In this tutorial, you will learn:
- What Amazon Q Developer CLI is and what its core features are.
- How extending it with web interaction and data retrieval capabilities can make it even more interesting.
- How to connect Amazon Q CLI to the Bright Data MCP server to create a powerful AI coding agent.
Let’s dive in!
What is Amazon Q Developer CLI?
Amazon Q Developer CLI is a command-line interface that allows developers to interact with Amazon Q Developer. If you are not familiar with it, Amazon Q Developer is a generative AI-powered assistant designed to help build, operate, and transform software.
Amazon Q Developer CLI, often referred to simply as Amazon Q CLI, is available through an open-source tool. It not only exposes Amazon Q Developer in your terminal but also improves its capabilities. Specifically, it allows you to perform various development tasks while understanding your codebase.
That speeds up development and AWS interactions through features like:
- Natural language interaction: Ask questions, receive answers, and get guidance on AWS architecture, resources, and general development tasks using conversational prompts.
- Agentic coding experience: Provides a dynamic and interactive coding experience, giving Amazon Q Developer the ability to read and write files locally, query AWS resources, write code, and assist with debugging issues based on the local CLI environment.
- Operational troubleshooting: Simplifies troubleshooting processes by enabling natural language interaction with AWS services, automated discovery of infrastructure, intelligent log analysis, root cause identification, and guided remediation.
- Code transformation: Facilitates code transformations, such as upgrading Java applications or porting .NET applications, through custom rules and automated modernization processes.
- Integration with AWS services: Can interact with many AWS services and provide command suggestions, reducing the need to memorize syntax or search for documentation.
Why You Should Supercharge Amazon Q CLI with Bright Data Web MCP
No matter which LLM you configure in Amazon Q CLI, they all share the same limitation: their knowledge is static!
After all, the data LLMs are trained on represents a snapshot in time, which can quickly become outdated. That is especially true in fast-moving fields like software development. Now, imagine giving your Amazon Q CLI agent the ability to:
- Consult live guides as it writes and understands code.
- Pull in fresh tutorials and documentation.
- Browse dynamic websites as easily as it can navigate your local files.
Those are exactly the functionalities you unlock by connecting Amazon Q CLI to Bright Data’s Web MCP (also referred to as Web MCP). This MCP server provides access to 60+ AI-ready tools—all powered by Bright Data’s AI infrastructure—built around real-time web interaction and data collection.
The two most commonly employed tools (even available in the free tier) are:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
scrape_as_markdown |
Scrape content from a single webpage with advanced extraction options, returning the data in Markdown. Can bypass bot detection and CAPTCHA. |
search_engine |
Extract search results from Google, Bing, or Yandex. Returns SERP data in JSON or Markdown format. |
Beyond these, there are ~60 other specialized tools to interact with web pages (e.g., scraping_browser_click) and collect structured data from multiple domains such as LinkedIn, Amazon, Yahoo Finance, TikTok, and more. For example, the web_data_linkedin_person_profile tool can retrieve structured profile information from public LinkedIn profile pages. |
Explore how Web MCP works inside Amazon Q CLI!
How to Integrate Bright Data’s Web MCP into Amazon Q CLI
Follow this guided section to learn how to install Amazon Q Developer CLI locally and configure it for Bright Data Web MCP integration. The result will be an enhanced coding agent with access to over 60 web tools.
Once set up, the CLI agent will be used in a sample task to:
- Scrape a LinkedIn profile page in real time to collect actual profile data.
- Store the collected data locally in a JSON file.
- Generate a Node.js script to load and process that data.
Follow the steps below to get started!
Note: This tutorial focuses on using Amazon Developer Q in the CLI. A similar setup can also be applied to integrate it directly into your IDE, as described in the official documentation.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, ensure you have the following:
- A macOS or Linux environment (Windows users must rely on the Windows Subsystem for Linux).
- Node.js installed locally (we recommend the latest LTS version).
- An Amazon AWS Builder ID.
- A Bright Data account with a configured API token.
No need to worry about the Bright Data setup just yet, as you will be guided through it in the next steps.
It is also helpful (but optional) to have some background knowledge, such as:
- General understanding of how MCP works.
- Some familiarity with Bright Data’s Web MCP and the tools it provides.
Step #1: Install Amazon Q Developer CLI
Follow the official guide for your operating system and install the Amazon Q CLI. If you are on Windows, you need to follow the Ubuntu non-GUI guide and apply it in your WSL instance.
During installation, you will be asked a couple of questions. Select the right answers according to your scenario:
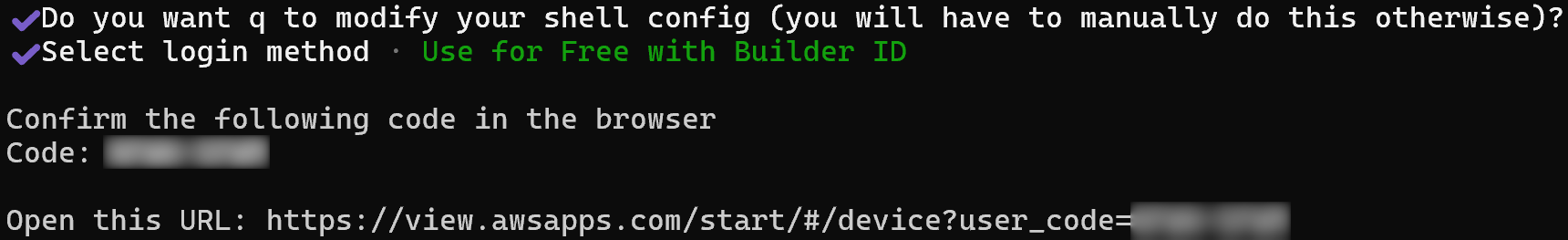
Next, authenticate the Amazon Q Developer CLI in your browser using the provided code. If you do not yet have an Amazon AWS Builder ID, you will be guided through the process of creating one.
