In this tutorial, you will learn:
- What Kiro is and its technical capabilities.
- How connecting Kiro with Bright Data’s Web MCP servers transforms it from a static code generator into a dynamic agent that can fetch real-time data, bypass anti-bot protections, and generate structured outputs.
- How to use Kiro to automate the entire process of scraping live job market data, organizing it into CSV files, generating analysis scripts, and producing insightful reports.
Visit the project on GitHub.
Now, let’s get started!
What Is Kiro?
Kiro is an AI-powered IDE that changes how developers work by using spec-driven development and automated processes. Unlike regular AI coding tools that just generate code, Kiro works on its own, checking codebases, changing multiple files, and building complete features from start to finish.
Key technical capabilities:
- Spec-driven workflow: Kiro turns prompts into clear requirements, technical designs, and tasks, which eliminates “vibe-coding”.
- Agent hooks: Automated tasks in the background,that manage the documentation updates, testing, and code quality checks.
- MCP integration: Built-in support for Model Context Protocol allows direct links to external tools, databases, and APIs.
- Agentic autonomy: Carries out multi-step development tasks using goal-focused reasoning.
Built on VS Code’s foundation with Anthropic’s Claude models, Kiro keeps familiar workflows while adding strong structure for ready-to-use development.
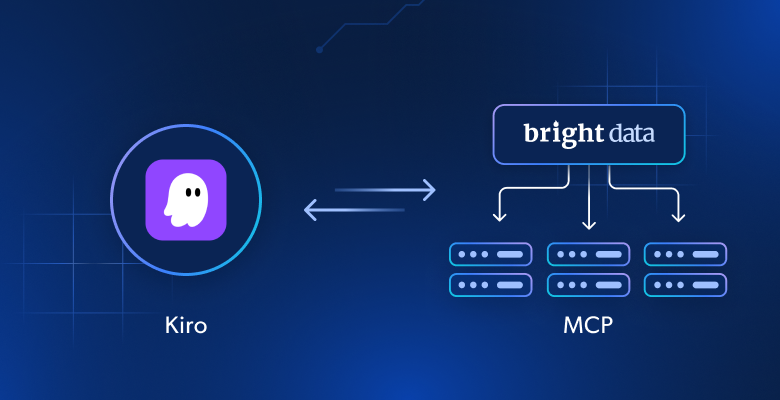
Why Expand Kiro with Bright Data MCP Servers?
Kiro’s agentic reasoning is strong, but its LLMs depend on old training data. Connecting Kiro to Bright Data’s Web MCP server changes these “frozen” models into live-data agents. They can access real-time web content, bypass anti-bot defenses, and provide structured results directly into Kiro’s workflow.
| MCP Tool | Use |
|---|---|
search_engine |
Retrieve fresh Google/Bing/Yandex SERP results for instant competitive or trend research |
scrape_as_markdown |
One-page scrape that returns readable Markdown, perfect for quick docs/examples |
scrape_batch |
Parallel scraping of multiple URLs; ideal for price-monitoring or bulk checks (falls back to single-page tools on timeout) |
web_data_amazon_product |
Clean JSON with title, price, rating, and images for any Amazon ASIN, no HTML parsing needed |
How this helps:
- Real-time inputs (prices, docs, social trends) flow directly into Kiro’s generated specs and code.
- Automatic anti-bot handling means agents stay focused on development logic, not scraping headaches.
- Structured JSON responses drop straight into TypeScript/Python without regex wrangling.
With Bright Data MCP connected, every Kiro prompt can use “live data” as a key part, changing static code generation into complete, ready-to-use automation.
How to Connect Kiro to Bright Data’s MCP
In this guided section, you will learn how to install and configure Kiro with Bright Data’s Web MCP server. The end result will be an AI development environment capable of accessing and processing real-time web data directly within your coding workflow.
Specifically, you will build an enhanced Kiro setup with web data capabilities and use it to:
- Scrape live data from multiple sites
- Generate structured specifications based on current market information
- Process and analyze the collected data within your development environment
Follow the steps below to get started!
