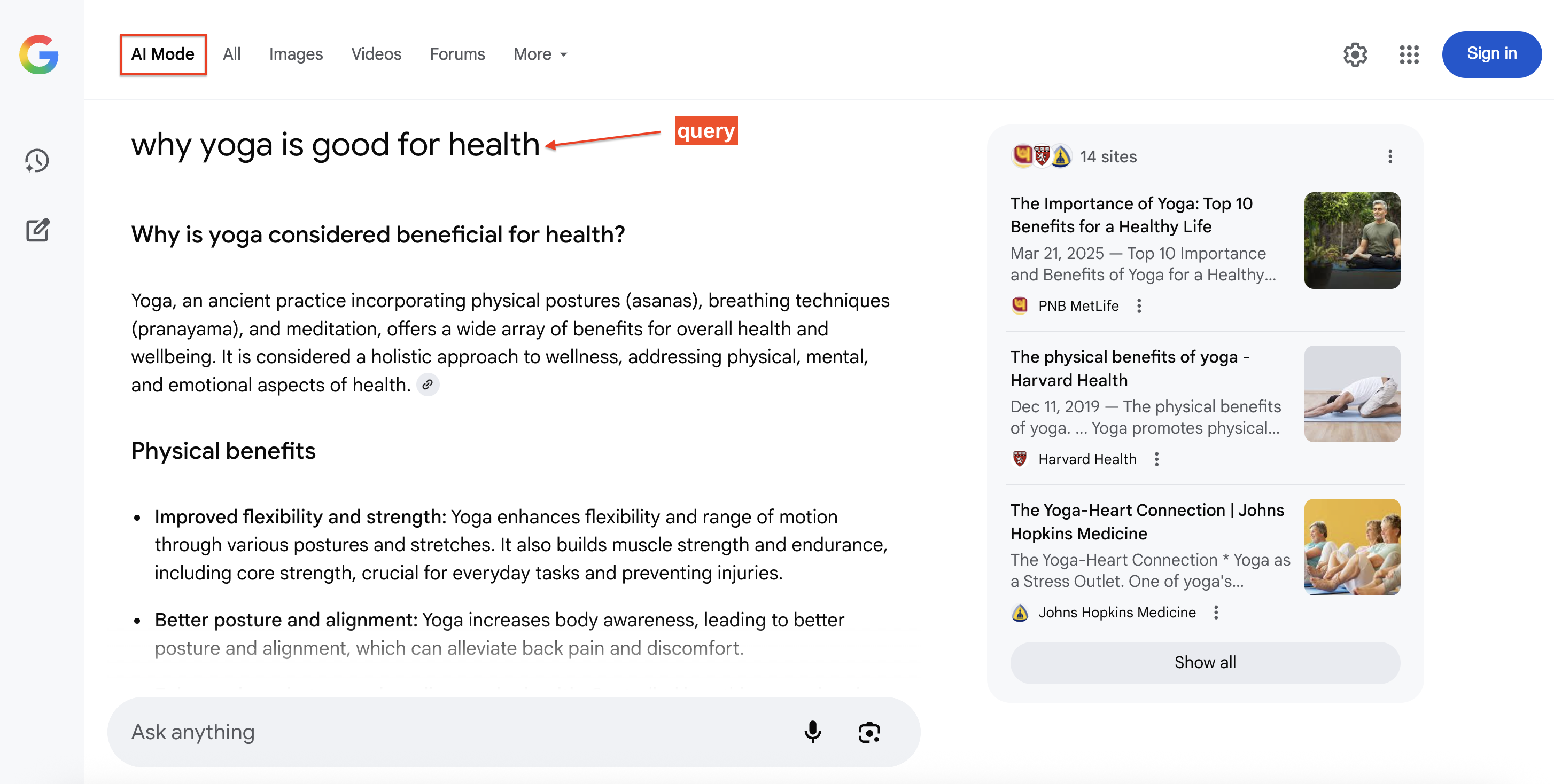
Google AI Mode is Google’s newer search experience that delivers synthesized, conversational responses at the top of results – letting users ask follow-up questions naturally. Each response includes prominent source links, making it easy to jump to underlying content.
Under the hood, AI Mode leverages Gemini alongside Google’s search systems using a “query fan-out” approach. This technique breaks questions into subtopics and runs multiple related searches in parallel, surfacing more relevant material than traditional single queries can provide.