If everything works as expected, you should see:

The Amazon Q CLI has been successfully installed on your machine.
Reload your system and start Amazon Q Developer CLI with:
qThe result should be:
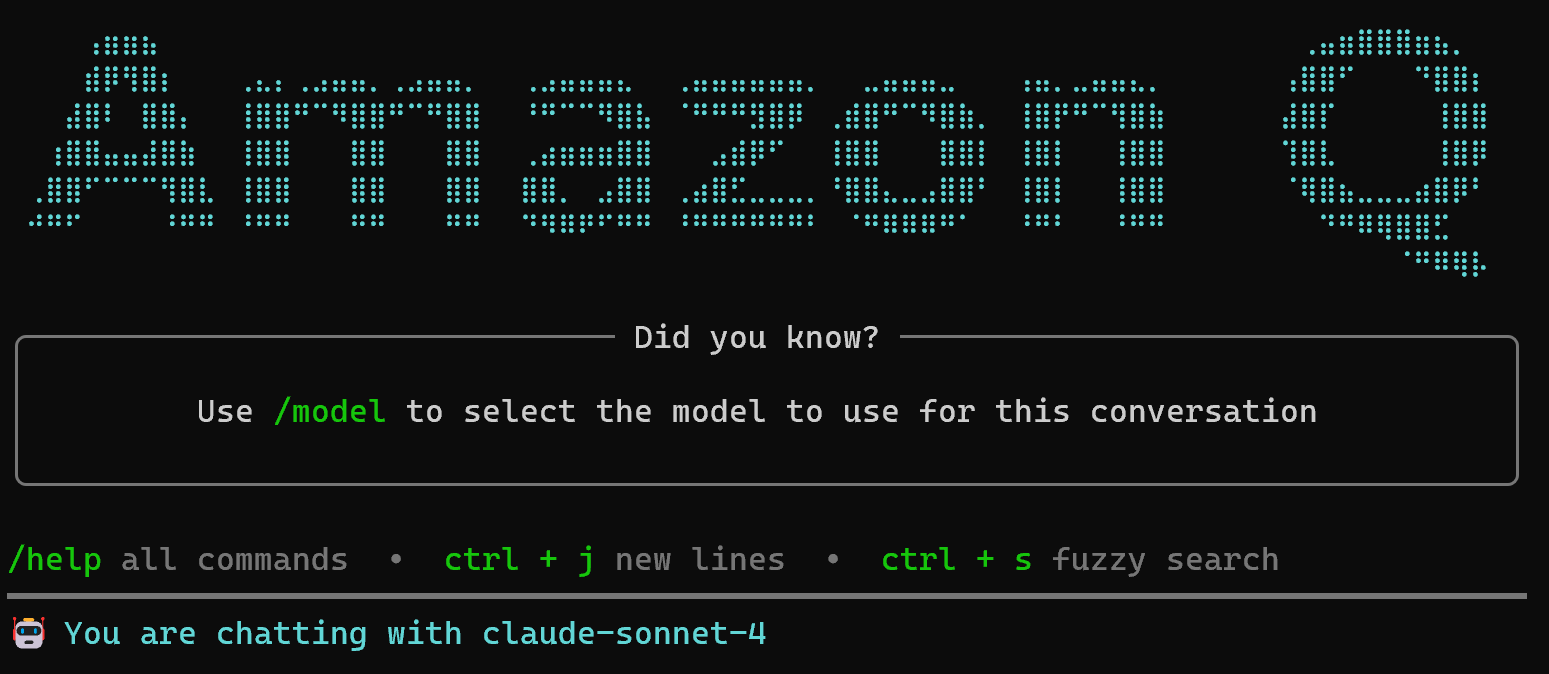
Notice how the default model is set to Claude Sonnet 4. You can change it at any time using the /model command. As of this writing, the following Anthropic models are available for chat sessions:
- Claude Sonnet 4 (default)
- Claude 3.7 Sonnet
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet
Great! Amazon Q Developer CLI is now installed and ready to use.
Step #2: Verify the Web MCP Works
Before connecting your Amazon Q agent to Bright Data’s Web MCP, first make sure your machine can run the MCP server.