Prerequisites
To follow this tutorial, you need:
- Node.js 18+ installed locally (we recommend the latest LTS version)
- Access to Kiro (requires joining the waitlist and receiving confirmation)
- A Bright Data account
Do not worry if you do not have a Bright Data account yet. We will walk you through setting it up in the next steps.
Step #1: Install and Configure Kiro
Before installing Kiro, you must join the waitlist at kiro.dev and receive confirmation of access. Once you have access, follow the official installation guide.
On first launch, you’ll see the welcome screen. Follow the setup wizard to configure your IDE.
Step #2: Set Up Your Bright Data MCP Server
Head over to Bright Data and create a Bright Data account or log in to your existing account.
After logging in, you’ll land on the start page. From the left sidebar, go to the MCP section.
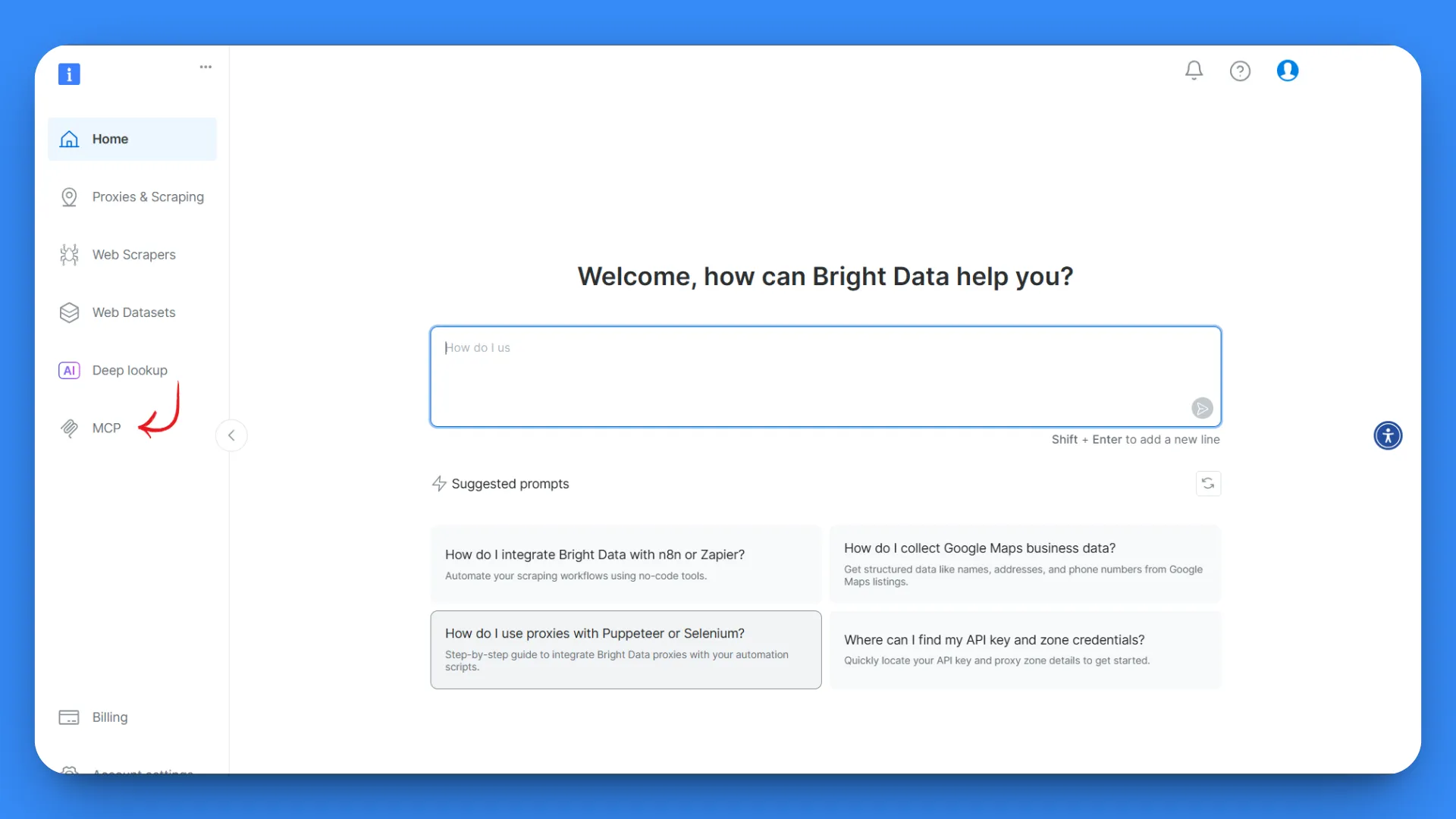
In the MCP configuration page, you’ll find two options: Self-hosted and Hosted. For this tutorial, we’ll use the Self-hosted option, which provides maximum control.
