In this article, you will learn:
- What Langfuse is and what it offers.
- Why enterprises and users need it for monitoring and tracking AI agents.
- How to integrate it into a complex, real-world AI agent built with LangChain, which connects to Bright Data for web search and scraping capabilities.
Let’s dive in!
What Is Langfuse?
Langfuse is an open-source and cloud-based LLM engineering platform that helps you debug, monitor, and improve large language model applications. It provides observability, tracing, prompt management, and evaluation tools that support the entire AI development workflow.
Its main features include:
- Observability and tracing: Gain deep visibility into your LLM apps with traces, session overviews, and metrics like cost, latency, and error rates. This is pivotal for understanding performance and diagnosing problems.
- Prompt management: A version-controlled system for creating, managing, and iterating on prompts collaboratively, without touching the codebase.
- Evaluation: Tools for evaluating application behavior, including human feedback collection, model-based scoring, and automated tests against datasets.
- Collaboration: Supports team workflows with annotations, comments, and shared insights.
- Extensibility: Fully open-source, with flexible integration options across different tech stacks.
- Deployment options: Available as a hosted cloud service (with a free tier) or as a self-hosted installation for teams needing full control over data and infrastructure.
Why Integrate Langfuse Into Your AI Agent
Monitoring AI agents with Langfuse is fundamental, especially for enterprises. Only that way can you achieve the level of observability, control, and reliability that production environments demand.
After all, in real scenarios, AI agents interact with sensitive data, complex business logic, and external APIs. Thus, you need a way to track and understand exactly how the agent behaves, what it costs, and how reliably it performs.
Langfuse provides end-to-end tracing, detailed metrics, and debugging tools that let (even non-technical) teams monitor every step of an AI workflow, from prompt inputs to model decisions and tool calls.
For enterprises, this means fewer blind spots, faster incident resolution, and stronger compliance with internal governance and external regulations. On top of that, Langfuse also supports prompt management and evaluation, allowing teams to version, test, and optimize prompts at scale.
How to Use Langfuse to Trace a Compliance-Tracking AI Agent Built With LangChain and Bright Data
To showcase Langfuse’s tracing and monitoring capabilities, you first need an AI agent to instrument. For this reason, we will build a real-world AI agent using LangChain, powered by Bright Data solutions for web search and scraping.
Note: Langfuse and Bright Data support a wide range of AI agent frameworks. LangChain was chosen here only for simplicity and demonstration purposes.
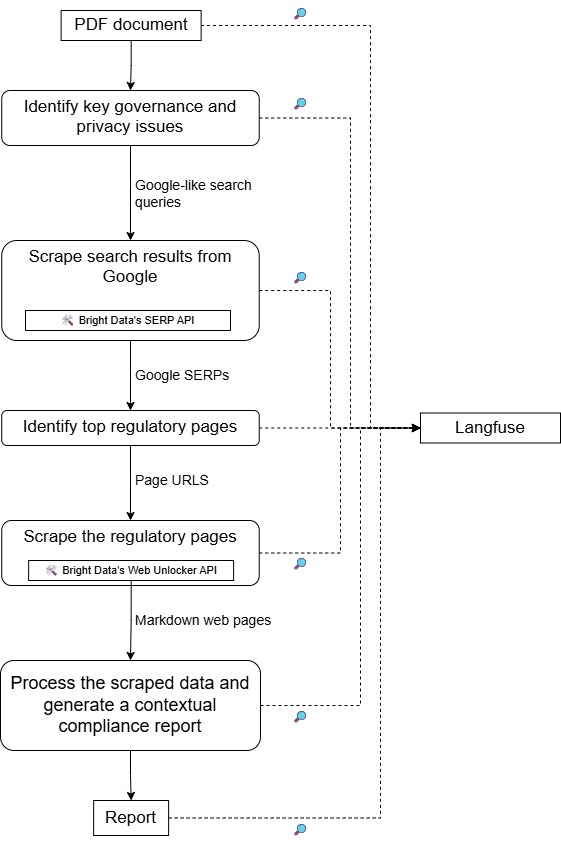
This enterprise-ready AI agent will handle compliance-related tasks by:
- Loading an internal PDF document describing an enterprise process (e.g., data processing workflows).
- Analyzing the document with an LLM to identify key privacy and regulatory aspects.
- Performing web searches for related topics using the Bright Data SERP API.
- Accessing the top pages (prioritizing government websites) in Markdown format via the Bright Data Web Unlocker API.
- Processing the collected information and providing updated insights to help avoid regulatory issues.
Next, this agent will be connected to Langfuse to trace runtime information, metrics, and other relevant data.
For a high-level architecture of this project, refer to the following schematic design:
Follow the instructions below!
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have the following:
- Python 3.10 or higher installed on your machine.
- An OpenAI API key.
- A Bright Data account with a SERP API and Web Unlocker API zones set up, along with an API key.
- A Langfuse account with both public and secret API keys configured.
Do not worry about setting up the Bright Data and Langfuse accounts right now, as you will be guided through that in the steps below. It is also helpful to have a basic understanding of AI agent instrumentation to see how Langfuse tracks and manages runtime data.
Step #1: Set Up Your LangChain AI Agent Project
Run the following command in your terminal to create a new folder for your LangChain AI agent project:
mkdir compliance-tracking-ai-agentThis compliance-tracking-ai-agent/ directory represents the project folder for your AI agent, which you will later instrument via Langfuse.
Navigate into the folder and create a Python virtual environment inside it:
cd compliance-tracking-ai-agent
python -m venv .venvOpen the project folder in your preferred Python IDE. Both Visual Studio Code with the Python extension and PyCharm are valid choices.
Inside the project folder, create a Python script named agent.py:
compliance-tracking-ai-agent/
├─── .venv/
└─── agent.py # <------------Currently, agent.py is empty. This is where you will later define your AI agent through LangChain.
Next, activate the virtual environment. On Linux or macOS, run in your terminal:
source venv/bin/activateEquivalently, on Windows, execute:
venv/Scripts/activateOnce activated, install the project dependencies with this command:
pip install langchain langchain-openai langgraph langchain-brightdata langchain-community pypdf python-dotenv langfuseThese libraries cover the following scope:
langchain,langchain-openai, andlanggraph: For building and managing an AI agent powered by an OpenAI model.langchain-brightdata: To Integrate LangChain with Bright Data services using official tools.langchain-communityandpypdf: Provide APIs to read and process PDF files through the underlyingpypdflibrary.python-dotenv: To load application secrets, such as API keys for third-party providers, from a.envfile.langfuse: To instrument your AI agent to collect useful traces and telemetry, either in the cloud or locally.
Done! You now have a fully set up Python development environment for building your AI agent.
Step #2: Configure Environment Variable Reading
Your AI agent will connect to third-party services, including OpenAI, Bright Data, and Langfuse. To avoid hardcoding credentials in your script and to make it production-ready for enterprise usage, configure the script to read them from a .env file. That is exactly why we installed python-dotenv!