If you have not already, start by creating a Bright Data account. If you already have one, just log in. For a quick setup, open the “MCP” page in your account and follow the instructions:
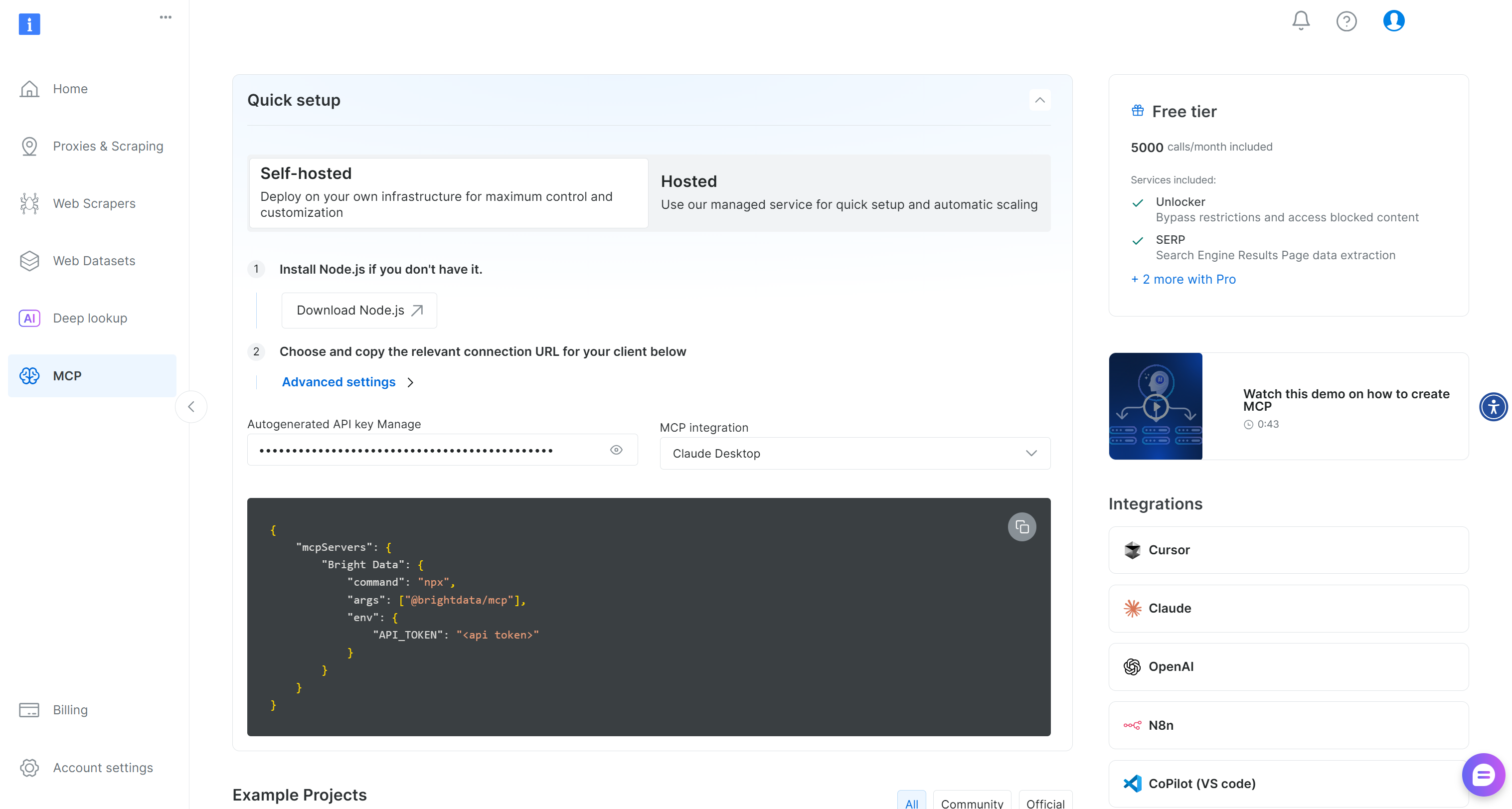
Otherwise, follow the steps below.
First, generate a Bright Data API key and store it in a safe place. In this guide, we will assume the API key has Admin permissions, as that makes the integration process simpler.
Then, run the following command to install the Web MCP globally:
npm install -g @brightdata/mcpCheck that the local MCP server works by executing:
API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>" npx -y @brightdata/mcpReplace the <YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API> placeholder with your actual Bright Data API token. The command sets the required API_TOKEN env and then starts the Web MCP via the @brightdata/mcp package.
If successful, you should see logs similar to the following:
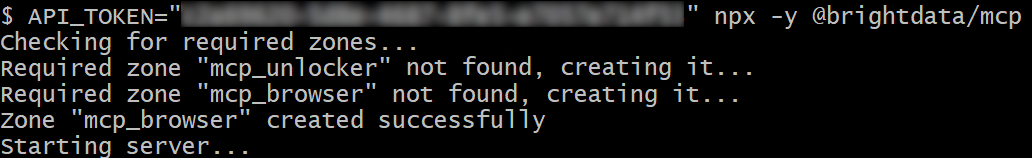
On first launch, the package creates two default zones in your Bright Data account:
mcp_unlocker: A zone for Web Unlocker.mcp_browser: A zone for Browser API.
These zones are required by the Web MCP to power all its 60+ tools.
