In this article, you will learn:
- How to build a production-ready AI agent that persists conversations to databases
- How to implement intelligent data extraction and entity tracking
- How to create robust error handling with automatic recovery
- How to enhance your agent with real-time web data from Bright Data
Let’s begin!
The Challenge of Stateless AI Conversations
Current AI agents usually work as stateless systems. They treat each conversation as a separate event. This lack of historical context makes users repeat information. As a result, it causes operational inefficiencies and user frustration. Additionally, businesses miss out on using long-term data for personalization or service improvement.
Data-persistent AI solves this issue by recording all interactions in a structured database. By keeping a continuous record, these systems can remember historical context, track specific entities over time, and use past interaction patterns to provide a consistent and personalized user experience.
What We Are Building: Database-Connected AI Agent System
We’ll build a production-ready AI agent that processes messages using LangChain and GPT-4. It saves each conversation to PostgreSQL. It extracts entities and insights in real-time. It keeps a complete conversation history across sessions. It manages errors with automatic retry systems. It offers monitoring with logging.
The system will handle:
- Database schema with proper relationships and indexes
- LangChain agent with custom database tools
- Automatic conversation persistence and entity extraction
- Background processing pipeline for data collection
- Error handling with transaction management
- Query interface for retrieving historical data
- RAG integration with Bright Data for web intelligence
Prerequisites
Set up your development environment with:
- Python 3.10 or higher. Required for modern async features and type hints
- PostgreSQL 14+ or SQLite 3.35+. Database for data persistence
- OpenAI API Key. For GPT-4 access. Get it from OpenAI Platform
- LangChain. Framework for building AI agents. See docs
- Python virtual environment. Keeps dependencies isolated. See
venvdocs
Environment Setup
Create your project directory and install dependencies:
mkdir database-agent
cd database-agent
python -m venv venv
# macOS/Linux: source venv/bin/activate
# Windows: venv\\Scripts\\activate
pip install langchain langchain-openai sqlalchemy psycopg2-binary python-dotenv pydanticCreate a new file called agent.py and add the following imports:
import os
import json
import logging
import time
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional
from queue import Queue
from threading import Thread
# SQLAlchemy imports
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, Integer, String, Text, DateTime, Float, JSON, ForeignKey, text
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, relationship, Session, declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.pool import QueuePool
from sqlalchemy.exc import SQLAlchemyError
# LangChain imports
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor, create_openai_functions_agent
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain.tools import Tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
# RAG imports
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
import requests
# Environment setup
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)Create a .env file with your credentials:
# Database Configuration
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://username:password@localhost:5432/agent_db"
# Or for SQLite: DATABASE_URL="sqlite:///./agent_data.db"
# API Keys
OPENAI_API_KEY="your-openai-api-key"
# Optional: Bright Data (for Step 7)
BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY="your-bright-data-api-key"
# Application Settings
AGENT_MODEL="gpt-4-turbo-preview"
CONNECTION_POOL_SIZE=5
MAX_RETRIES=3You need:
- Database URL: Connection string for PostgreSQL or SQLite
- OpenAI API Key: For agent intelligence via GPT-4
- Bright Data API Key: Optional, for real-time web data in Step 7
Building Your Database-Connected AI Agent
Step 1: Designing the Database Schema
Design tables for users, conversations, messages, and extracted entities. The schema uses foreign keys and relationships to maintain data integrity.
Base = declarative_base()
class User(Base):
"""User profile table - stores user information and preferences."""
__tablename__ = 'users'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
user_id = Column(String(255), unique=True, nullable=False, index=True)
name = Column(String(255))
email = Column(String(255))
preferences = Column(JSON, default={})
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
last_active = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow, onupdate=datetime.utcnow)
# Relationships
conversations = relationship("Conversation", back_populates="user", cascade="all, delete-orphan")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<User(user_id='{self.user_id}', name='{self.name}')>"
class Conversation(Base):
"""Conversation session table - tracks individual conversation sessions."""
__tablename__ = 'conversations'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(String(255), unique=True, nullable=False, index=True)
user_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('users.id'), nullable=False)
title = Column(String(500))
summary = Column(Text)
status = Column(String(50), default='active') # active, archived, deleted
meta_data = Column(JSON, default={})
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
updated_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow, onupdate=datetime.utcnow)
# Relationships
user = relationship("User", back_populates="conversations")
messages = relationship("Message", back_populates="conversation", cascade="all, delete-orphan")
entities = relationship("Entity", back_populates="conversation", cascade="all, delete-orphan")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Conversation(id='{self.conversation_id}', user='{self.user_id}')>"
class Message(Base):
"""Individual message table - stores each message in a conversation."""
__tablename__ = 'messages'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('conversations.id'), nullable=False, index=True)
role = Column(String(50), nullable=False) # user, assistant, system
content = Column(Text, nullable=False)
tokens = Column(Integer)
model = Column(String(100))
meta_data = Column(JSON, default={})
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
# Relationships
conversation = relationship("Conversation", back_populates="messages")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Message(role='{self.role}', conversation='{self.conversation_id}')>"
class Entity(Base):
"""Extracted entities table - stores named entities extracted from conversations."""
__tablename__ = 'entities'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('conversations.id'), nullable=False, index=True)
entity_type = Column(String(100), nullable=False, index=True) # person, organization, location, etc.
entity_value = Column(String(500), nullable=False)
context = Column(Text)
confidence = Column(Float, default=0.0)
meta_data = Column(JSON, default={})
extracted_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
# Relationships
conversation = relationship("Conversation", back_populates="entities")
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Entity(type='{self.entity_type}', value='{self.entity_value}')>"
class AgentLog(Base):
"""Agent operation logs table - stores operational logs for monitoring."""