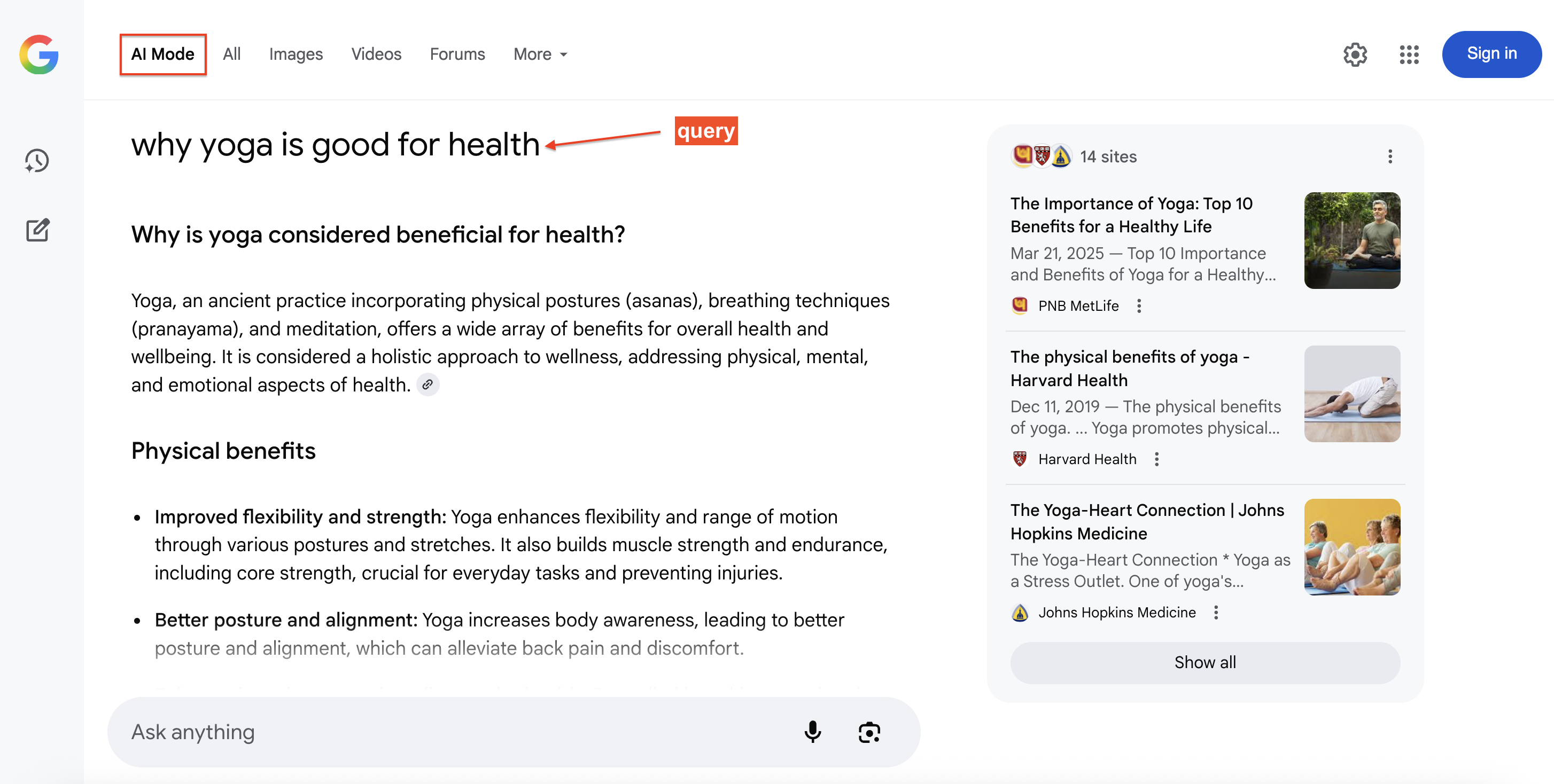
Here’s an example of Google AI Mode answering a search query with cited sources (right side) that users can click for additional detail:
Why scrape Google AI Mode data?
Google AI Mode data provides measurable insights that significantly impact SEO, product development, and competitive research.
- Citation share tracking. Monitor which domains Google AI references for your target queries, including ranking order and frequency over time. This indicates topical authority and helps measure whether content improvements lead to increased AI response inclusion.
- Competitive intelligence. Capture which brands, products, or locations appear in recommendation and comparison queries. This reveals market positioning, competitive dynamics, and attributes that AI responses emphasize.
- Content gap analysis. Compare key facts in AI Mode responses with your existing content to identify opportunities for creating structured content like FAQs, guides, or data tables that earn citations.
- Brand monitoring. Review AI-generated responses about your brand or industry to identify outdated information and update your content accordingly.
- Research and development. Store AI Mode responses with metadata (timestamps, locations, entities) to fuel internal AI systems, support research teams, and enhance RAG applications.
Method 1 – manual scraping with browser automation
Scraping Google AI Mode requires sophisticated browser automation due to the dynamic, JavaScript-heavy nature of AI-generated content. Browser automation frameworks like Playwright, Selenium, or Puppeteer use real browser engines to execute JavaScript, wait for content to load, and replicate the human browsing experience – important for capturing dynamically generated AI responses.
Here’s how Google AI Mode appears in search results:
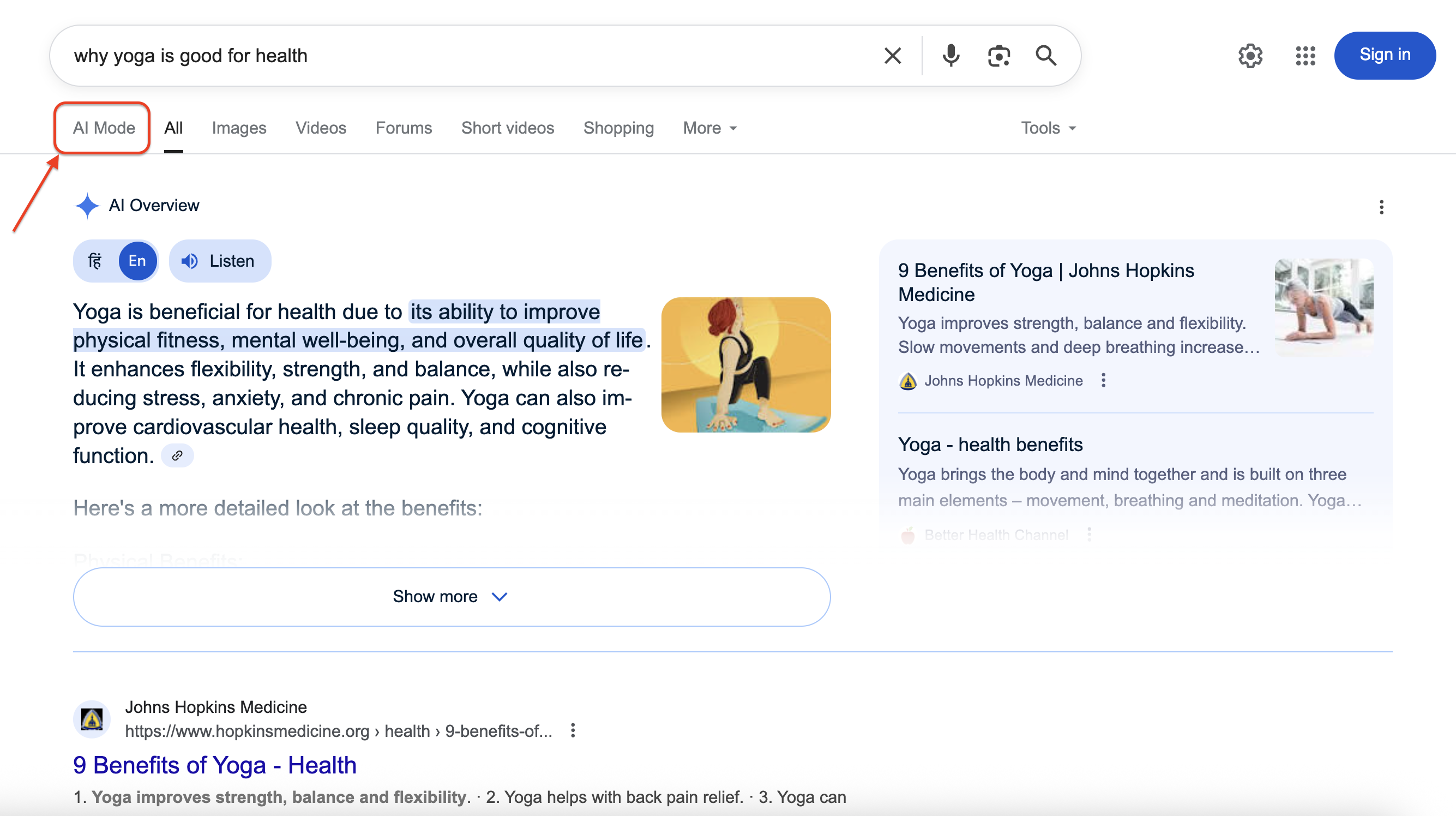
Clicking on AI Mode reveals the full conversational interface with detailed responses and source citations. Our goal is to programmatically access and extract this rich, structured information.
Step 1 – environment setup and prerequisites
Install the latest version of Python, then install the necessary dependencies. For this tutorial, install Playwright by running these commands in your terminal:
pip install playwright
playwright installThis command installs Playwright and downloads the required browser binaries (browser executables needed for automation).
Step 2 – import dependencies and setup
Import the essential libraries for the scraping task:
import asyncio
import urllib.parse