In agent.py, start by adding the following import:
from dotenv import load_dotenvNext, create a .env file in your project folder:
compliance-tracking-ai-agent/
├─── .venv/
├─── agent.py
└─── .env # <------------This file will store all your credentials, API keys, and secrets.
In agent.py, load the environment variables from .env with this line of code:
load_dotenv()Cool! Your script can now safely read values from the .env file.
Step #3: Prepare Your Bright Data Account
The LangChain Bright Data tools work by connecting to the Bright Data services configured in your account. Specifically, the two tools required for this project are:
BrightDataSERP: Retrieves search engine results to find relevant regulatory web pages. It connects to Bright Data’s SERP API.BrightDataUnblocker: Accesses any public website, even if geo-restricted or bot-protected. This allows the agent to scrape content from individual web pages and learn from them. It connects to Bright Data’s Web Unblocker API.
In other words, to use these two tools, you need a Bright Data account with both a SERP API and a Web Unblocker API zone set up. Let’s configure them!
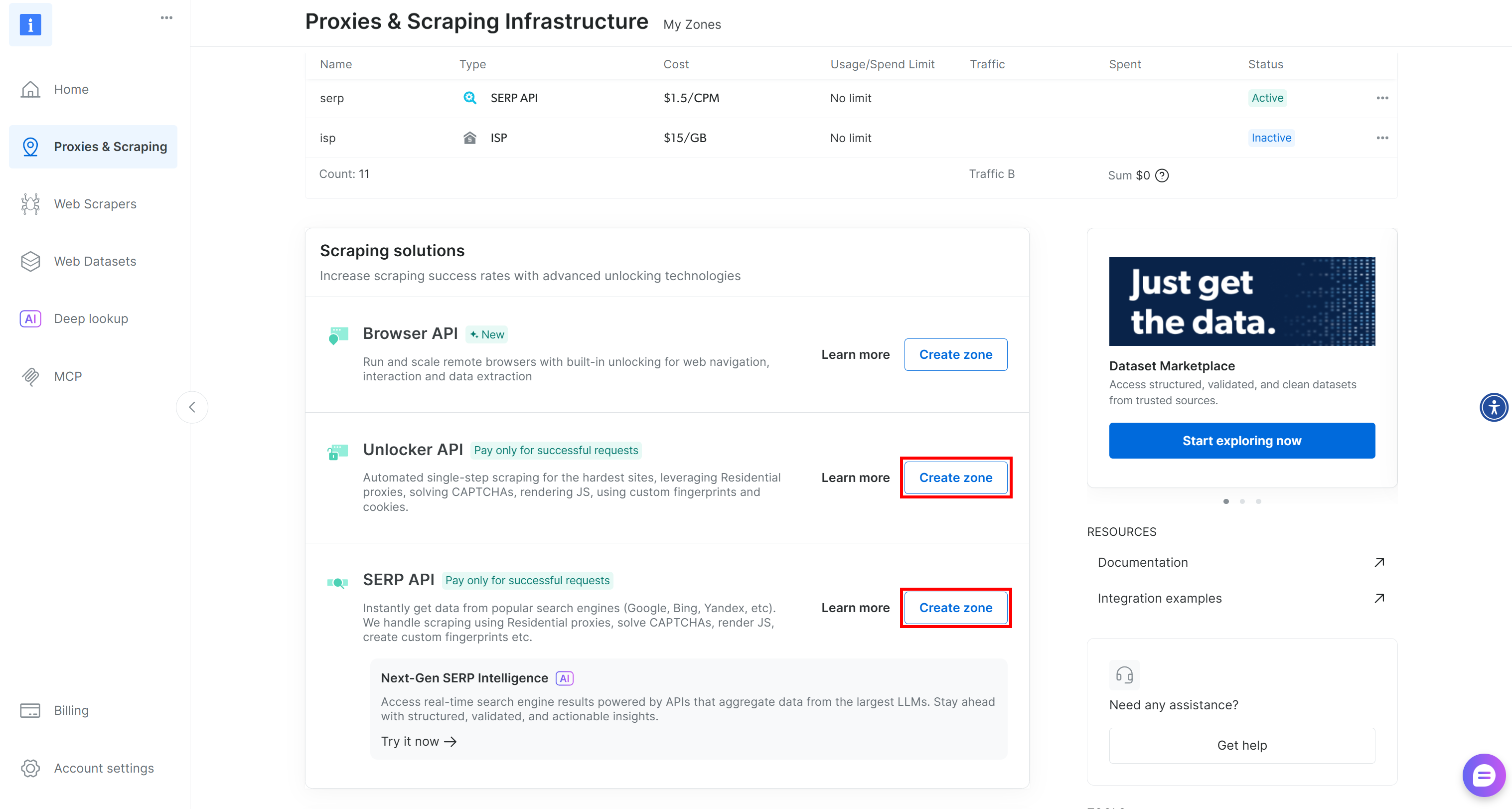
If you do not have a Bright Data account yet, start by creating one. Otherwise, log in. Go to your dashboard, then navigate to the “Proxies & Scraping” page. There, check the “My Zones” table:
If the table already contains a Web Unblocker API zone called unlocker and a SERP API zone called serp, you are good to go. That is because:
- The
BrightDataSERPLangChain tool automatically connects to a SERP API zone namedserp. - The
BrightDataUnblockerLangChain tool automatically connects to a Web Unblocker API zone namedweb_unlocker.
For more details, refer to the Bright Data x LangChain documentation.
If you do not have those two required zones in place, you can create them easily. Scroll down on the “Unblocker API” and “SERP API” cards, press the “Create zone” button, and follow the wizard to add the two zones with the required names:
For step-by-step guidance, refer to these two documentation pages:
Lastly, you need to tell the LangChain Bright Data tools how to connect to your account. This is done using your Bright Data API key, which is utilized for authentication.
Generate your Bright Data API key and store it in your .env file like this:
BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"This is it! You now have all the prerequisites in place to connect your LangChain script to Bright Data solutions via the official tools.
Step #4: Configure the LangChain Bright Data Tools
In your agent.py file, prepare the LangChain Bright Data tools as follows:
from langchain_brightdata import BrightDataUnlocker, BrightDataSERP
bright_data_serp_api_tool = BrightDataSERP()
bright_data_web_unlocker_api_tool = BrightDataUnlocker() Note: You do not need to manually specify your Bright Data API key. Both tools automatically attempt to read it from the BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY environment variable, which you set earlier in your .env file.
Step #5: Integrate the LLM
Your AI agent for compliance tracking needs a brain, which is represented by an LLM model. In this example, the chosen LLM provider is OpenAI. So, begin by adding your OpenAI API key to the .env file:
OPENAI_API_KEY="<YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY>"Next, in the agent.py file, initialize the LLM integration like this:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-5-mini",
) Note: The configured model here is GPT-5 Mini, but you can use any other OpenAI model.