__tablename__ = 'agent_logs'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
conversation_id = Column(String(255), index=True)
level = Column(String(50), nullable=False) # INFO, WARNING, ERROR
operation = Column(String(255), nullable=False)
message = Column(Text, nullable=False)
error_details = Column(JSON)
execution_time = Column(Float) # in seconds
created_at = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
def __repr__(self):
return f"<AgentLog(level='{self.level}', operation='{self.operation}')>"The schema defines five core tables. User stores profiles with JSON preferences for flexible data. Conversation tracks sessions with status tracking. Message holds individual exchanges with role indicators for user versus assistant messages. Entity captures extracted information with confidence scores. AgentLog provides operation tracking for monitoring. Foreign keys maintain referential integrity. Indexes on frequently queried fields optimize performance. The cascade="all, delete-orphan" setting cleans up related records when parent records are deleted.
Step 2: Setting Up the Database Connection Layer
Configure the database connection manager with SQLAlchemy. The manager handles connection pooling, health checks, and automatic retry logic for reliability.
class DatabaseManager:
"""
Manages database connections and operations.
Features:
- Connection pooling for efficient resource usage
- Health checks to verify database connectivity
- Automatic table creation
"""
def __init__(self, database_url: str, pool_size: int = 5, max_retries: int = 3):
"""
Initialize database manager.
Args:
database_url: Database connection string (e.g., 'sqlite:///./agent_data.db')
pool_size: Number of connections to maintain in the pool
max_retries: Maximum number of retry attempts for failed operations
"""
self.database_url = database_url
self.max_retries = max_retries
# Create engine with connection pooling
self.engine = create_engine(
database_url,
poolclass=QueuePool,
pool_size=pool_size,
max_overflow=10,
pool_pre_ping=True, # Verify connections before using
echo=False # Set to True for SQL debugging
)
# Create session factory
self.SessionLocal = sessionmaker(
bind=self.engine,
autocommit=False,
autoflush=False
)
logger.info(f"✓ Database engine created with {pool_size} connection pool")
def initialize_database(self):
"""Create all tables in the database."""
try:
Base.metadata.create_all(bind=self.engine)
logger.info("✓ Database tables created successfully")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"❌ Failed to create database tables: {e}")
raise
def get_session(self) -> Session:
"""Get a new database session for performing operations."""
return self.SessionLocal()
def health_check(self) -> bool:
"""
Check database connectivity.
Returns:
bool: True if database is healthy, False otherwise
"""
try:
with self.engine.connect() as conn:
conn.execute(text("SELECT 1"))
logger.info("✓ Database health check passed")
return True
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"❌ Database health check failed: {e}")
return FalseThe DatabaseManager establishes connections using SQLAlchemy’s connection pooling. Setting pool_size=5 maintains five persistent connections for efficiency. The pool_pre_ping option validates connections before use. This prevents stale connection errors. The retry mechanism attempts failed operations up to three times with exponential backoff. It handles transient network issues.
Step 3: Building the LangChain Agent Core
Create the AI agent using LangChain with custom tools that interact with the database. The agent uses function calling to save information and retrieve conversation history.
class DataPersistentAgent:
"""
AI Agent with database persistence capabilities.
This agent:
- Remembers conversations across sessions
- Saves and retrieves user information
- Extracts and stores important entities
- Provides personalized responses based on history
"""
def __init__(
self,
db_manager: DatabaseManager,
model_name: str = "gpt-4-turbo-preview",
temperature: float = 0.7
):
"""
Initialize the data-persistent agent.
Args:
db_manager: Database manager instance
model_name: LLM model to use (default: gpt-4-turbo-preview)
temperature: Model temperature for response generation
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.model_name = model_name
# Initialize LLM
self.llm = ChatOpenAI(
model=model_name,
temperature=temperature,
openai_api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
)
# Create tools for agent
self.tools = self._create_agent_tools()
# Create agent prompt
self.prompt = self._create_agent_prompt()
# Initialize memory
self.memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history",
return_messages=True
)
# Create agent
self.agent = create_openai_functions_agent(
llm=self.llm,
tools=self.tools,
prompt=self.prompt
)
# Create agent executor
self.agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=self.agent,
tools=self.tools,
memory=self.memory,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5
)
logger.info(f"✓ Data-persistent agent initialized with {model_name}")
def _create_agent_tools(self) -> List[Tool]:
"""Create custom tools for database operations."""
def save_user_info(user_data: str) -> str:
"""Save user information to database."""
try:
data = json.loads(user_data)
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=data['user_id']).first()
if not user:
user = User(**data)
session.add(user)
else:
for key, value in data.items():
setattr(user, key, value)
session.commit()
session.close()
return f"✓ User information saved successfully"
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to save user info: {e}")
return f"❌ Error saving user info: {str(e)}"
def retrieve_user_history(user_id: str) -> str:
"""Retrieve user's conversation history."""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
return "No user found"
conversations = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(user_id=user.id).order_by(Conversation.created_at.desc()).limit(5).all()
history = []
for conv in conversations:
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conv.id).all()
history.append({
'conversation_id': conv.conversation_id,
'created_at': conv.created_at.isoformat(),
'message_count': len(messages),
'summary': conv.summary
})
session.close()
return json.dumps(history, indent=2)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to retrieve history: {e}")
return f"❌ Error retrieving history: {str(e)}"
def extract_entities(text: str) -> str:
"""Extract entities from text and save to database."""
try:
entities = []
# Simple keyword extraction (replace with proper NER)
keywords = ['important', 'key', 'critical']
for keyword in keywords:
if keyword in text.lower():
entities.append({
'entity_type': 'keyword',
'entity_value': keyword,
'confidence': 0.8
})
return json.dumps(entities, indent=2)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to extract entities: {e}")
return f"❌ Error extracting entities: {str(e)}"
tools = [
Tool(
name="SaveUserInfo",
func=save_user_info,
description="Save user information to the database. Input should be a JSON string with user details."
),
Tool(
name="RetrieveUserHistory",
func=retrieve_user_history,
description="Retrieve a user's conversation history from the database. Input should be the user_id."
),
Tool(
name="ExtractEntities",
func=extract_entities,
description="Extract important entities from text and save to database. Input should be the text to analyze."
)
]
return tools
def _create_agent_prompt(self) -> ChatPromptTemplate:
"""Create agent prompt template."""
system_message = """You are a helpful AI assistant with the ability to remember and learn from conversations.