from playwright.async_api import async_playwrightLibrary breakdown:
- asyncio – enables asynchronous programming for improved performance and concurrent operations.
- urllib.parse – handles URL encoding to ensure queries are properly formatted for web requests.
- playwright – provides browser automation capabilities to interact with Google like a human user.
Step 3 – function architecture and parameters
Define the main scraping function with clear parameters and return values:
async def scrape_google_ai_mode(query: str, output_path: str = "ai_response.txt") -> bool:Function parameters:
- query – search term to submit to Google AI Mode.
- output_path – file destination for saving the response (defaults to “ai_response.txt”).
- Returns a boolean value indicating the success (True) or failure (False) of content extraction.
Step 4 – url construction and AI Mode activation
Construct the search URL that triggers Google’s AI Mode interface:
url = f"https://www.google.com/search?q={urllib.parse.quote_plus(query)}&udm=50"Key components:
- urllib.parse.quote_plus(query) – safely encodes the search query, converting spaces to ‘+’ and escaping special characters.
- udm=50 – critical parameter that activates Google’s AI Mode interface.
Step 5 – browser configuration and anti-detection
Launch a browser instance configured to avoid detection while maintaining realistic behavior:
async with async_playwright() as pw:
browser = await pw.chromium.launch(
headless=False, args=["--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled"]
)
page = await browser.new_page(
user_agent="Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) "
"AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) "
"Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
)Configuration details:
- headless=False – displays the browser window for debugging (set to True for production environments).
- -disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled – removes automation detection indicators.
- User agent – mimics a legitimate Chrome browser on macOS to reduce the likelihood of bot detection.
These anti-detection measures help the scraper appear as a normal user browsing Google rather than an automated script.
Step 6 – navigation and dynamic content loading
Navigate to the constructed URL and wait for dynamic content to fully load:
await page.goto(url, wait_until="networkidle")
await page.wait_for_timeout(2000)Loading strategy explanation:
- wait_until=”networkidle” – waits until network activity stops, indicating the page has fully loaded.
- wait_for_timeout – additional buffer for AI content generation.