To confirm they were created, log in to your Bright Data dashboard and go to the “Proxies & Scraping Infrastructure” page. You should see the two zones listed:
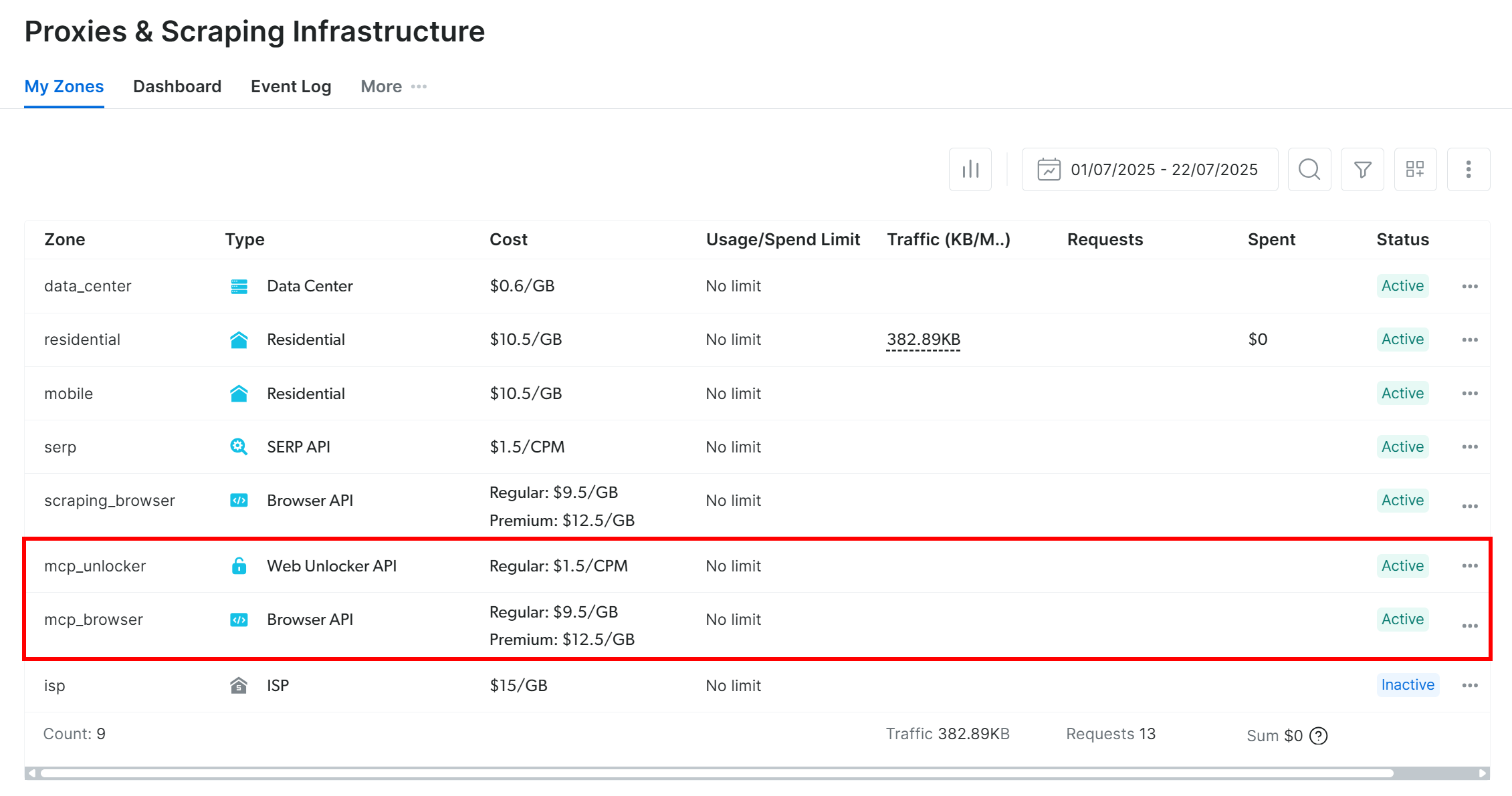
If your API token does not have Admin permissions, these zones will not be created for you. In that case, you have to add them manually in the dashboard and configure their names via environment variables (see the GitHub page for details).
Note: By default, the MCP server only exposes the search_engine and scrape_as_markdown tools (which can be used for free!).
To unlock advanced features—like browser automation and structured data feeds—enable Pro mode. To do so, set the PRO_MODE=true environment variable before launching the MCP server:
API_TOKEN="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API>" PRO_MODE="true" npx -y @brightdata/mcpKeep in mind that Pro mode unlocks all 60+ tools, but it is not included in the free tier and may incur additional charges.
Perfect! You confirmed that the Web MCP server works on your machine. Stop the server process, as you will configure the Amazon Q CLI to launch and connect to it automatically.
Step #3: Configure Bright Data’s Web MCP in Amazon Q CLI
Amazon Q CLI supports global MCP integration through a custom JSON configuration file located in the ~/.aws/amazonq folder.
As shown in the official MCP integration blog post, create a new file named mcp.json inside the Amazon Q CLI config directory:
nano ~/.aws/amazonq/mcp.jsonMake sure it contains the JSON configuration below:
{
"mcpServers": {
"brightData": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@brightdata/mcp"
],
"env": {
"API_TOKEN": "<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>",
"PRO_MODE": "true"
}
}
}
}Replace <YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY> with the Bright Data API key you generated and tested earlier. For more details about the configuration syntax, refer to the official documentation.
In the above JSON content:
- The
mcpServersobject defines the MCP servers known by Amazon Q CLI. - The
brightDataentry specifies the command (npx) along with the required environment variables. Here,API_TOKENauthenticates the Web MCP, whilePRO_MODEis optional (but recommended to unlock the full set of available tools).