You have access to the following tools:
- SaveUserInfo: Save user information to remember for future conversations
- RetrieveUserHistory: Look up past conversations with a user
- ExtractEntities: Extract and save important information from conversations
Use these tools to provide personalized, context-aware responses. Always check if you have previous conversations with a user before responding.
Be proactive about saving important information for future conversations."""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system_message),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history"),
("human", "{input}"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="agent_scratchpad")
])
return prompt
def chat(self, user_id: str, message: str, conversation_id: Optional[str] = None) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Process a chat message and persist to database.
This method handles:
1. Creating or retrieving conversations
2. Saving user messages to database
3. Generating agent responses
4. Saving agent responses to database
5. Logging operations for monitoring
Args:
user_id: Unique identifier for the user
message: User's message text
conversation_id: Optional conversation ID to continue existing conversation
Returns:
dict: Contains conversation_id, response, and execution_time
"""
start_time = datetime.utcnow()
try:
# Get or create conversation
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
if conversation_id:
conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation_id).first()
else:
# Create new conversation
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
user = User(user_id=user_id, name=user_id)
session.add(user)
session.commit()
conversation = Conversation(
conversation_id=f"conv_{user_id}_{datetime.utcnow().timestamp()}",
user_id=user.id,
title=message[:100]
)
session.add(conversation)
session.commit()
# Save user message
user_message = Message(
conversation_id=conversation.id,
role="user",
content=message,
model=self.model_name
)
session.add(user_message)
session.commit()
# Get agent response
response = self.agent_executor.invoke({
"input": f"[User ID: {user_id}] {message}"
})
# Save assistant message
assistant_message = Message(
conversation_id=conversation.id,
role="assistant",
content=response['output'],
model=self.model_name
)
session.add(assistant_message)
session.commit()
# Log operation
execution_time = (datetime.utcnow() - start_time).total_seconds()
log_entry = AgentLog(
conversation_id=conversation.conversation_id,
level="INFO",
operation="chat",
message="Chat processed successfully",
execution_time=execution_time
)
session.add(log_entry)
session.commit()
# Extract conversation_id before closing session
conversation_id_result = conversation.conversation_id
session.close()
logger.info(f"✓ Chat processed for user {user_id} in {execution_time:.2f}s")
return {
'conversation_id': conversation_id_result,
'response': response['output'],
'execution_time': execution_time
}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"❌ Error processing chat: {e}")
# Log error
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
error_log = AgentLog(
conversation_id=conversation_id or "unknown",
level="ERROR",
operation="chat",
message=str(e),
error_details={'exception_type': type(e).__name__}
)
session.add(error_log)
session.commit()
session.close()
raiseThe DataPersistentAgent wraps LangChain’s function calling agent with database tools. The SaveUserInfo tool persists user data by creating or updating User records. The RetrieveHistory tool queries past conversations to provide context. The system prompt instructs the agent to be proactive about saving information and checking history. The ConversationBufferMemory maintains short-term context within sessions. Database storage provides long-term persistence across sessions.
Step 3.5: Creating the Data Collection Module
Build tools to extract and structure data from conversations. The collector generates summaries, extracts preferences, and identifies entities using the LLM.
class DataCollector:
"""
Collects and structures data from agent conversations.
This module:
- Generates conversation summaries
- Extracts user preferences from conversation history
- Identifies and saves named entities
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager, llm: ChatOpenAI):
"""
Initialize data collector.
Args:
db_manager: Database manager instance
llm: Language model for text analysis
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.llm = llm
logger.info("✓ Data collector initialized")
def extract_conversation_summary(self, conversation_id: str) -> str:
"""
Generate and save conversation summary using LLM.
Args:
conversation_id: ID of conversation to summarize
Returns:
str: Generated summary text
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation_id).first()
if not conversation:
return "Conversation not found"
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation.id).all()
# Build conversation text
conv_text = "\n".join([
f"{msg.role}: {msg.content}" for msg in messages
])
# Generate summary using LLM
summary_prompt = f"""Summarize the following conversation in 2-3 sentences, capturing the main topics and outcomes:
{conv_text}
Summary:"""
summary_response = self.llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=summary_prompt)])
summary = summary_response.content
# Update conversation with summary
conversation.summary = summary
session.commit()
session.close()
logger.info(f"✓ Generated summary for conversation {conversation_id}")
return summary
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to generate summary: {e}")
return ""
def extract_user_preferences(self, user_id: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Extract and save user preferences from conversation history.
Args:
user_id: ID of user to analyze
Returns:
dict: Extracted preferences
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
return {}
# Get recent conversations
conversations = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(user_id=user.id).order_by(Conversation.created_at.desc()).limit(10).all()
all_messages = []
for conv in conversations:
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conv.id).all()
all_messages.extend([msg.content for msg in messages if msg.role == "user"])
if not all_messages:
return {}
# Analyze preferences using LLM
analysis_prompt = f"""Analyze the following messages from a user and extract their preferences, interests, and communication style.
Messages:
{chr(10).join(all_messages[:20])}
Return a JSON object with the following structure:
{{
"interests": ["interest1", "interest2"],
"communication_style": "description",
"preferred_topics": ["topic1", "topic2"],
"language_preference": "language"
}}"""
response = self.llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=analysis_prompt)])
try:
# Extract JSON from response
content = response.content
if '```json' in content:
content = content.split('```json')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
elif '```' in content:
content = content.split('```')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
preferences = json.loads(content)
# Update user preferences
user.preferences = preferences
session.commit()
logger.info(f"✓ Extracted preferences for user {user_id}")
return preferences
except json.JSONDecodeError:
logger.warning("Failed to parse preferences JSON")
return {}
finally:
session.close()
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to extract preferences: {e}")
return {}
def extract_entities_with_llm(self, conversation_id: str) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Extract named entities using LLM.