Step 7 – content location and DOM extraction
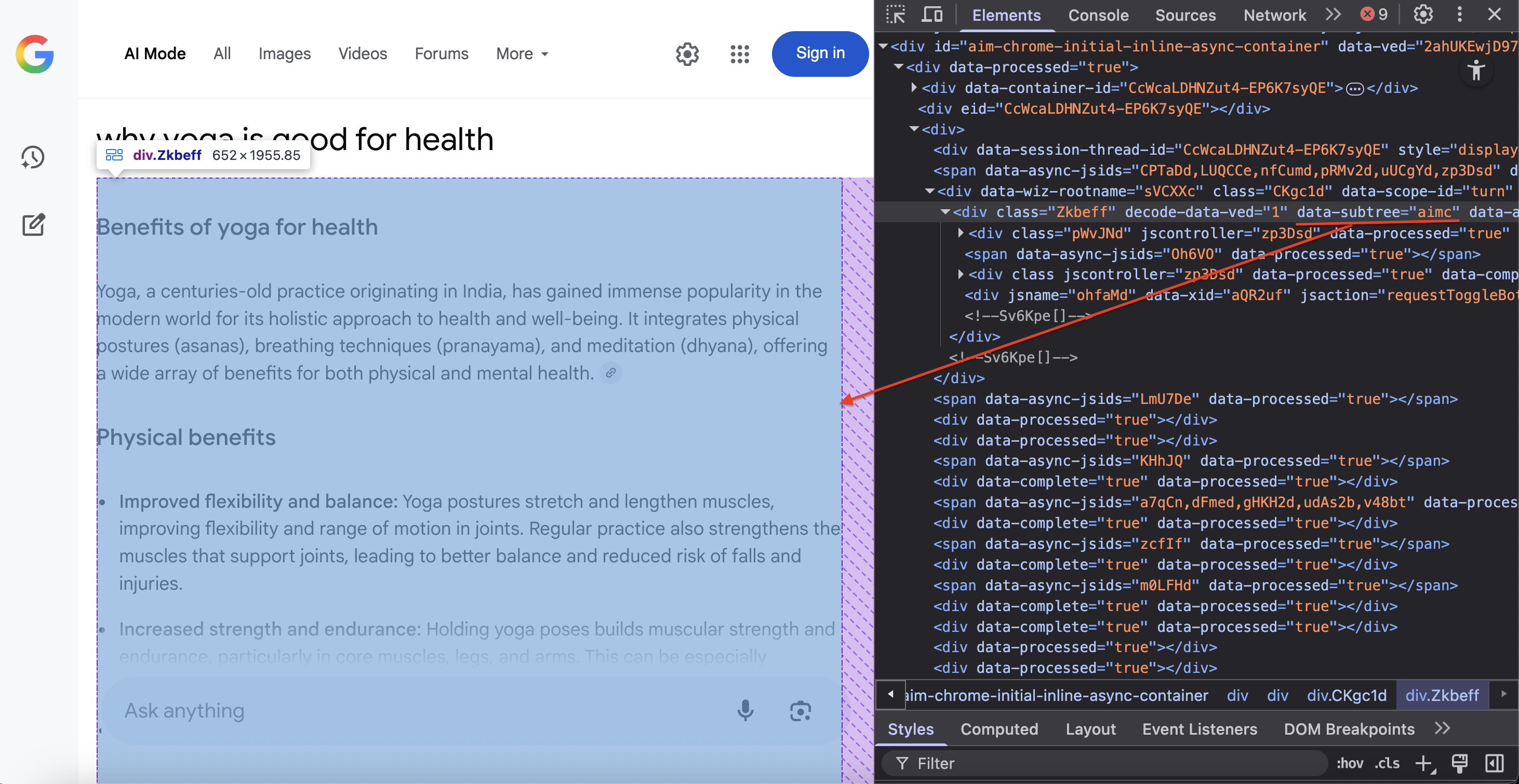
Locate the specific DOM container that houses Google’s AI Mode content:
container = await page.query_selector('div[data-subtree="aimc"]')The CSS selector div[data-subtree=”aimc”] targets Google’s AIMC (AI Mode Container).
Step 8 – data extraction and storage
Extract the text content and save it to the specified file:
if container:
text = (await container.inner_text()).strip()
if text:
with open(output_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(text)
print(f"Saved AI response to '{output_path}' ({len(text):,} characters)")
await browser.close()
return True
else:
print("AI Mode container found but contains no content.")
else:
print("No AI Mode content detected on page.")
await browser.close()
return FalseProcess flow:
- Verify AI container exists on the page using DOM querying.
- Extract plain text content without HTML markup using inner_text().
- Save content to the specified file with UTF-8 encoding.
- Properly close browser resources to prevent memory leaks.
Step 9 – execute the scraping function
Run the complete scraping operation by calling the function with your desired query:
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(scrape_google_ai_mode("why yoga is good for health"))Complete code
Here’s the complete code combining all steps:
import asyncio
import urllib.parse
from playwright.async_api import async_playwright
async def scrape_google_ai_mode(
query: str, output_path: str = "ai_response.txt"
) -> bool:
url = f"https://www.google.com/search?q={urllib.parse.quote_plus(query)}&udm=50"
async with async_playwright() as pw:
browser = await pw.chromium.launch(
headless=False, args=["--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled"]
)
page = await browser.new_page(
user_agent="Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) "
"AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) "
"Chrome/139.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
)
await page.goto(url, wait_until="networkidle")
await page.wait_for_timeout(1000)
container = await page.query_selector('div[data-subtree="aimc"]')
if container:
text = (await container.inner_text()).strip()
if text:
with open(output_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(text)
print(
f"Saved AI response to '{output_path}' ({len(text):,} characters)"
)
await browser.close()
return True
else:
print("AI Mode container found but empty.")
else:
print("No AI Mode content found.")
await browser.close()
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(scrape_google_ai_mode("why yoga is good for health"))When executed successfully, this script creates a text file containing the extracted AI response:

Great job! You’ve successfully scraped Google AI Mode content.
Challenges and limitations of manual scraping
Manual scraping comes with significant operational challenges that become more pronounced at scale.
- Anti-bot detection and CAPTCHA verification. Google implements sophisticated detection mechanisms that identify automated traffic patterns. After a limited number of requests, the system triggers CAPTCHA verification, effectively blocking further data collection.
- Infrastructure and maintenance complexity. Successful large-scale operations demand various techniques to avoid getting blocked, like high-quality residential proxy networks, user agent rotation, browser fingerprinting evasion, and sophisticated request distribution strategies. This creates substantial technical overhead and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Dynamic content and layout changes. Google frequently updates its interface structure, which can break existing parsers overnight, demanding immediate attention and code updates to maintain functionality.
- Parsing complexity. AI Mode responses contain nested structures, dynamic citations, and variable formatting that require sophisticated parsing logic. Maintaining accuracy across different response types demands extensive testing and error handling.