In short, the mcp.json file instructs all Amazon Q Developer CLI instances to run the same npx command you tested earlier, with the necessary environment variables.
Cool! The CLI agent can now launch and connect directly to the Bright Data Web MCP server.
Step #4: Verify the Web MCP Tools Are Available
Check that the MCP integration works by relaunching the Amazon Q CLI:
qThis time, you should see a message indicating that the configured MCP server has been loaded:
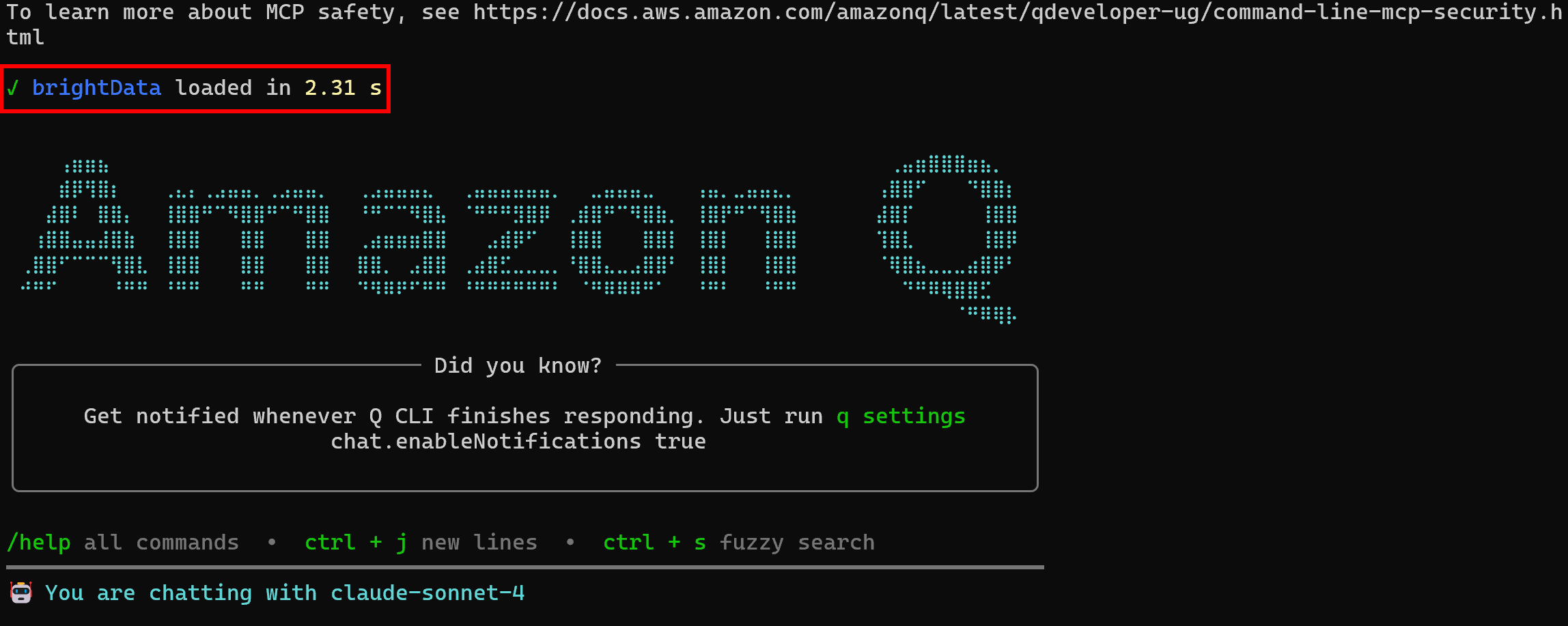
This confirms that the Bright Data MCP server has been started and connected to as planned.
To verify that all tools are available, run the /tools command:
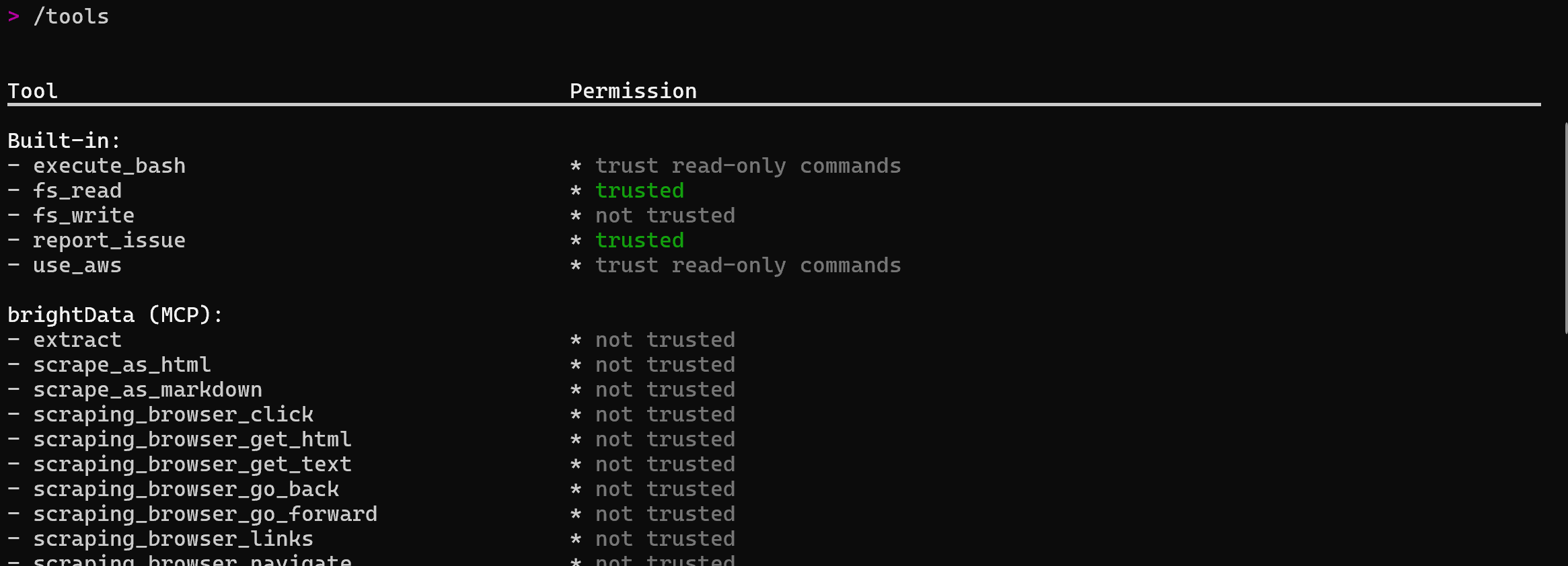
Here, if PRO_MODE is enabled, you should see 60+ tools listed. Otherwise, the list will contain only the two basic tools: scrape_as_markdown and search_engine.