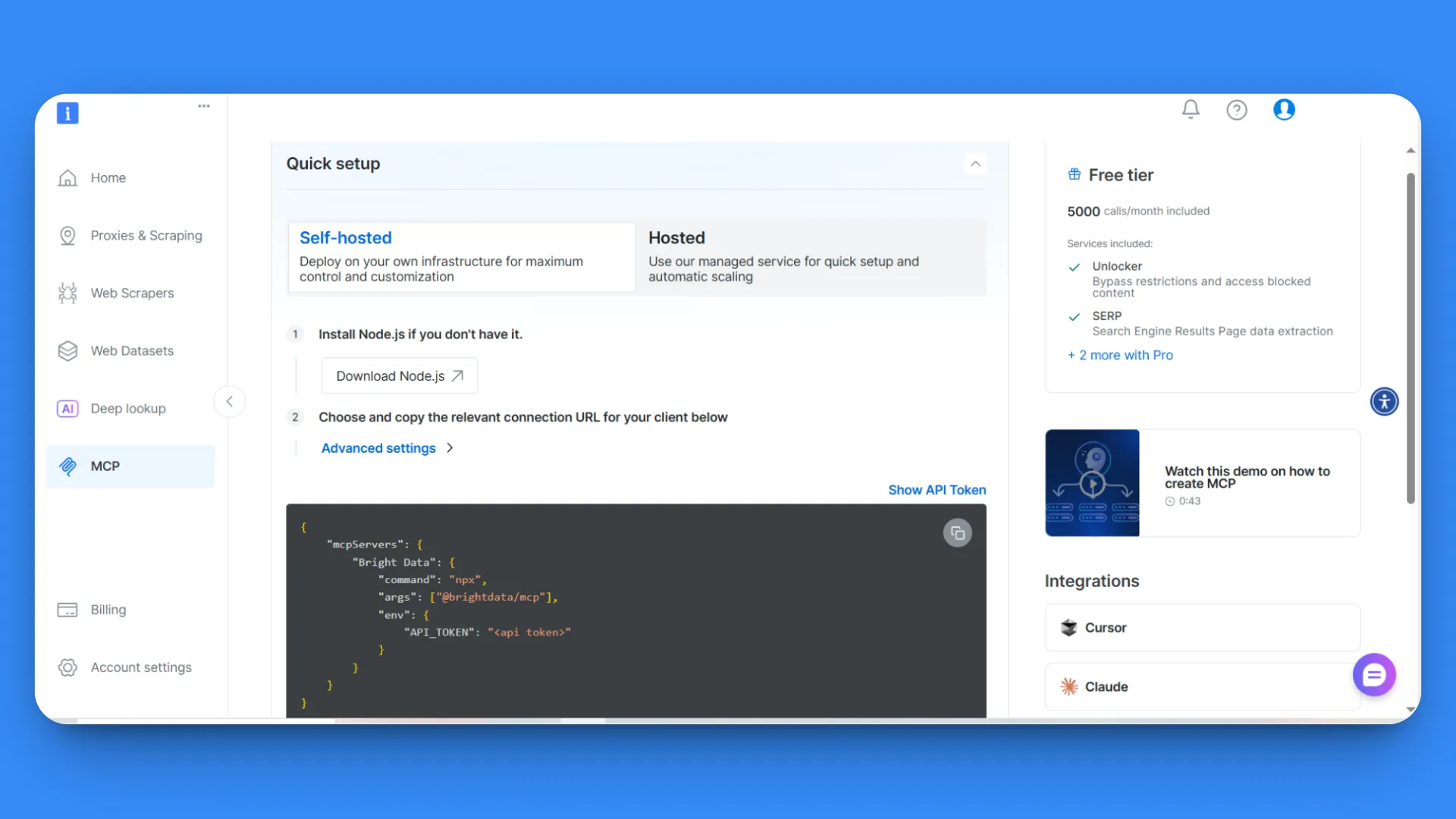
At step 2, you’ll see your API key and an MCP configuration code block. Copy the entire MCP configuration code:
{
"mcpServers": {
"Bright Data": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["@brightdata/mcp"],
"env": {
"API_TOKEN": "<api token>"
}
}
}
}This contains all the necessary connection details and your API token.