If you do not want to use OpenAI, follow the official LangChain guides to connect to any other LLM provider.
Great! You now have everything you need to define a LangChain AI agent.
Step #6: Define the AI Agent
A LangChain agent requires an LLM, some optional tools, and a system prompt to define the agent’s behavior.
Combine all of those components into a LangChain agent like this:
from langchain.agents import create_agent
# Define system prompt that instructs the agent on its compliance and privacy-focused task
system_prompt = """
You are a compliance-tracking expert. Your role is to analyze documents for potential regulatory and privacy issues.
Your analysis is supported by researching updated rules and authoritative sources online using Bright Data's tools, including the SERP API and Web Unlocker.
Provide accurate, enterprise-ready insights, ensuring all findings are supported by quotes from both the original document and authoritative external sources.
"""
# List of tools available to the agent
tools=[bright_data_serp_api_tool, bright_data_web_unlocker_api_tool]
# Define the AI agent
agent = create_agent(
llm=llm,
tools=tools,
system_prompt=system_prompt,
)The create_agent() function builds a graph-based agent runtime using LangGraph. A graph is made up of nodes (steps) and edges (connections) that define how your agent processes information. The agent moves through this graph, executing different types of nodes. For more details, refer to the official documentation.
Basically, the agent variable now represents your AI agent with Bright Data integration for compliance tracking and analysis. Fantastic!
Step #7: Launch the Agent
Before launching the agent, you need a prompt describing the compliance tracking task and the document to analyze.
Start by reading the input PDF document:
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFDirectoryLoader
# Load all PDF documents from the input folder
input_folder = "./input"
loader = PyPDFDirectoryLoader(input_folder)
# Load all pages from all PDFs in the input folder
docs = loader.load()
# Combine all pages from the PDFs into a single string for analysis
internal_document_to_analyze = "\n\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in docs])This uses LangChain’s pypdf community document loader to read all pages from the PDFs in your input/ folder and aggregate their text into a single string variable.
Add an input/ folder inside your project directory:
compliance-tracking-ai-agent/
├─── .venv/
├─── input/ # <------------
├─── agent.py
└─── .envThat folder will contain the PDF files that the agent will analyze for privacy, regulatory, or compliance-related issues.
Assuming your input/ folder contains a single document, the internal_document_to_analyze variable will hold its full text. This can now be embedded into a prompt that clearly instructs the agent to perform the analysis task:
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
# Define a prompt template to guide the agent through the workflow
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
Given the following PDF content:
1. Have the LLM analyze it to identify the main key aspects worth exploring in terms of privacy.