Args:
conversation_id: ID of conversation to analyze
Returns:
list: List of extracted entities
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation_id).first()
if not conversation:
return []
messages = session.query(Message).filter_by(conversation_id=conversation.id).all()
conv_text = "\n".join([msg.content for msg in messages])
# Extract entities using LLM
entity_prompt = f"""Extract named entities from the following conversation. Identify:
- People (PERSON)
- Organizations (ORG)
- Locations (LOC)
- Dates (DATE)
- Products (PRODUCT)
- Technologies (TECH)
Conversation:
{conv_text}
Return a JSON array of entities with format:
[
{{"type": "PERSON", "value": "John Doe", "context": "mentioned as team lead"}},
{{"type": "ORG", "value": "Acme Corp", "context": "customer company"}}
]"""
response = self.llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=entity_prompt)])
try:
content = response.content
if '```json' in content:
content = content.split('```json')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
elif '```' in content:
content = content.split('```')[1].split('```')[0].strip()
entities_data = json.loads(content)
# Save entities to database
saved_entities = []
for entity_data in entities_data:
entity = Entity(
conversation_id=conversation.id,
entity_type=entity_data['type'],
entity_value=entity_data['value'],
context=entity_data.get('context', ''),
confidence=0.9 # LLM extraction has high confidence
)
session.add(entity)
saved_entities.append(entity_data)
session.commit()
session.close()
logger.info(f"✓ Extracted {len(saved_entities)} entities from conversation {conversation_id}")
return saved_entities
except json.JSONDecodeError:
logger.warning("Failed to parse entities JSON")
return []
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to extract entities: {e}")
return []The DataCollector uses the LLM to analyze conversations. The extract_conversation_summary method creates concise summaries of conversations. The extract_user_preferences method analyzes message patterns to identify user interests and communication styles. The extract_entities_with_llm method uses structured prompts to extract named entities like people, organizations, and technologies. All extracted data is saved to the database for future reference.
Step 4: Building the Smart Data Processing Pipeline
Implement background processing to handle data collection without blocking the agent. The pipeline uses worker threads and queues to process summaries and entities.
class DataProcessingPipeline:
"""
Asynchronous data processing pipeline.
This pipeline:
- Processes conversations in the background
- Generates summaries
- Extracts entities without blocking main flow
- Updates user preferences periodically
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager, collector: DataCollector, batch_size: int = 10):
"""
Initialize processing pipeline.
Args:
db_manager: Database manager instance
collector: Data collector for processing operations
batch_size: Number of items to process in each batch
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.collector = collector
self.batch_size = batch_size
# Processing queues
self.summary_queue = Queue()
self.entity_queue = Queue()
self.preference_queue = Queue()
# Worker threads
self.workers = []
self.running = False
logger.info("✓ Data processing pipeline initialized")
def start(self):
"""Start background processing workers."""
self.running = True
# Create worker threads
summary_worker = Thread(target=self._process_summaries, daemon=True)
entity_worker = Thread(target=self._process_entities, daemon=True)
preference_worker = Thread(target=self._process_preferences, daemon=True)
summary_worker.start()
entity_worker.start()
preference_worker.start()
self.workers = [summary_worker, entity_worker, preference_worker]
logger.info("✓ Started 3 background processing workers")
def stop(self):
"""Stop background processing workers."""
self.running = False
for worker in self.workers:
worker.join(timeout=5)
logger.info("✓ Stopped background processing workers")
def queue_conversation_for_processing(self, conversation_id: str, user_id: str):
"""
Add conversation to processing queues.
Args:
conversation_id: ID of conversation to process
user_id: ID of user for preference extraction
"""
self.summary_queue.put(conversation_id)
self.entity_queue.put(conversation_id)
self.preference_queue.put(user_id)
logger.info(f"✓ Queued conversation {conversation_id} for processing")
def _process_summaries(self):
"""Worker for processing conversation summaries."""
while self.running:
try:
if not self.summary_queue.empty():
conversation_id = self.summary_queue.get()
self.collector.extract_conversation_summary(conversation_id)
self.summary_queue.task_done()
else:
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error in summary worker: {e}")
def _process_entities(self):
"""Worker for processing entity extraction."""
while self.running:
try:
if not self.entity_queue.empty():
conversation_id = self.entity_queue.get()
self.collector.extract_entities_with_llm(conversation_id)
self.entity_queue.task_done()
else:
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error in entity worker: {e}")
def _process_preferences(self):
"""Worker for processing user preferences."""
while self.running:
try:
if not self.preference_queue.empty():
user_id = self.preference_queue.get()
self.collector.extract_user_preferences(user_id)
self.preference_queue.task_done()
else:
time.sleep(1)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Error in preference worker: {e}")
def get_queue_status(self) -> Dict[str, int]:
"""
Get current queue sizes.
Returns:
dict: Queue sizes for each processing type
"""
return {
'summary_queue': self.summary_queue.qsize(),
'entity_queue': self.entity_queue.qsize(),
'preference_queue': self.preference_queue.qsize()
}The ProcessingPipeline decouples data collection from message processing. When a conversation completes, it’s added to queues rather than processed right away. Separate worker threads pull from these queues and process items in the background. This prevents data collection from blocking agent responses. The daemon=True setting ensures workers terminate when the main program exits. Queue status monitoring helps track processing backlogs.
Step 5: Adding Real-time Monitoring and Logging
Create a monitoring system to track agent performance, detect errors, and generate reports. The monitor analyzes logs to provide operational insights.
class AgentMonitor:
"""
Real-time monitoring and metrics collection.
This module:
- Tracks performance metrics
- Monitors system health
- Generates analytics reports
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager):
"""
Initialize agent monitor.
Args:
db_manager: Database manager instance
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
logger.info("✓ Agent monitor initialized")
def get_performance_metrics(self, hours: int = 24) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Get performance metrics for the specified time period.