- Scalability limitations. Manual approaches struggle with bulk processing, concurrent request management, and consistent performance across geographic regions and search verticals.
These limitations highlight why many organizations prefer specialized solutions that handle the complexity professionally. This brings us to exploring Bright Data’s purpose-built Google AI Mode Scraper API.
Method 2 – Google AI Mode Scraper API
Bright Data’s Google AI Mode Scraper API provides a production-ready solution that eliminates the complexity of maintaining scraping infrastructure while offering enterprise-grade reliability and performance. The API extracts comprehensive data points, including answer HTML, answer text, attached links, citations, and 12 additional fields.
Key features
- Automated antibot and proxy management. The API leverages Bright Data’s extensive residential proxy network of over 150M IP addresses, combined with advanced antibot evasion techniques. This infrastructure eliminates CAPTCHA encounters and IP blocking concerns.
- Structured data output. The API delivers consistently formatted data in multiple export formats, including JSON, NDJSON, and CSV for flexible integration options.
- Enterprise-grade scalability. Built for high-volume operations, the API processes thousands of queries efficiently with predictable cost scaling through our pay-per-successful-result pricing model.
- Geographic customization. Specifying target countries for location-specific results allows you to understand how AI responses vary across different markets and user demographics.
- Zero-maintenance operation. Our team continuously monitors and adapts the scraper to Google’s changes. When Google modifies AI Mode interfaces or implements new antibot measures, updates deploy automatically without requiring any action from your development team.
The result? comprehensive Google AI Mode data extraction with enterprise reliability and no infrastructure overhead.
Getting started with the Google AI Mode Scraper API
The implementation process involves account setup and API key generation for new Bright Data users, followed by choosing your preferred integration method. Create your free Bright Data account and generate your API authentication token in 4 simple steps.
After that, navigate to the Bright Data Web Scrapers Library and search for “google” to locate the available scraper options. Click on “google.com”.
Then select the “Google AI Mode Search” option from the interface.
The scraper offers both no-code and API-based implementation methods to accommodate different technical requirements and team capabilities.
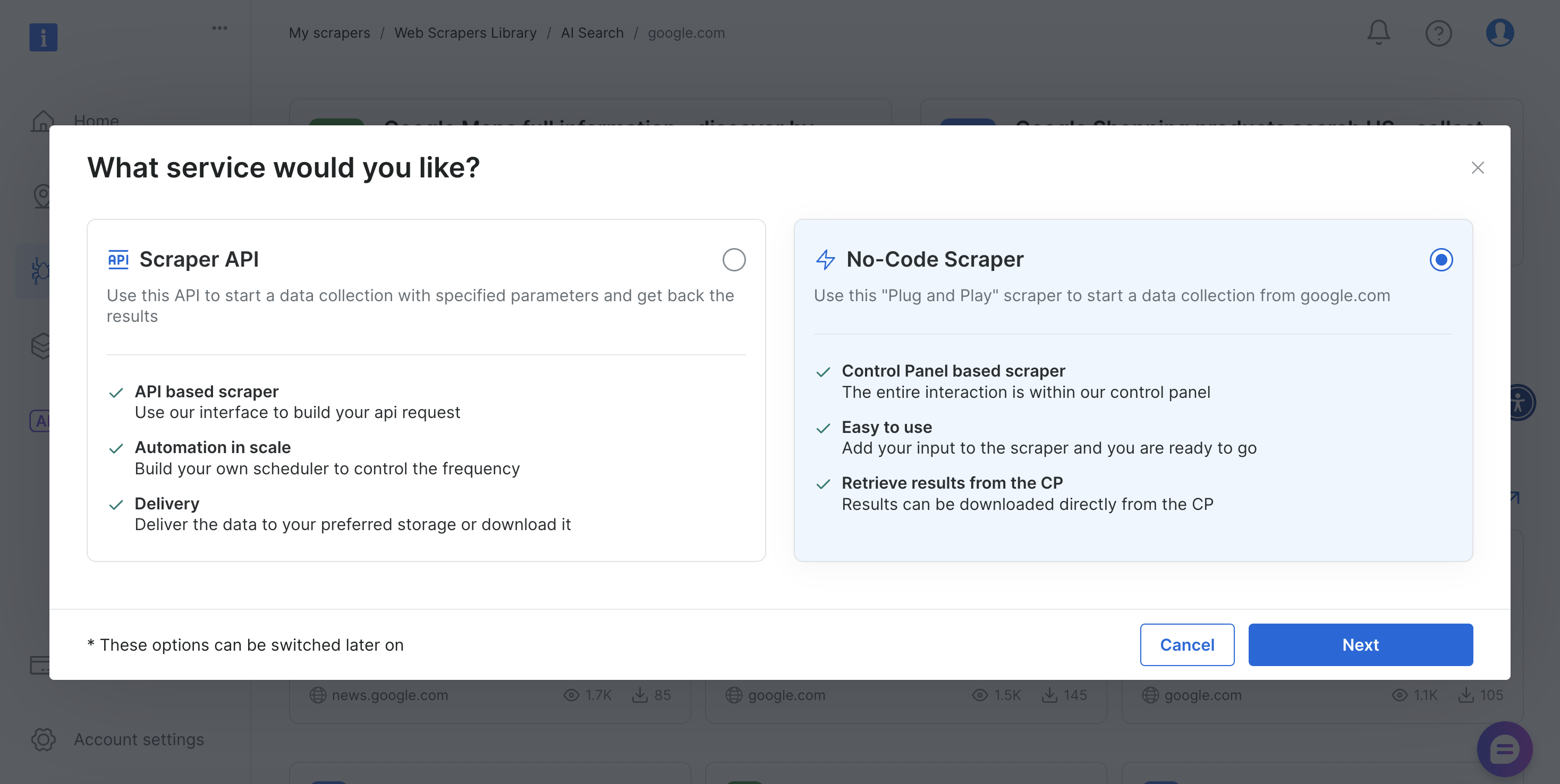
Let’s explore both approaches.