2. Translate those aspects into up to 3 very short (no more than 5 words), concise, specific search queries suitable for Google.
3. Perform web searches for those queries using Bright Data's SERP API tool (searching for pages in English, limited to the United States).
4. Access up to the top 5 web, non-PDF pages (giving priority to government websites) in Markdown data format using Bright Data's Web Unlocker tool.
5. Process the collected information and create a final, concise report that includes quotes from the original document and insights from the scraped pages to avoid regulatory issues.
PDF CONTENT:
{pdf}
""")
# Fill the template with the content from the PDFs
prompt = prompt_template.format(pdf=internal_document_to_analyze)Finally, pass the prompt to the agent and execute it:
# Stream the agent's response while tracking each step with Langfuse
for step in agent.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]},
stream_mode="values",
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()Mission complete! Your Bright Data–powered LangChain AI agent is now ready to handle enterprise-grade document analysis and regulatory research tasks.
Step #8: Get Started with Langfuse
You have now reached a point where your AI agent is implemented. This is typically when you want to add Langfuse for production tracking and monitoring. After all, you usually instrument agents that are already in place.
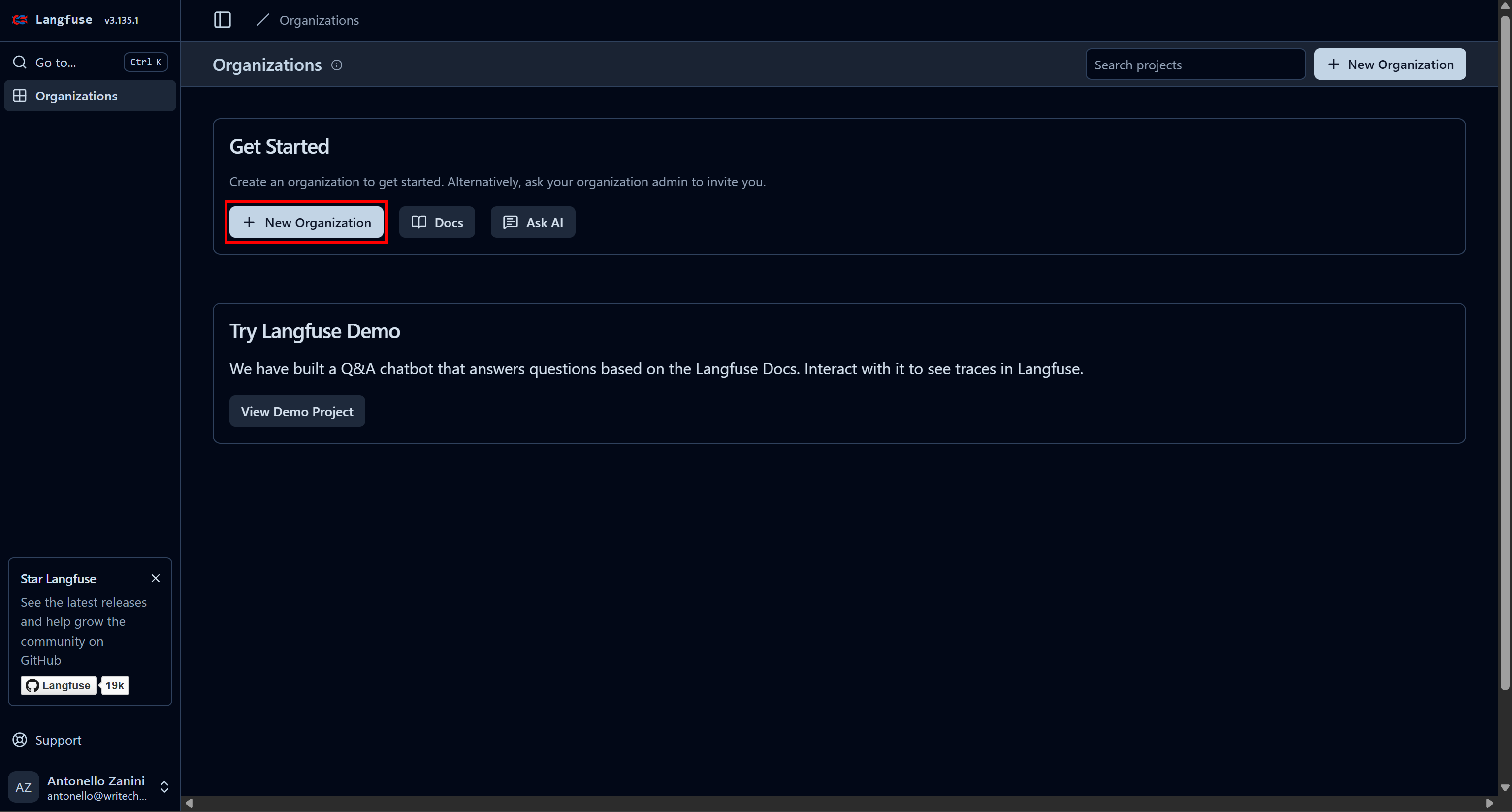
Start by creating a Langfuse account. You will be redirected to the “Organizations” page, where you need to create a new organization. To do so, click the “New Organization” button:
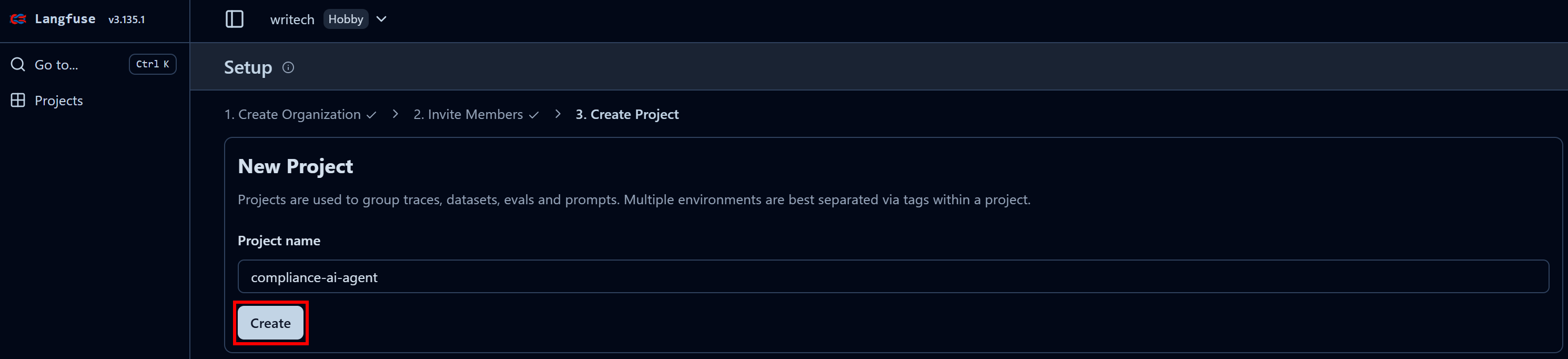
Give your organization a name and continue through the wizard until the final “Create Project” step:
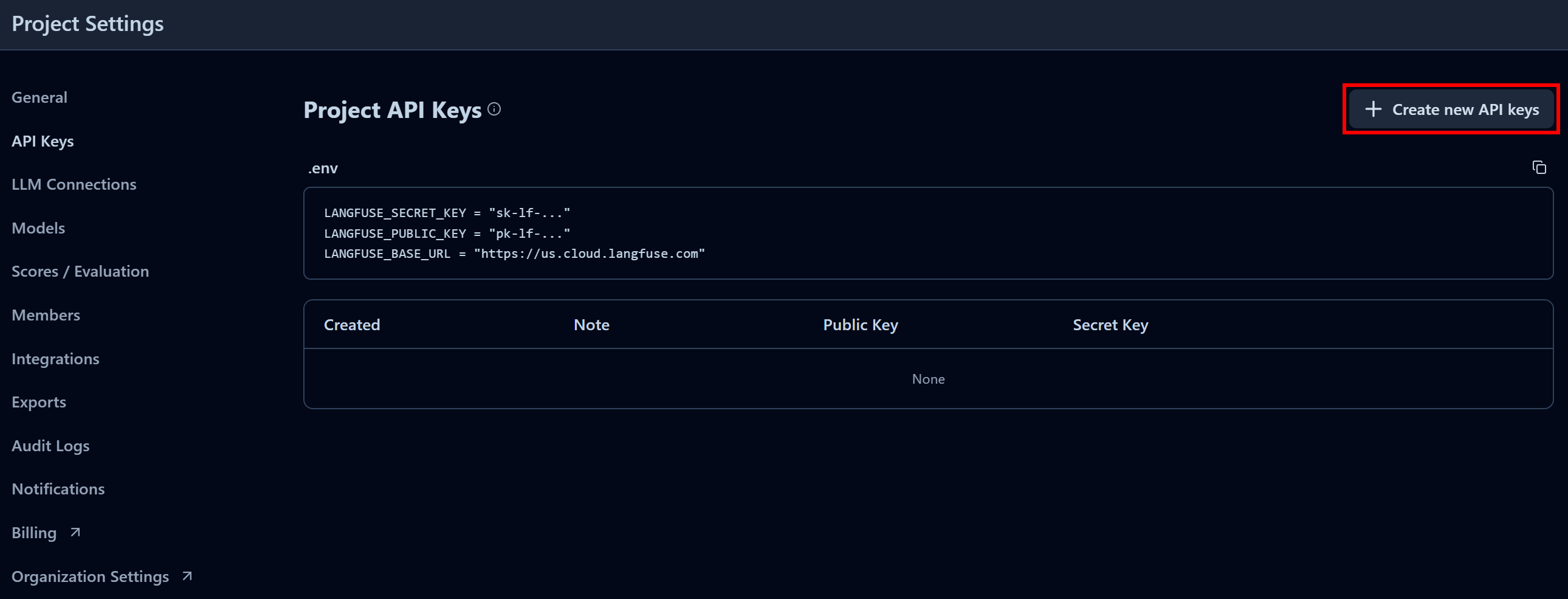
In the last step, name your project like “compliance-tracking-ai-agent”, and press the “Create” button. You will then be redirected to the “Project Settings” view. From there, navigate to the “API Keys” page:
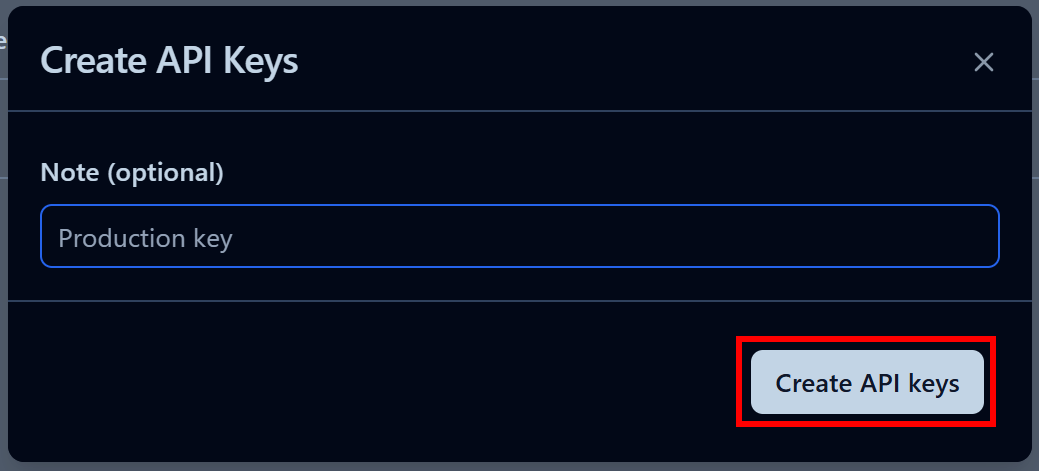
In the “Project API Keys” section, click “Create new API keys”:
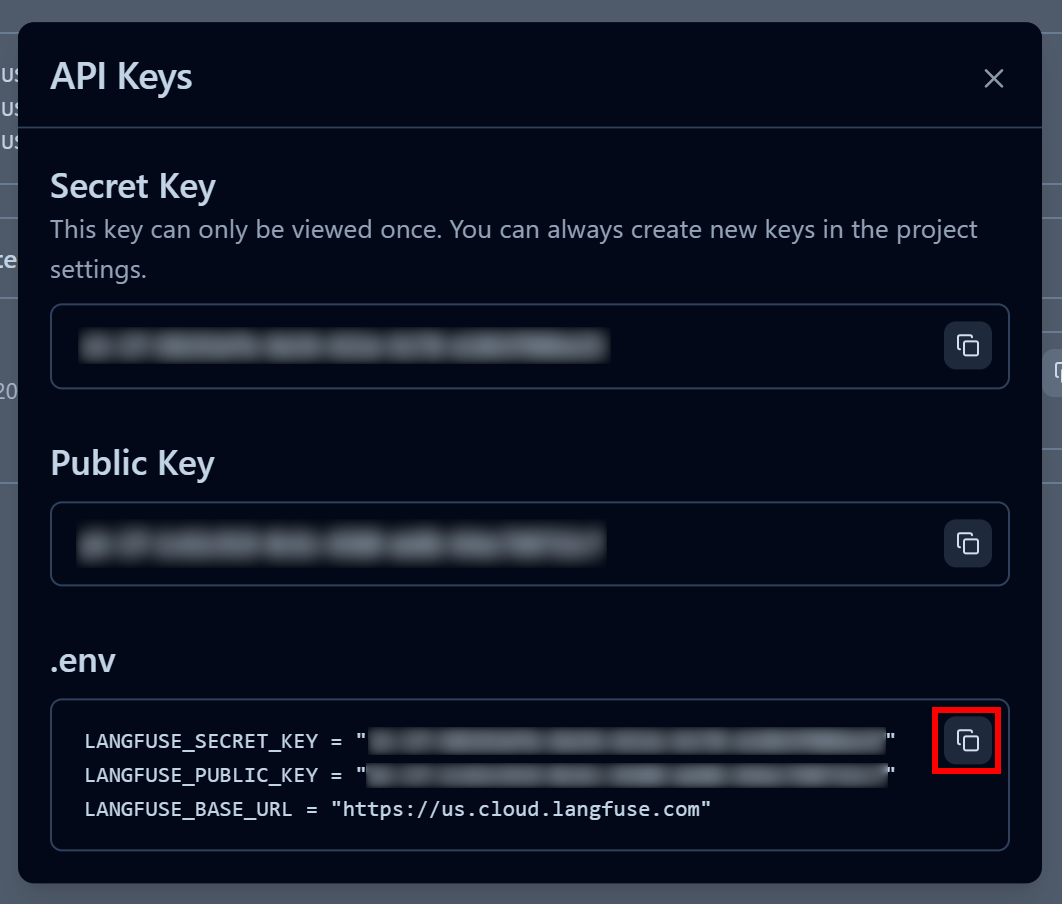
In the modal that appears, give your API key a name and click “Create API keys”:
You will receive a public and secret API key. For quick integration, click the “Copy to clipboard” button in the “.env” section:
Next, paste the copied environment variables into your project’s .env file:
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY = "<YOUR_LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY>"
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY = "<YOUR_LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY>"
LANGFUSE_BASE_URL = "<YOUR_LANGFUSE_BASE_URL>"Wonderful! Your script can now connect to your Langfuse Cloud account and send useful trace information for monitoring and observability.
Step #9: Integrate Langfuse Tracking
Langfuse comes with full support for LangChain (as well as many other AI agent building frameworks), so no custom code is required.
To connect your LangChain AI agent to Langfuse, all you need to do is just initialize the Langfuse client and create a callback handler:
from langfuse import get_client
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
# Load environment variables from .env file
load_dotenv()
# Initialize Langfuse client for tracking and observability
langfuse = get_client()
# Create a Langfuse callback handler to capture Langchain agent interactions
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
Then, pass the Langfuse callback handler when invoking the agent:
for step in agent.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]},
stream_mode="values",
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]} # <--- Langfuse integration
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()Here we go! Your LangChain AI agent is now fully instrumented. All runtime information will be sent to Langfuse and can be viewed in the web app.
Step #10: Final Code
Your agent.py file should now contain:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain_brightdata import BrightDataUnlocker, BrightDataSERP
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFDirectoryLoader
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langfuse import get_client
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
# Load environment variables from .env file
load_dotenv()
# Initialize Langfuse client for tracking and observability
langfuse = get_client()
# Create a Langfuse callback handler to capture Langchain agent interactions
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
# Initialize Bright Data tools
bright_data_serp_api_tool = BrightDataSERP()
bright_data_web_unlocker_api_tool = BrightDataUnlocker()
# Initialize the large language model
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-5-mini",
)
# Define system prompt that instructs the agent on its compliance and privacy-focused task
system_prompt = """
You are a compliance-tracking expert. Your role is to analyze documents for potential regulatory and privacy issues.
Your analysis is supported by researching updated rules and authoritative sources online using Bright Data's tools, including the SERP API and Web Unlocker.
Provide accurate, enterprise-ready insights, ensuring all findings are supported by quotes from both the original document and authoritative external sources.
"""
# List of tools available to the agent
tools=[bright_data_serp_api_tool, bright_data_web_unlocker_api_tool]
# Define the AI agent
agent = create_agent(
llm=llm,
tools=tools,
system_prompt=system_prompt,
)
# Load all PDF documents from the input folder
input_folder = "./input"
loader = PyPDFDirectoryLoader(input_folder)
# Load all pages from all PDFs in the input folder
docs = loader.load()
# Combine all pages from the PDFs into a single string for analysis
internal_document_to_analyze = "\n\n".join([doc.page_content for doc in docs])
# Define a prompt template to guide the agent through the workflow
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("""
Given the following PDF content:
1. Have the LLM analyze it to identify the main key aspects worth exploring in terms of privacy.
2. Translate those aspects into up to 3 very short (no more than 5 words), concise, specific search queries suitable for Google.