Args:
hours: Number of hours to look back
Returns:
dict: Performance metrics including operation counts and error rates
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
cutoff_time = datetime.utcnow() - timedelta(hours=hours)
# Query logs
logs = session.query(AgentLog).filter(
AgentLog.created_at >= cutoff_time
).all()
# Calculate metrics
total_operations = len(logs)
error_count = len([log for log in logs if log.level == "ERROR"])
avg_execution_time = sum([log.execution_time or 0 for log in logs]) / max(total_operations, 1)
# Get conversation counts
conversations = session.query(Conversation).filter(
Conversation.created_at >= cutoff_time
).count()
messages = session.query(Message).join(Conversation).filter(
Message.created_at >= cutoff_time
).count()
session.close()
metrics = {
'time_period_hours': hours,
'total_operations': total_operations,
'error_count': error_count,
'error_rate': error_count / max(total_operations, 1),
'avg_execution_time': avg_execution_time,
'conversations_created': conversations,
'messages_processed': messages
}
logger.info(f"✓ Generated performance metrics for last {hours} hours")
return metrics
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to get performance metrics: {e}")
return {}
def health_check(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Perform health check.
Returns:
dict: Health status including database connectivity and error rates
"""
try:
# Check database connectivity
db_healthy = self.db_manager.health_check()
# Check recent error rate
metrics = self.get_performance_metrics(hours=1)
recent_errors = metrics.get('error_count', 0)
# Determine overall health
is_healthy = db_healthy and recent_errors < 10
health_status = {
'status': 'healthy' if is_healthy else 'degraded',
'database_connected': db_healthy,
'recent_errors': recent_errors,
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
}
logger.info(f"✓ Health check: {health_status['status']}")
return health_status
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Health check failed: {e}")
return {
'status': 'unhealthy',
'error': str(e),
'timestamp': datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
}The AgentMonitor provides observability into system operations. It tracks metrics like total operations, error rates, and average execution times by querying the AgentLog table. The get_metrics method calculates statistics over configurable time windows. The get_error_report method retrieves detailed error information for debugging. This monitoring enables proactive issue detection. High error rates trigger investigation before users are impacted.
Step 6: Building the Query Interface
Create query capabilities to retrieve and analyze stored data. The interface provides methods for searching conversations, tracking entities, and generating analytics.
class DataQueryInterface:
"""
Interface for querying stored agent data.
This module provides methods to:
- Query user analytics
- Retrieve conversation history
- Search for specific information
"""
def __init__(self, db_manager: DatabaseManager):
"""
Initialize query interface.
Args:
db_manager: Database manager instance
"""
self.db_manager = db_manager
logger.info("✓ Query interface initialized")
def get_user_analytics(self, user_id: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Get analytics for a specific user.
Args:
user_id: ID of user to analyze
Returns:
dict: User analytics including conversation counts and preferences
"""
try:
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
user = session.query(User).filter_by(user_id=user_id).first()
if not user:
return {}
# Get conversation count
conversation_count = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(user_id=user.id).count()
# Get message count
message_count = session.query(Message).join(Conversation).filter(
Conversation.user_id == user.id
).count()
# Get entity count
entity_count = session.query(Entity).join(Conversation).filter(
Conversation.user_id == user.id
).count()
# Get time range
first_conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(
user_id=user.id
).order_by(Conversation.created_at).first()
last_conversation = session.query(Conversation).filter_by(
user_id=user.id
).order_by(Conversation.created_at.desc()).first()
session.close()
analytics = {
'user_id': user_id,
'name': user.name,
'conversation_count': conversation_count,
'message_count': message_count,
'entity_count': entity_count,
'preferences': user.preferences,
'first_interaction': first_conversation.created_at.isoformat() if first_conversation else None,
'last_interaction': last_conversation.created_at.isoformat() if last_conversation else None,
'avg_messages_per_conversation': message_count / max(conversation_count, 1)
}
logger.info(f"✓ Generated analytics for user {user_id}")
return analytics
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to get user analytics: {e}")
return {}The QueryInterface provides methods to access stored data. The get_user_conversations method retrieves full conversation history with optional message inclusion. The search_conversations method performs full-text search across message content using SQL’s ILIKE operator. The get_entity_mentions method finds all conversations where specific entities were mentioned. The get_user_analytics method generates statistics about user activity. These queries enable building dashboards, generating reports, and creating personalized experiences.
Step 7: Building a RAG with Real-Time Web Data from Bright Data
Enhance your database-connected agent with RAG capabilities from Bright Data’s real-time web intelligence. This integration combines your conversation history with fresh web data for better responses.
class BrightDataRAGEnhancer:
"""
Enhance data-persistent agent with Bright Data web intelligence.
This module:
- Fetches real-time web data from Bright Data
- Ingests web data into vector store for RAG
- Enhances agent with web-augmented knowledge
"""
def __init__(self, api_key: str, db_manager: DatabaseManager):
"""
Initialize RAG enhancer with Bright Data.
Args:
api_key: Bright Data API key
db_manager: Database manager instance
"""
self.api_key = api_key
self.db_manager = db_manager
self.base_url = "https://api.brightdata.com"
# Initialize vector store for RAG
self.embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
self.vector_store = Chroma(
embedding_function=self.embeddings,
persist_directory="./chroma_db"
)
self.text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=200
)
logger.info("✓ Bright Data RAG enhancer initialized")
def fetch_dataset_data(
self,
dataset_id: str,
filters: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
limit: int = 1000
) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Fetch data from Bright Data Dataset Marketplace.
Args:
dataset_id: ID of dataset to fetch
filters: Optional filters for data
limit: Maximum number of records to fetch
Returns:
list: Retrieved dataset records
"""
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {self.api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
endpoint = f"{self.base_url}/datasets/v3/snapshot/{dataset_id}"
params = {
"format": "json",
"limit": limit
}
if filters:
params["filter"] = json.dumps(filters)
try:
response = requests.get(endpoint, headers=headers, params=params)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
logger.info(f"✓ Retrieved {len(data)} records from Bright Data dataset {dataset_id}")
return data
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to fetch Bright Data dataset: {e}")
return []
def ingest_web_data_to_rag(
self,
dataset_records: List[Dict[str, Any]],
text_fields: List[str],
metadata_fields: Optional[List[str]] = None
) -> int:
"""
Ingest web data into RAG vector store.