Wonderful! The Bright Data Web MCP integration in Amazon Q CLI is working perfectly.
Step #5: Run a Task in Amazon Q CLI
Put the new web capabilities of your Amazon Q Developer CLI agent to the test with a prompt like the following:
Extract data from https://it.linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini and save it to a local file named profile.json. Then, create a simple Node.js script that loads the JSON file and outputs its contents.Type the prompt and press Enter to execute it. You should see behavior similar to this:

The GIF has been sped up, but this is what happens step by step:
- The agent identifies that it needs to retrieve LinkedIn data. To do this, the LLM selects the appropriate MCP tool (
web_data_linkedin_person_profile) and prepares the correct arguments extracted from the prompt (https://it.linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini). - You are prompted to approve the execution of the selected tool.
- Once approved, the agent collects the target data, shows it to you, and asks for permission to save it to a local
profile.jsonfile. - After granting permission, the LinkedIn profile data is stored in the
profile.jsonfile. - The agent shows a Node.js script (
load_profile.js) to read the data fromprofile.jsonand print it, asking for permission to create the file. - Once permission is given, the
load_profile.jsfile is created. - Finally, the agent provides instructions on how to run the generated Node.js script.
During execution, you can confirm that the correct Bright Data Web MCP tool was utilized by checking the logs:
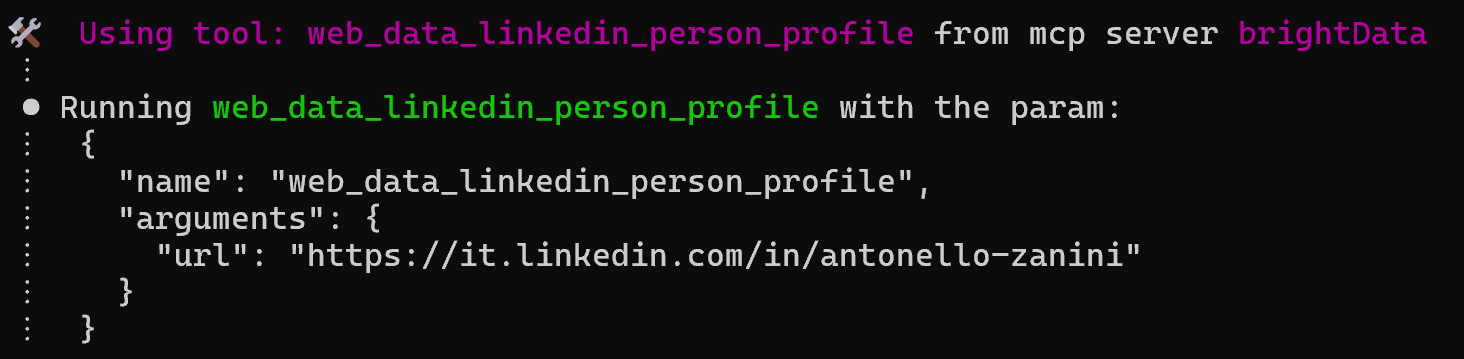
Fantastic! Everything worked as intended. Next, check the output and try running the resulting Node.js script.