3. Perform web searches for those queries using Bright Data's SERP API tool (searching for pages in English, limited to the United States).
4. Access up to the top 5 web, non-PDF pages (giving priority to government websites) in Markdown data format using Bright Data's Web Unlocker tool.
5. Process the collected information and create a final, concise report that includes quotes from the original document and insights from the scraped pages to avoid regulatory issues.
PDF CONTENT:
{pdf}
""")
# Fill the template with the content from the PDFs
prompt = prompt_template.format(pdf=internal_document_to_analyze)
# Stream the agent's response while tracking each step with Langfuse
for step in agent.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]},
stream_mode="values",
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]} # <--- Langfuse integration
):
step["messages"][-1].pretty_print()Wow! In just around 75 lines of Python code, you just built an enterprise-ready AI agent for regulatory and compliance analysis, thanks to LangChain, Bright Data, and Langfuse.
Step #11: Run the Agent
Remember, your AI agent requires a PDF file to work on. For this example, assume you want to run the regulatory analysis on the following document:
This is a sample, enterprise-style document that outlines, at a high level, user data processing practices applied by a company.
Save it as user-data-processing-workflow.pdf and place it inside the input/ folder in your project directory:
This way, the script will be able to access it and embed it in the agent’s prompt.
Execute the LagnChain AI agent with:
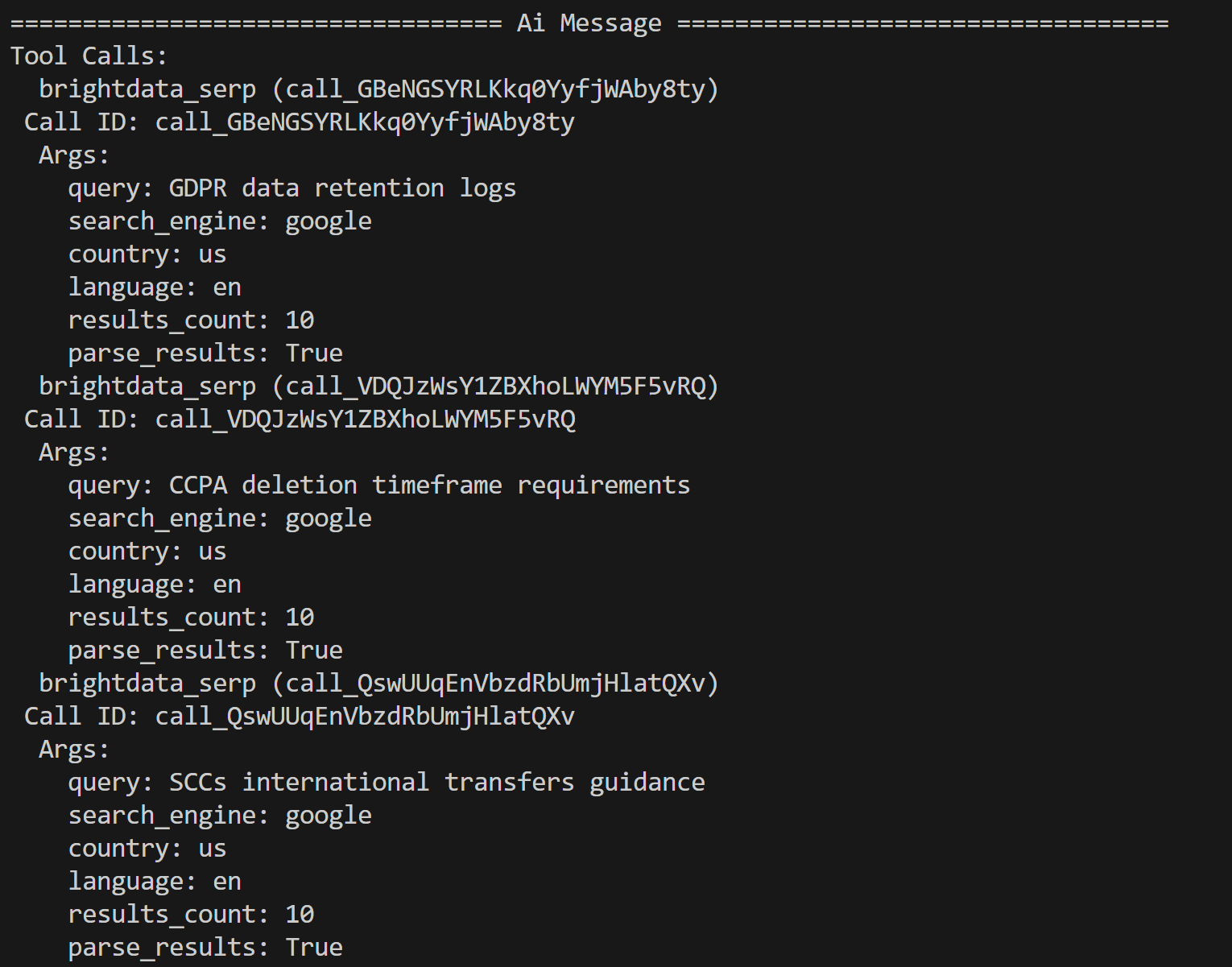
python agent.py In the terminal, you will see traces from the Bright Data tools calls, like this:
The AI agent identified the following three search queries for further research based on the PDF content:
- “GDPR data retention logs”
- “CCPA deletion timeframe requirements”
- “SCCs international transfers guidance”
These queries are contextual to potential regulatory and privacy issues highlighted by the LLM in the input document.
From the results returned by the Bright Data SERP API—which contains Google search results for these queries—the agent selects the top pages and scrapes them via the Web Unblocker API tool:
The content from these pages is then processed and condensed in a final regulatory analysis report.
Et voilà! Your AI agent works like a charm. Time to check the effect of the Langfuse integration for observability and tracking.