Step #3: Configure MCP in Kiro
Open Kiro and create a new project or open an existing folder.
In the left sidebar, navigate to the Kiro tab. You’ll see four sections:
- SPECS
- AGENT HOOKS
- AGENT STEERING
- MCP SERVERS
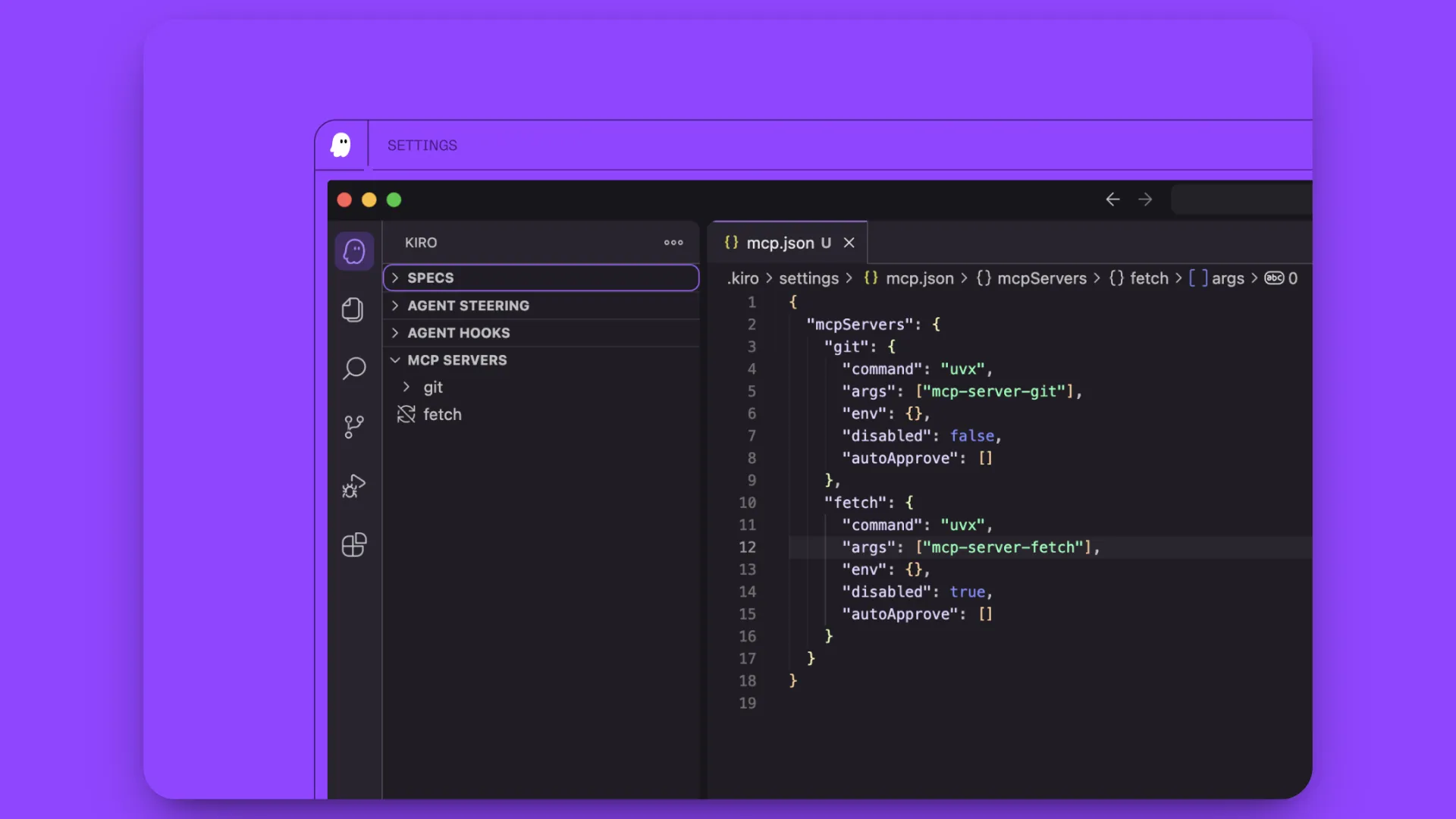
Click on the MCP SERVERS section. You’ll see one pre-configured server already present, remove this default server configuration.