Args:
dataset_records: Records from Bright Data
text_fields: Fields to use as text content
metadata_fields: Fields to include in metadata
Returns:
int: Number of document chunks ingested
"""
try:
documents = []
for record in dataset_records:
# Combine text fields
text_content = " ".join([
str(record.get(field, ""))
for field in text_fields
if record.get(field)
])
if not text_content.strip():
continue
# Build metadata
metadata = {
"source": "bright_data",
"record_id": record.get("id", "unknown"),
"timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
}
if metadata_fields:
for field in metadata_fields:
if field in record:
metadata[field] = record[field]
# Split text into chunks
chunks = self.text_splitter.split_text(text_content)
for chunk in chunks:
documents.append({
"content": chunk,
"metadata": metadata
})
# Add to vector store
if documents:
texts = [doc["content"] for doc in documents]
metadatas = [doc["metadata"] for doc in documents]
self.vector_store.add_texts(
texts=texts,
metadatas=metadatas
)
logger.info(f"✓ Ingested {len(documents)} document chunks into RAG")
return len(documents)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to ingest web data to RAG: {e}")
return 0
def create_rag_enhanced_agent(
self,
base_agent: DataPersistentAgent
) -> DataPersistentAgent:
"""
Enhance existing agent with RAG capabilities.
Args:
base_agent: Base agent to enhance
Returns:
DataPersistentAgent: Enhanced agent with RAG tool
"""
def rag_search(query: str) -> str:
"""Search both conversation history and web data."""
try:
# Retrieve from conversation history
session = self.db_manager.get_session()
messages = session.query(Message).filter(
Message.content.ilike(f'%{query}%')
).order_by(Message.created_at.desc()).limit(5).all()
results = []
for msg in messages:
results.append({
'content': msg.content,
'source': 'conversation_history',
'relevance': 0.8
})
session.close()
# Retrieve from vector store (web data)
try:
vector_results = self.vector_store.similarity_search_with_score(query, k=5)
for doc, score in vector_results:
results.append({
'content': doc.page_content,
'source': 'web_data',
'relevance': 1 - score
})
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to retrieve from vector store: {e}")
if not results:
return "No relevant information found."
# Format context
context_text = "\n\n".join([
f"[{item['source']}] {item['content'][:200]}..."
for item in results[:5]
])
return f"Retrieved context:\n{context_text}"
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"RAG search failed: {e}")
return f"Error performing search: {str(e)}"
# Add RAG tool to agent
rag_tool = Tool(
name="SearchKnowledgeBase",
func=rag_search,
description="Search both conversation history and real-time web data for relevant information. Input should be a search query."
)
base_agent.tools.append(rag_tool)
# Recreate agent with new tools
base_agent.agent = create_openai_functions_agent(
llm=base_agent.llm,
tools=base_agent.tools,
prompt=base_agent.prompt
)
base_agent.agent_executor = AgentExecutor(
agent=base_agent.agent,
tools=base_agent.tools,
memory=base_agent.memory,
verbose=True,
handle_parsing_errors=True,
max_iterations=5
)
logger.info("✓ Enhanced agent with RAG capabilities")
return base_agentThe BrightDataEnhancer integrates real-time web data into your agent. The fetch_dataset method retrieves structured data from Bright Data’s marketplace. The ingest_to_rag method processes and chunks this data. It stores it in a Chroma vector database for semantic search. The retrieve_context method performs hybrid retrieval. It combines database history with vector similarity search. The create_rag_tool method packages this functionality as a LangChain tool the agent uses. The enhance_agent method adds this RAG capability to your existing agent. It enables the agent to answer questions using both internal conversation history and fresh external data.
Running Your Complete Data-Persistent Agent System
Bring all components together to create a functional system.
def main():
"""Main execution flow demonstrating all components working together."""
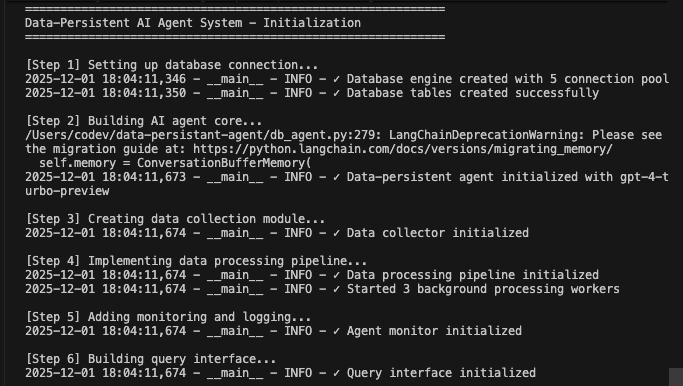
print("=" * 60)
print("Data-Persistent AI Agent System - Initialization")
print("=" * 60)
# Step 1: Initialize database
print("\n[Step 1] Setting up database connection...")
db_manager = DatabaseManager(
database_url=os.getenv("DATABASE_URL"),
pool_size=5,
max_retries=3
)
db_manager.initialize_database()
# Step 2: Initialize core agent
print("\n[Step 2] Building AI agent core...")
agent = DataPersistentAgent(
db_manager=db_manager,
model_name=os.getenv("AGENT_MODEL", "gpt-4-turbo-preview")
)
# Step 3: Initialize data collector
print("\n[Step 3] Creating data collection module...")
collector = DataCollector(db_manager, agent.llm)
# Step 4: Initialize processing pipeline
print("\n[Step 4] Implementing data processing pipeline...")
pipeline = DataProcessingPipeline(db_manager, collector)
pipeline.start()
# Step 5: Initialize monitoring
print("\n[Step 5] Adding monitoring and logging...")
monitor = AgentMonitor(db_manager)
# Step 6: Initialize query interface
print("\n[Step 6] Building query interface...")
query_interface = DataQueryInterface(db_manager)
# Step 7: Optional Bright Data RAG Enhancement
print("\n[Step 7] RAG Enhancement (Optional)...")