Step #12: Inspect the Agent Traces in Langfuse
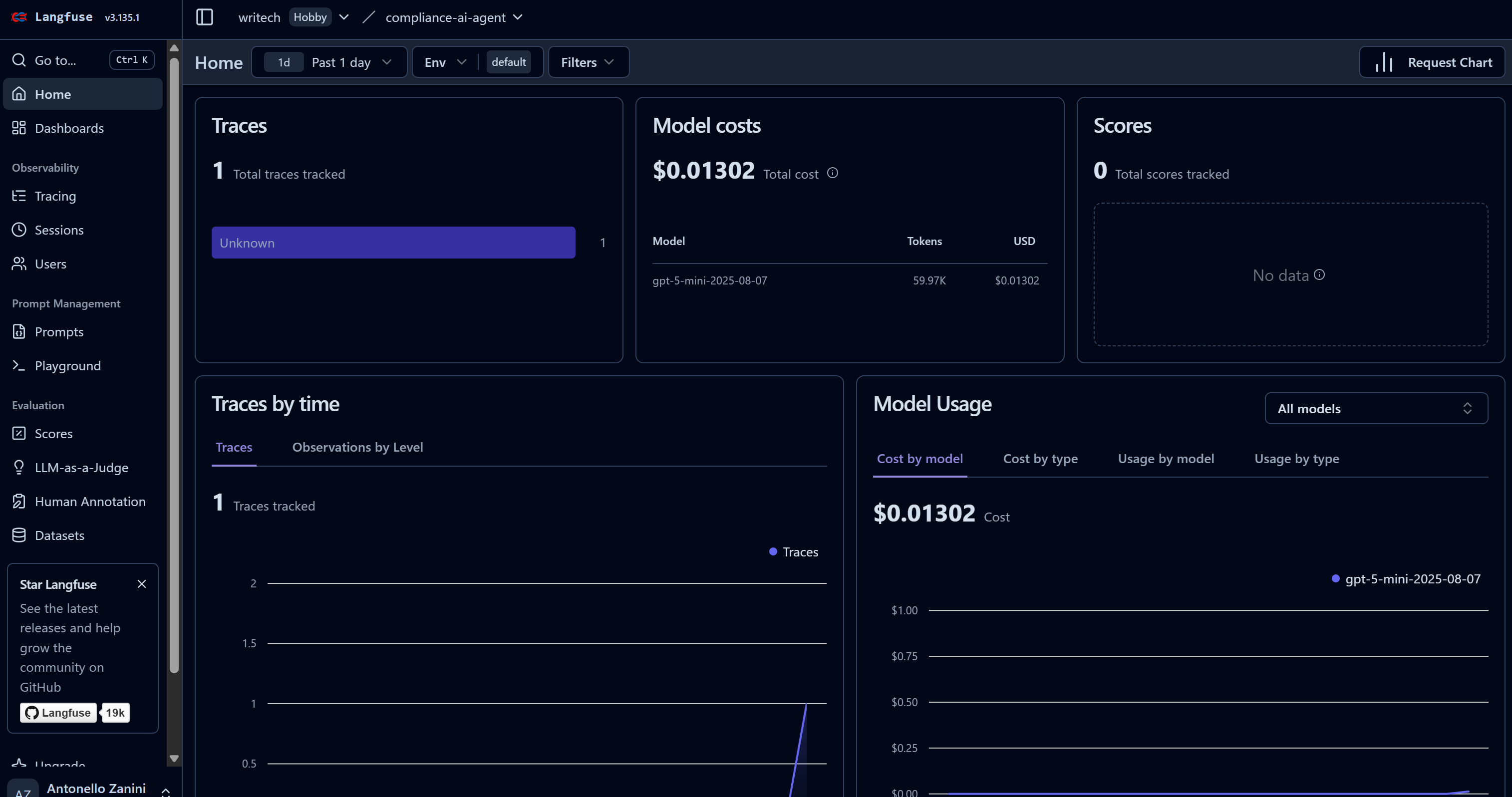
As soon as your AI agent starts performing its task, you will see data appearing in your Langfuse dashboard. In particular, note how the “Traces” count goes from 0 to 1 and how the model costs increase:
This dashboard helps you to monitor costs as well as many other useful metrics.
To view all information on a specific agent run, go to the “Tracing” page and click on the corresponding trace row for your agent:
A panel will open on the left side of the web page, showing detailed information for each step performed by your agent.
Focus on the first “ChatOpenAI” node. This highlights that the agent has already called the Bright Data SERP API three times, while the Web Unlocker API is yet to be called:
Here, you can also inspect the system prompt configured in your code and the user prompts passed to the agent. Additionally, you access information such as latency, cost, timestamps, and more. Plus, an interactive flowchart in the bottom-left corner helps visualize and explore the agent’s run step by step.
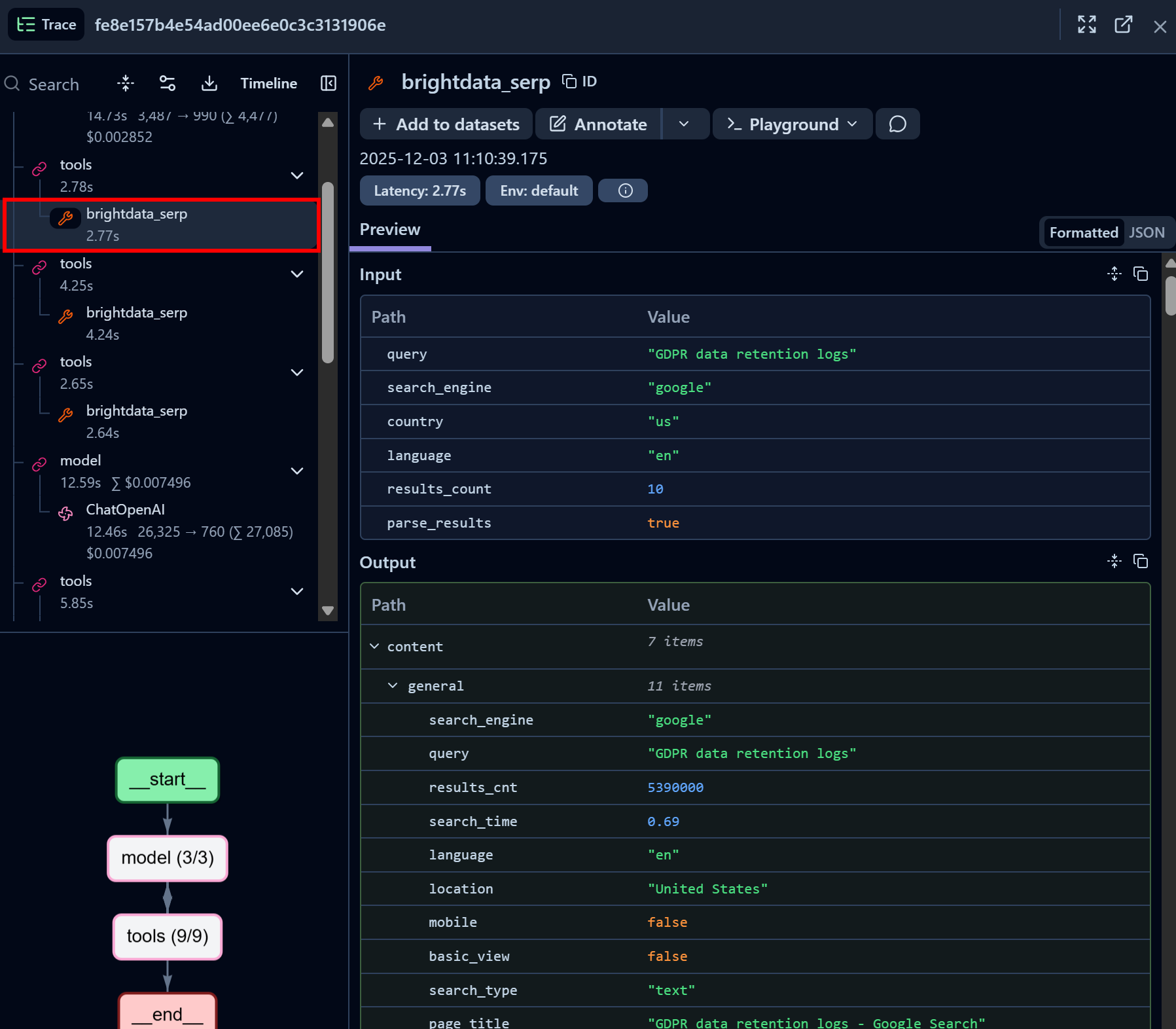
Now, inspect a Bright Data SERP API tool call node:
Notice how the Bright Data SERP API LangChain tool successfully returned SERP data for the given search query in JSON format (which is great for LLM ingestion in AI agents). This demonstrates that the integration with the Bright Data SERP API is working perfectly.