Interactive scraping (No-code scraper)
The web-based interface offers a user-friendly approach for those who prefer not to work with code. You can enter search queries directly through the dashboard or upload CSV files containing multiple queries for batch processing. The platform handles everything automatically and delivers results as downloadable files.
Required parameters:
- URL – default set to https://google.com/aimode (this remains constant).
- Prompt – your search query or question for Google’s AI analysis.
- Country – geographic location for region-specific results (optional).
Additional configuration:
- Delivery settings – select your preferred output format and delivery method.
- Custom schema – choose which data fields to include in your export.
- Batch processing – process multiple queries simultaneously via CSV upload.
Let’s perform a simple search using the prompt “how meditation helps mental health” with “India” as the target country. Click the “Start collecting” button to begin the process.
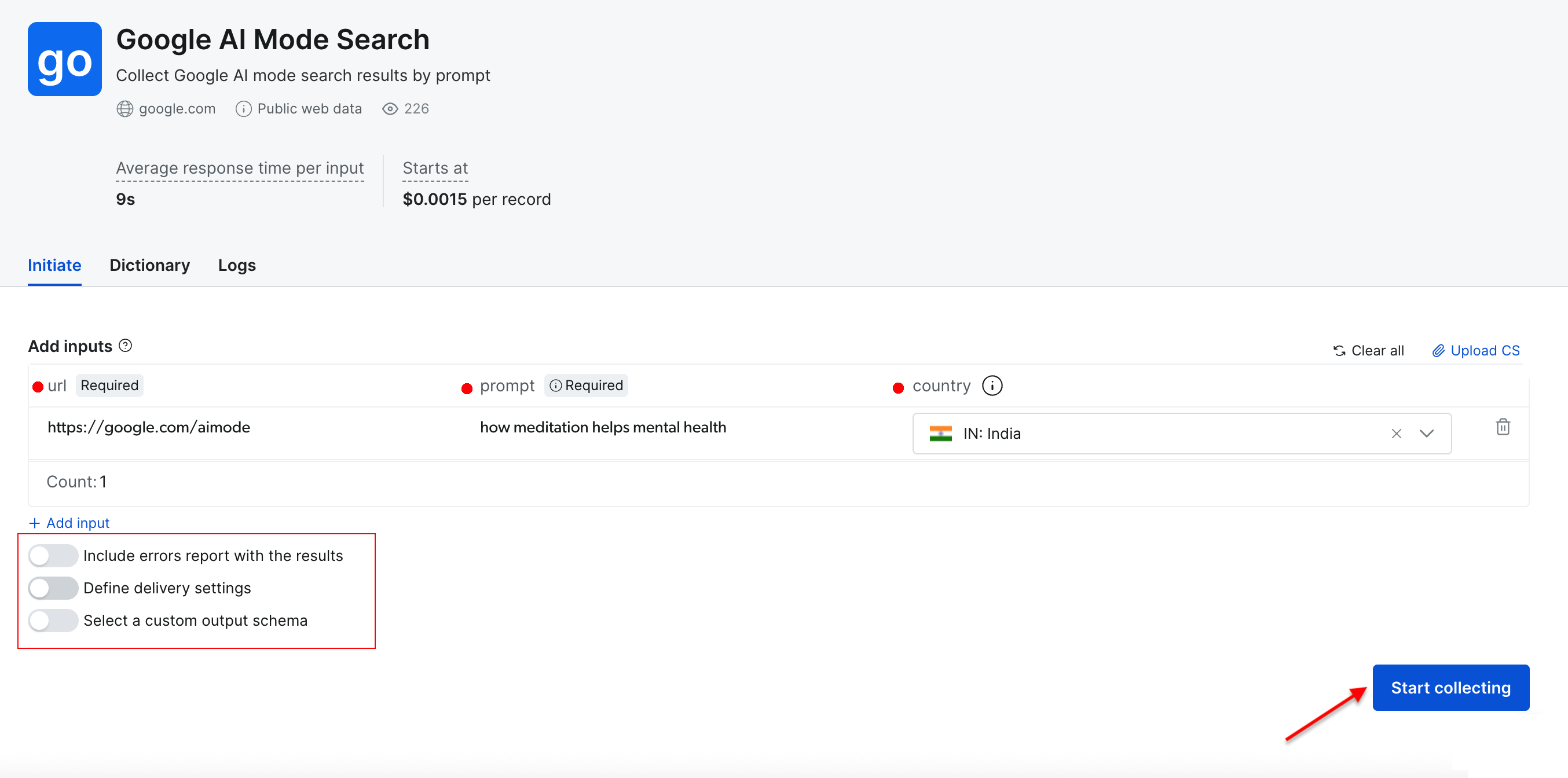
The dashboard provides real-time progress tracking (Ready, Running), and upon completion, you can download your results in your preferred format.