bright_data_key = os.getenv("BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY")
if bright_data_key and bright_data_key != "your-bright-data-api-key":
print("Fetching real-time web data from Bright Data...")
enhancer = BrightDataRAGEnhancer(bright_data_key, db_manager)
# Example: Fetch and ingest web data
web_data = enhancer.fetch_dataset_data(
dataset_id="example_dataset_id",
limit=100
)
if web_data:
enhancer.ingest_web_data_to_rag(
dataset_records=web_data,
text_fields=["title", "content", "description"],
metadata_fields=["url", "published_date"]
)
# Enhance agent with RAG
agent = enhancer.create_rag_enhanced_agent(agent)
print("✓ Agent enhanced with Bright Data RAG capabilities")
else:
print("⚠️ Bright Data API key not found - skipping web data integration")
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("Demo Conversations")
print("=" * 60)
# Demo user interactions
test_user = "demo_user_001"
# First conversation
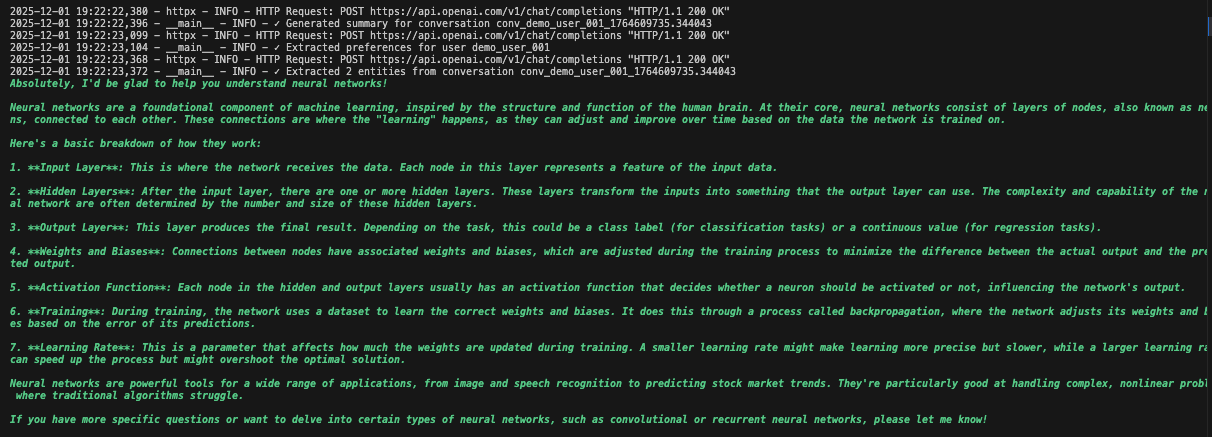
print("\n📝 Conversation 1:")
response1 = agent.chat(
user_id=test_user,
message="Hi! I'm interested in learning about machine learning."
)
print(f"Agent: {response1['response']}\n")
# Queue for processing
pipeline.queue_conversation_for_processing(
response1['conversation_id'],
test_user
)
# Second conversation
print("📝 Conversation 2:")
response2 = agent.chat(
user_id=test_user,
message="Help me understand neural networks?",
conversation_id=response1['conversation_id']
)
print(f"Agent: {response2['response']}\n")
# Wait for background processing
print("⏳ Processing data in background...")
time.sleep(5)
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("Analytics & Monitoring")
print("=" * 60)
# Get performance metrics
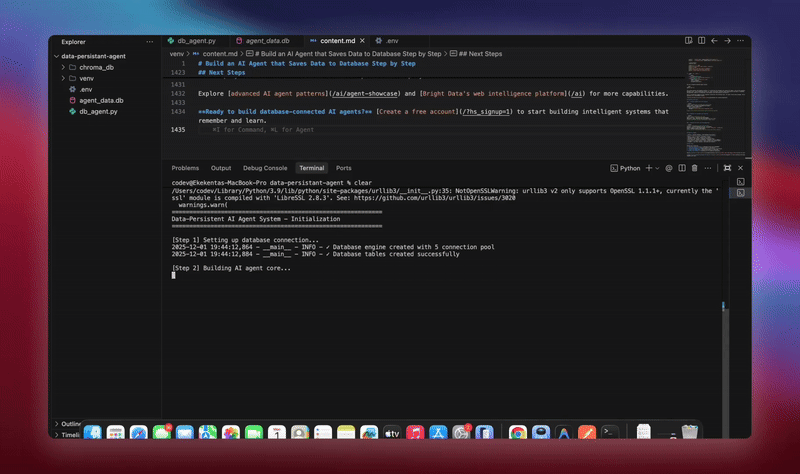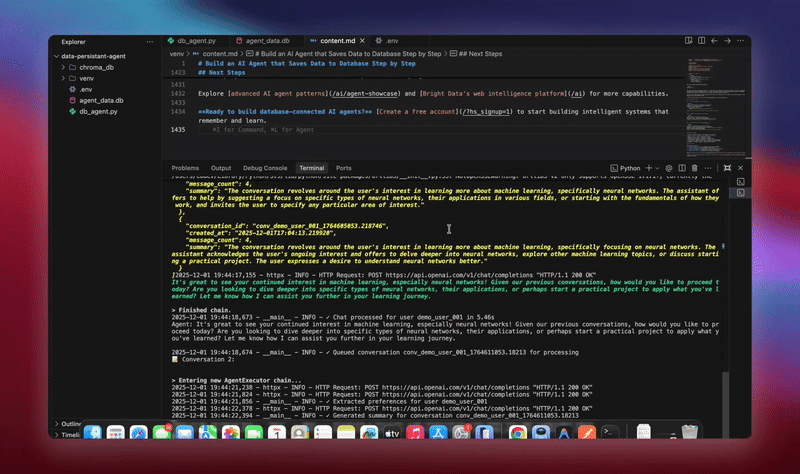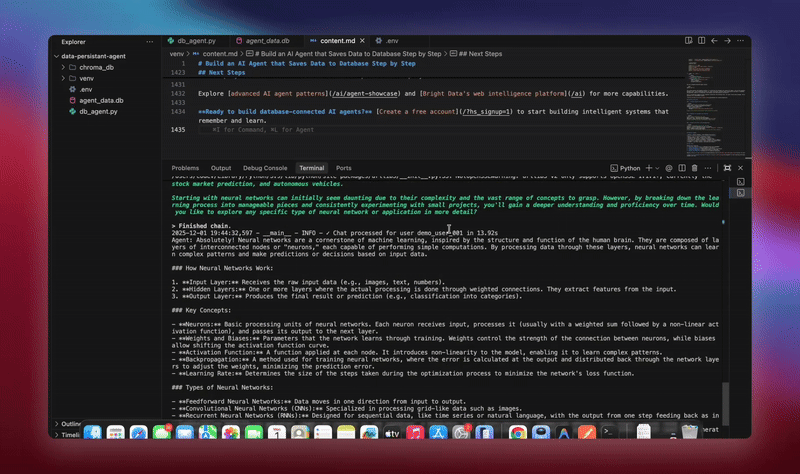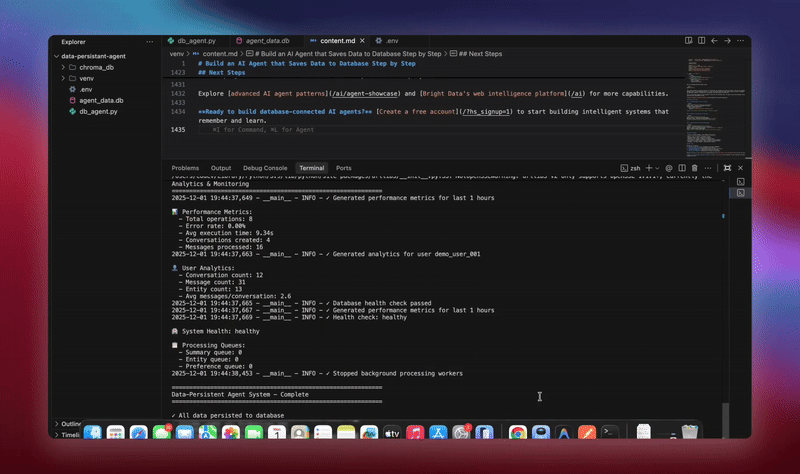
metrics = monitor.get_performance_metrics(hours=1)
print(f"\n📊 Performance Metrics:")
print(f" - Total operations: {metrics.get('total_operations', 0)}")
print(f" - Error rate: {metrics.get('error_rate', 0):.2%}")
print(f" - Avg execution time: {metrics.get('avg_execution_time', 0):.2f}s")
print(f" - Conversations created: {metrics.get('conversations_created', 0)}")
print(f" - Messages processed: {metrics.get('messages_processed', 0)}")
# Get user analytics
analytics = query_interface.get_user_analytics(test_user)
print(f"\n👤 User Analytics:")
print(f" - Conversation count: {analytics.get('conversation_count', 0)}")
print(f" - Message count: {analytics.get('message_count', 0)}")
print(f" - Entity count: {analytics.get('entity_count', 0)}")
print(f" - Avg messages/conversation: {analytics.get('avg_messages_per_conversation', 0):.1f}")
# Health check
health = monitor.health_check()
print(f"\n🏥 System Health: {health['status']}")
# Queue status
queue_status = pipeline.get_queue_status()
print(f"\n📋 Processing Queues:")
print(f" - Summary queue: {queue_status['summary_queue']}")
print(f" - Entity queue: {queue_status['entity_queue']}")
print(f" - Preference queue: {queue_status['preference_queue']}")
# Stop pipeline
pipeline.stop()