Step #6: Explore the Output
At the end of the CLI coding agent execution, your working directory should contain:
├── profile.json
└── load_rofile.js Open the project directory in Visual Studio Code (or your favorite IDE), and inspect the profile.json file:
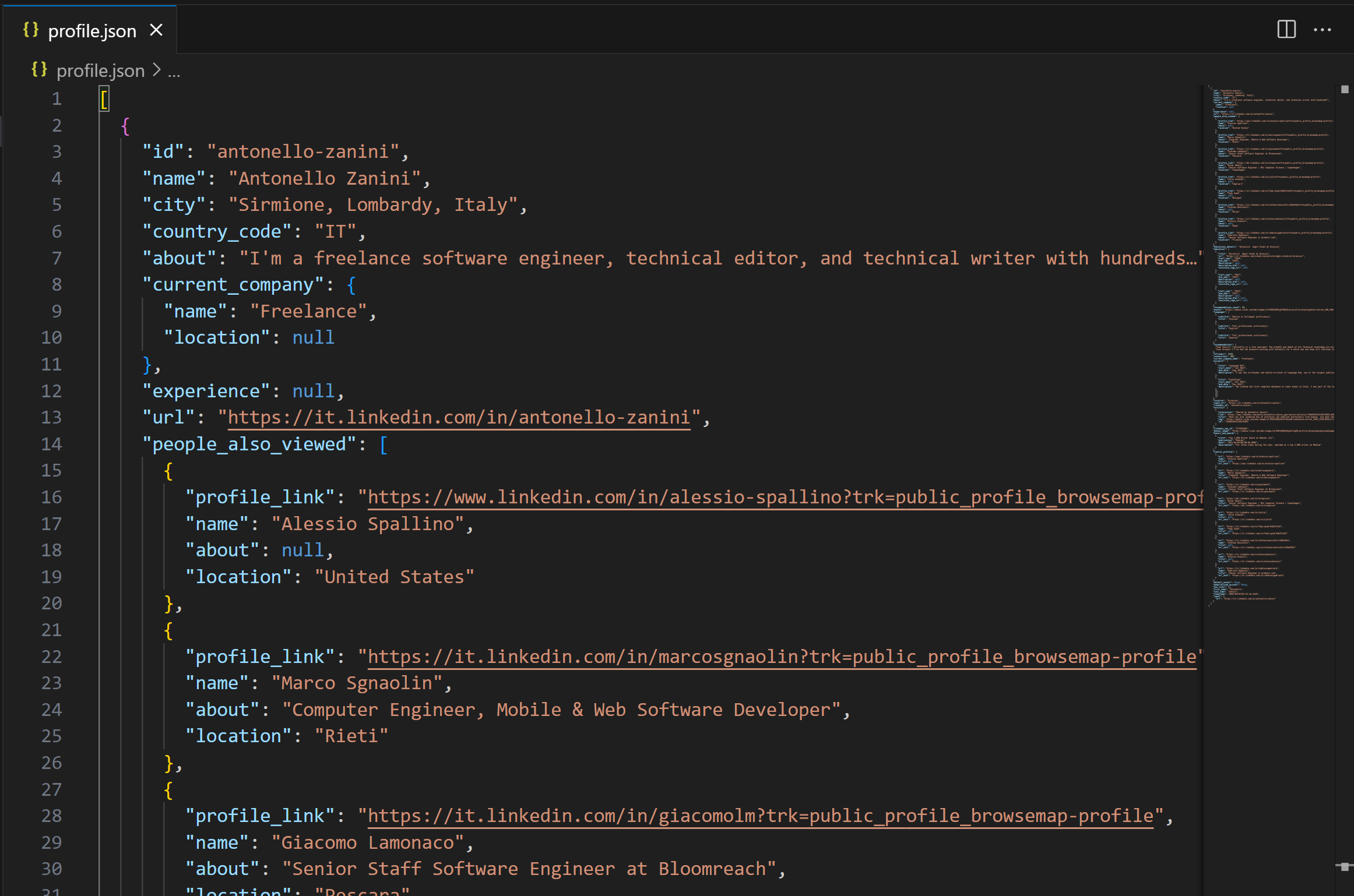
Important: The data in profile.json comes from the Bright Data LinkedIn Scraper, which was called through the dedicated web_data_linkedin_person_profile MCP tool. In other words, what you see is real LinkedIn data—not hallucinated, or made-up content generated by Sonnet 4!
The LinkedIn data was retrieved correctly, as you can verify by taking a look at the public LinkedIn profile page referenced in the prompt.
Do not forget that scraping LinkedIn is notoriously challenging because of its sophisticated anti-bot systems. A regular LLM cannot perform this task reliably, which proves how powerful your coding agent has become thanks to the Web MCP integration.