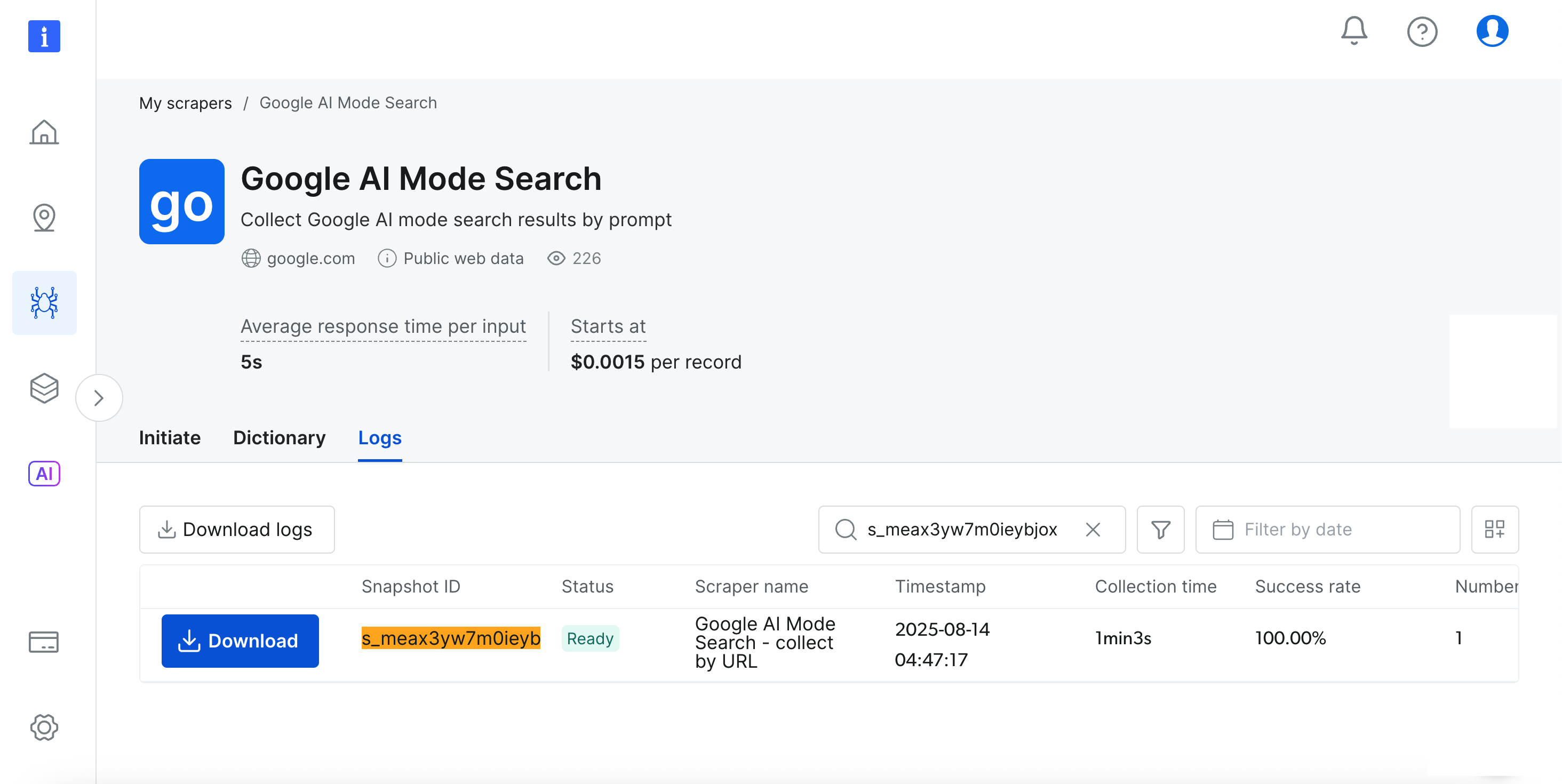
Pretty awesome, right?
API-based scraping (Scraper API)
The programmatic approach offers greater flexibility and automation capabilities through RESTful API endpoints. The comprehensive API request builder and management interface provides full control over your scraping operations:
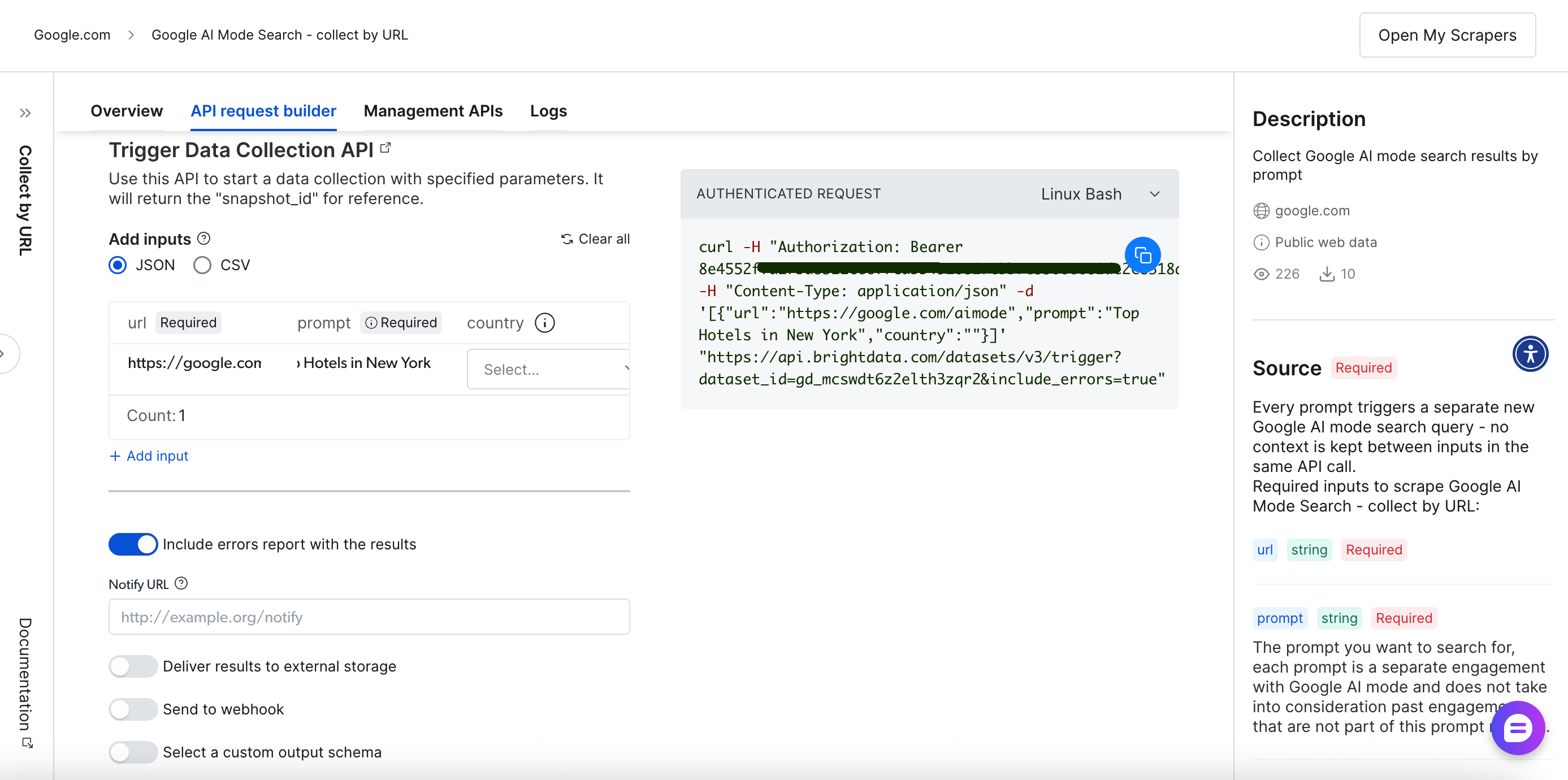
Let’s walk through the API-based scraping process.