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("Data-Persistent Agent System - Complete")
print("=" * 60)
print("\n✓ All data persisted to database")
print("✓ Background processing completed")
print("✓ System ready for production use")
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
main()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n\n⚠️ Shutting down gracefully...")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"System error: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()Run your database-connected agent system:
python agent.pyThe system executes the complete workflow. It initializes the database and creates all tables. It sets up the LangChain agent with database tools. It starts background workers for processing. It processes demo conversations and saves to database. It extracts entities and generates summaries in background. It displays real-time analytics and metrics.
You’ll see detailed logging as each component initializes and processes data. The agent stores every message. It extracts insights. It maintains full conversation context.
Practical Use Cases
1. Customer Support with Full History
# Agent retrieves past interactions
support_agent = DataPersistentAgent(db_manager)
response = support_agent.chat(
user_id="customer_123",
message="I'm still having that connection issue"
)
# Agent sees previous conversations about connection problems2. Personal AI Assistant with Learning
# Agent learns preferences over time
query_interface = QueryInterface(db_manager)
analytics = query_interface.get_user_analytics("user_456")
# Shows interaction patterns, preferences, common topics3. Research Assistant with Knowledge Base
# Combine conversation history with web data
enhancer = BrightDataEnhancer(api_key, db_manager)
enhancer.ingest_to_rag(research_data, ["title", "abstract", "content"])
agent = enhancer.enhance_agent(agent)
# Agent references both past discussions and latest researchBenefits Summary
| Feature | Without Database | With Database Persistence |
|---|---|---|
| Memory | Lost on restart | Permanent storage |
| Personalization | None | Based on full history |
| Analytics | Not possible | Complete interaction data |
| Error Recovery | Manual intervention | Automatic retry & logging |
| Scalability | Single instance | Multi-instance with shared state |
| Insights | Lost after session | Extracted and tracked |
Wrapping Up
You now have a production-ready AI agent system that persists conversations to databases. The system stores every interaction, extracts entities and insights, maintains full conversation history, and provides monitoring with automatic error recovery.
Enhance it by adding user authentication for secure access, building dashboards to visualize analytics, implementing embeddings for semantic search, creating API endpoints for integration, or deploying with Docker for scalability. The modular design allows easy customization for your specific needs.
Explore advanced AI agent patterns and Bright Data’s web intelligence platform for more capabilities.
Create a free account to start building intelligent systems that remember and learn.