If you have ever tried scraping Google search results in Python, you know how challenging it can be. Thanks to Bright Data’s SERP API, this process is immediate, fast, and fully AI-ready.
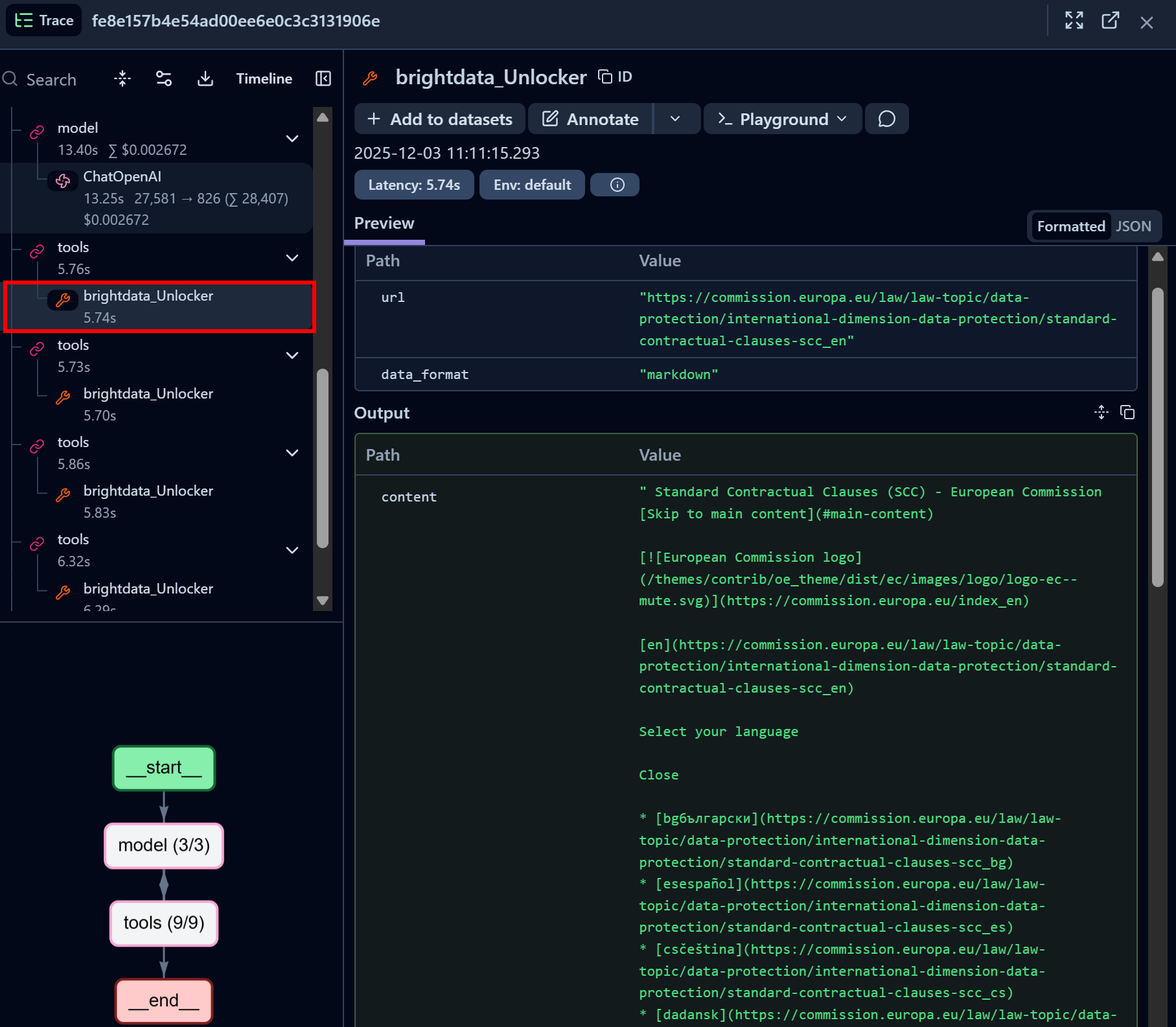
Similarly, focus on a Bright Data Web Unlocker API tool call node:
The Bright Data Web Unlocker LangChain tool successfully accessed the identified page and returned it in Markdown format.
Web Unlocker API gives your AI agent the ability to programmatically access any governance website (or other web pages) without worrying about blocks, getting an AI-optimized version of the page suitable for LLM ingestion as a result.
Terrific! The Langfuse + LangChain + Bright Data integration is now complete. Langfuse can be integrated with many other AI agent-building solutions, all of which are supported by Bright Data as well.
Next Steps
To make this AI agent with Langfuse integration even more enterprise-grade, consider the following insights:
- Add prompt management: Use Langfuse’s prompt management features to store, version, and retrieve prompts for your LLM applications.
- Export reports: Generate a final report and either save it to disk, store it in a shared folder, or send it via email to the relevant stakeholders.
- Define custom dashboard: Customize the Langfuse dashboard to display only the metrics relevant to your team or stakeholders.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to monitor and track your AI agent using Langfuse. In detail, you saw how to instrument a LangChain AI agent powered by Bright Data’s AI-ready web access solutions.
As discussed, just like Langfuse, Bright Data integrates with a wide range of AI solutions, from open-source tools to enterprise-ready platforms. This allows you to enhance your agent with powerful web data retrieval and browsing capabilities while monitoring its performance and behavior through Langfuse.
Sign up for Bright Data for free and start experimenting with our AI-ready web data solutions today!