Next, inspect the load_profile.js file:
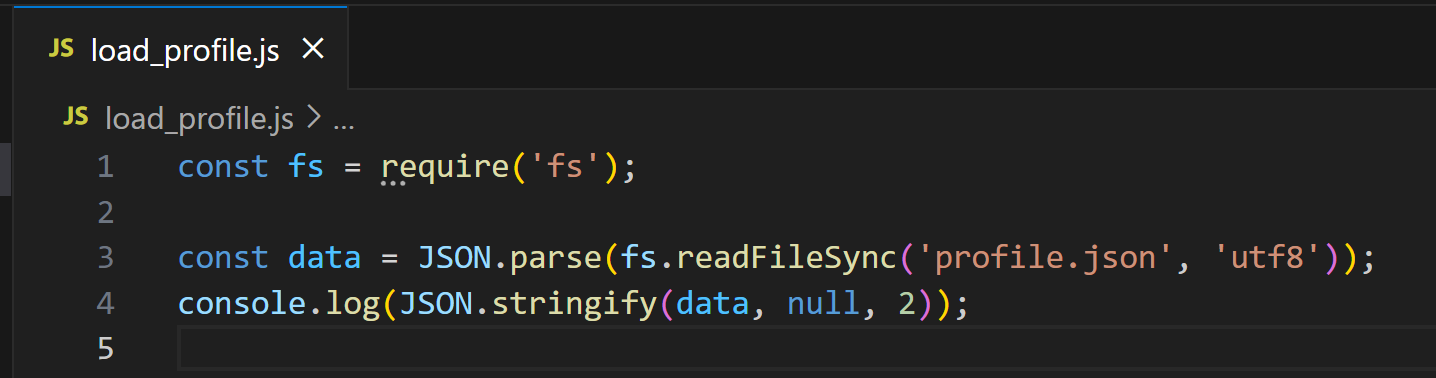
Test the Node.js script with:
node load_profile.jsThe output should be:
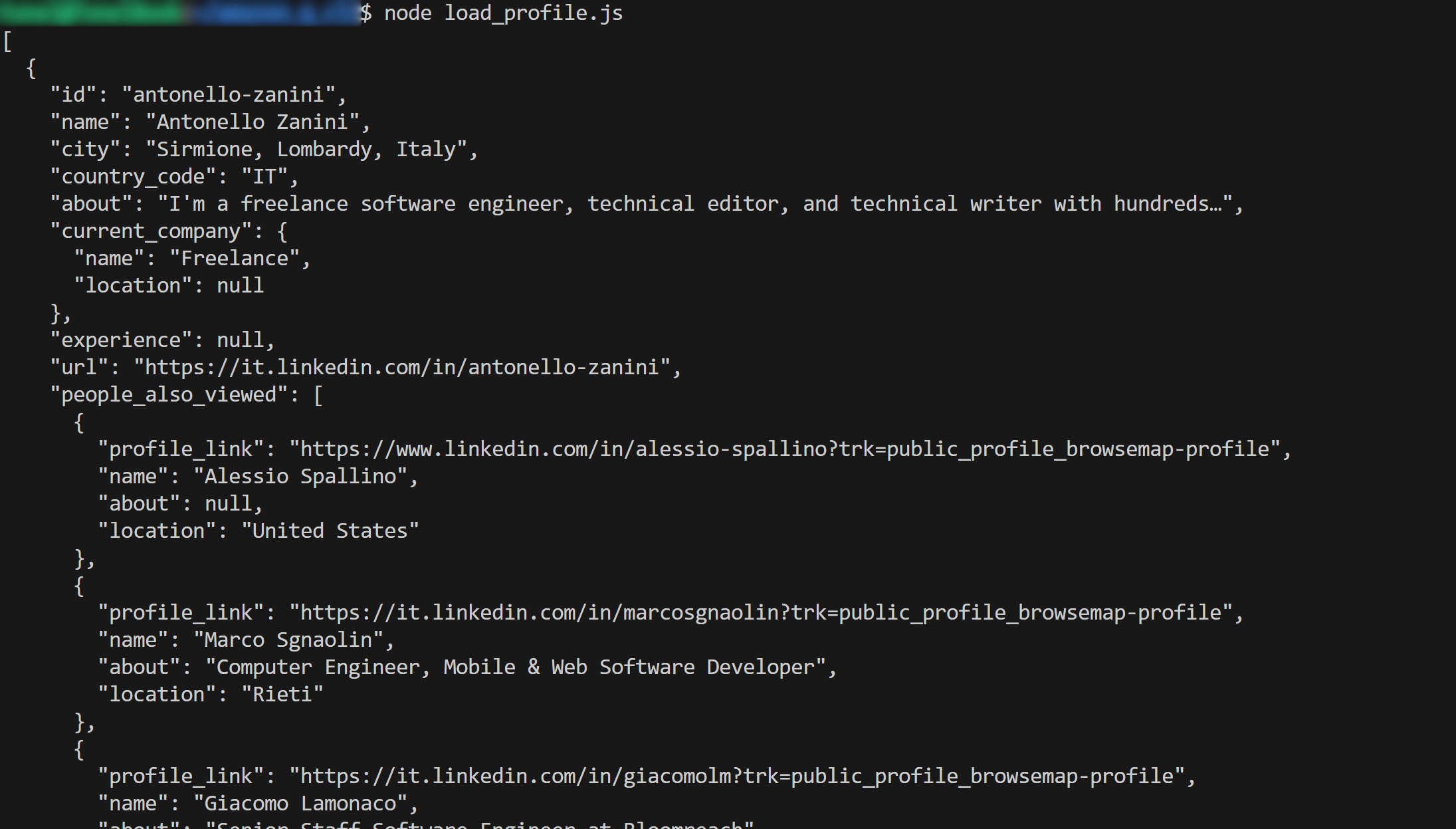
Notice how the AI-generated script prints the LinkedIn scraped data as planned.
Et voilà! Try your Amazon Q CLI + Web MCP agent with different prompts and explore advanced LLM-driven data workflows directly in the CLI.
Conclusion
In this blog post, you saw how to connect Amazon Developer Q CLI to Bright Data’s Web MCP (which now comes with a free tier!). The result is an enriched AI coding agent with access to over 60 tools for web data extraction and interaction.
To build complex AI agents, explore the full range of products and services available in the Bright Data AI infrastructure. These solutions support a long list of agentic scenarios, including CLI integrations.
Create a free Bright Data account today and start experimenting with our AI-ready web data tools!