Step 1 – trigger data collection
First, trigger the data collection using one of these methods:
Single query execution:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_TOKEN>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '[
{
"url": "https://google.com/aimode",
"prompt": "health tips for computer users",
"country": "US"
}
]' \
"https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/trigger?dataset_id=gd_mcswdt6z2elth3zqr2&include_errors=true"Batch processing with CSV upload:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_TOKEN>" \
-F 'data=@/path/to/your/queries.csv' \
"https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/trigger?dataset_id=gd_mcswdt6z2elth3zqr2&include_errors=true"Request components:
- Authentication – bearer token in the header for secure access.
- Dataset ID – specific identifier for Google AI Mode scraper.
- Input Format – JSON array or CSV file containing query parameters.
- Error Handling – include the errors parameter for comprehensive feedback.
You can also select your delivery method via webhook for automated result handling.
Step 2 – monitor job progress
Use the returned Snapshot ID to track collection progress:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_TOKEN>" \
"https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/progress/<snapshot_id>"The response indicates “running” during data collection and “ready” when results are available for download.
Step 3 – download results
Download the snapshot content or deliver it to the specified storage. Retrieve completed results in your preferred format:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_TOKEN>" \
"https://api.brightdata.com/datasets/v3/snapshot/<snapshot_id>?format=json"The API returns comprehensive structured data for each query:
{
"url": "https://www.google.co.in/search?q=health+tips+for+computer+users&hl=en&udm=50&aep=11&...",
"prompt": "health tips for computer users",
"answer_html": "<html>...complete HTML response...</html>",
"answer_text": "Health tips for computer users\n\nSpending extended periods in front of a computer can lead to various health concerns, including eye strain, musculoskeletal pain, and reduced physical activity...",
"links_attached": [
{
"url": "https://www.aao.org/eye-health/tips-prevention/computer-usage",
"text": null,
"position": 1
},
{
"url": "https://uhs.princeton.edu/health-resources/ergonomics-computer-use",
"text": null,
"position": 2
}
],
"citations": [
{
"url": "https://www.ramsayhealth.co.uk/blog/lifestyle/five-healthy-tips-for-working-at-a-computer",
"title": null,
"description": "Ramsay Health Care",
"icon": "https://...icon-url...",
"domain": "https://www.ramsayhealth.co.uk",
"cited": false
},
{
"url": "https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24802-computer-vision-syndrome",
"title": null,
"description": "Cleveland Clinic",
"icon": "https://...icon-url...",
"domain": "https://my.clevelandclinic.org",
"cited": false
}
],
"country": "IN",
"answer_text_markdown": "Health tips for computer users...",
"timestamp": "2026-08-07T05:02:56.887Z",
"input": {
"url": "https://google.com/aimode",
"prompt": "health tips for computer users",
"country": "IN"
}
}So simple and effective!
This straightforward API workflow integrates seamlessly into any application or project. The Bright Data API request builder also provides code examples in multiple programming languages for easy implementation.
Bottom line
We’ve explored 2 approaches: a do-it-yourself solution using Python and Playwright, and Bright Data’s turnkey Google AI Mode Scraper API.
In the rapidly evolving search landscape, where algorithms and interfaces change frequently, having a robust and well-maintained scraping infrastructure is invaluable. The API eliminates the need to constantly update parsing logic or manage IP restrictions, allowing you to focus entirely on analyzing the rich AI-generated insights from Google’s search results and extracting maximum value from the data.
Do this next
- Expand your Google data collection. Since you’re already working with Google AI Mode, consider exploring additional Google data sources. We also have a comprehensive guide on Scraping Google AI Overviews for broader coverage. You can access specialized capabilities for Google News, Maps, Search, Trends, Reviews, Hotels, Videos, and Flights.
- Test without risk. All main products include free trial options, plus we match first deposits up to $500. This gives you space to experiment with expanded functionality before making commitments.
- Scale with integrated solutions. As your needs grow, consider the Web MCP server, which connects AI applications directly to web data without custom development for every site. Start now with a free plan of 5,000 monthly requests!
- Enterprise infrastructure when ready. Many teams start with individual projects like yours and later need robust infrastructure for larger operations. The complete platform provides the underlying infrastructure when you’re ready to expand.
Not sure about the next step? Talk to our team – we’ll map it for you.