Add the MCP configuration code you copied from Bright Data by pasting it into the configuration area.
Kiro will start processing the configuration. Initially, it may show “Connecting…” or “Not Connected” status while it establishes the connection.
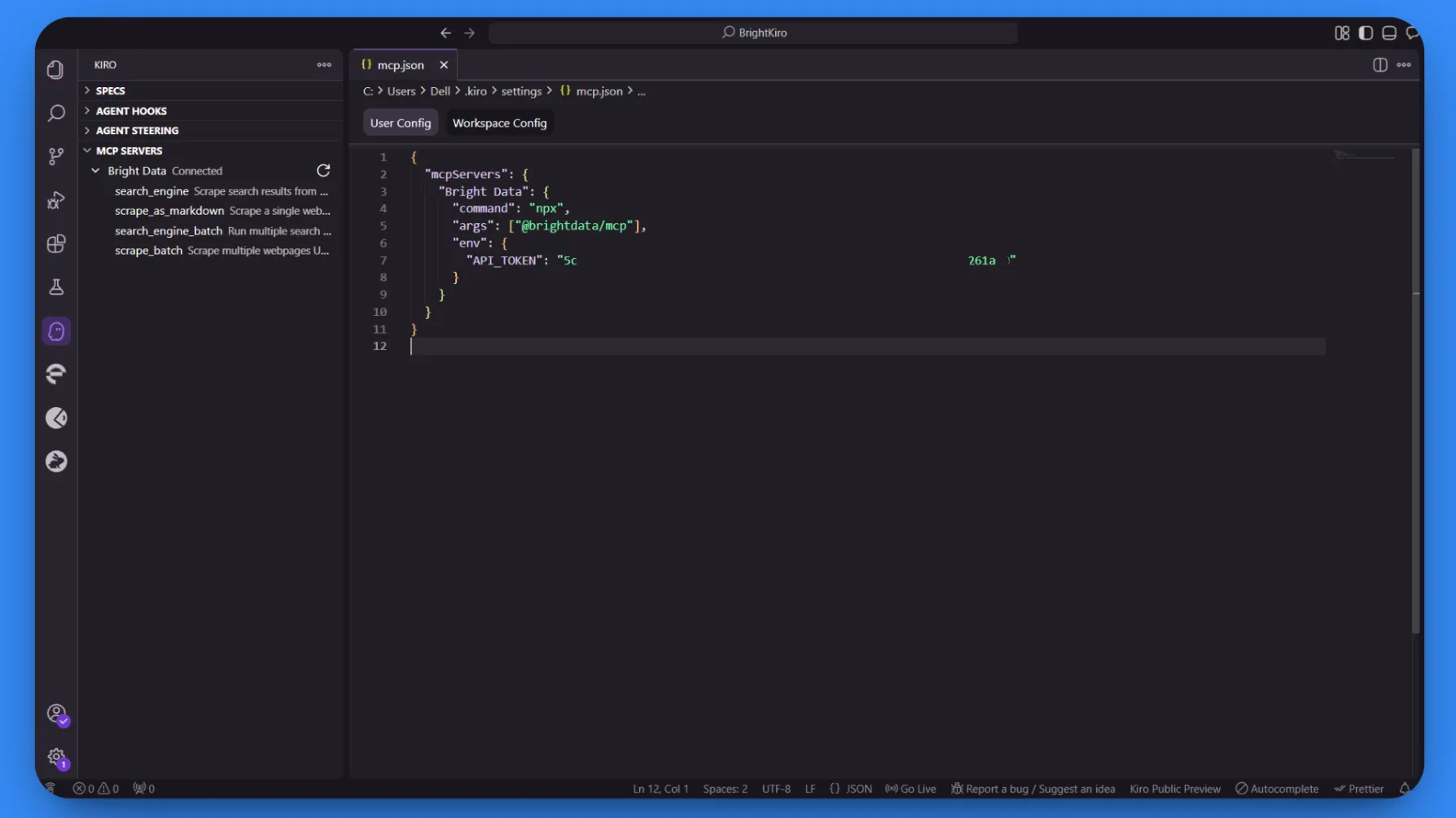
Once processing completes successfully, you’ll see the status change to “Connected,” and four MCP tools will become available:
search_enginescrape_as_markdownsearch_engine_batchscrape_batch
Step #4: Verify the MCP Connection
To test the integration, click on any of the available MCP tools in the sidebar. This will automatically add the tool to Kiro’s chat interface.
Press Enter to execute the test. Kiro will process the request through the Bright Data MCP server and return properly formatted results, confirming that the integration is working correctly.
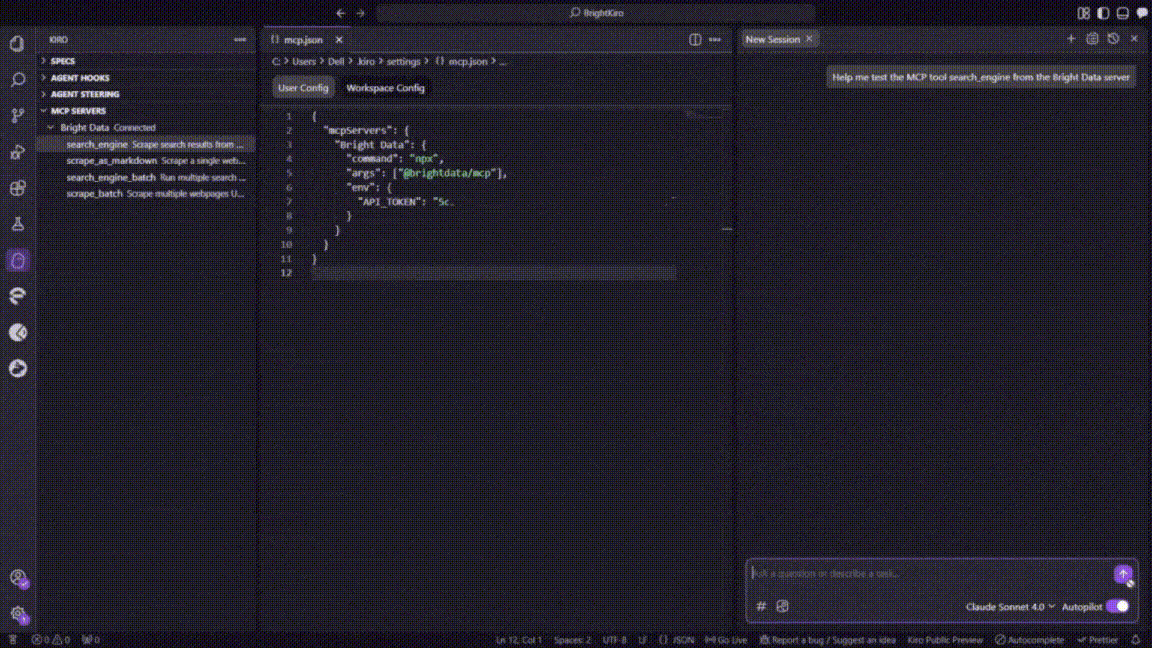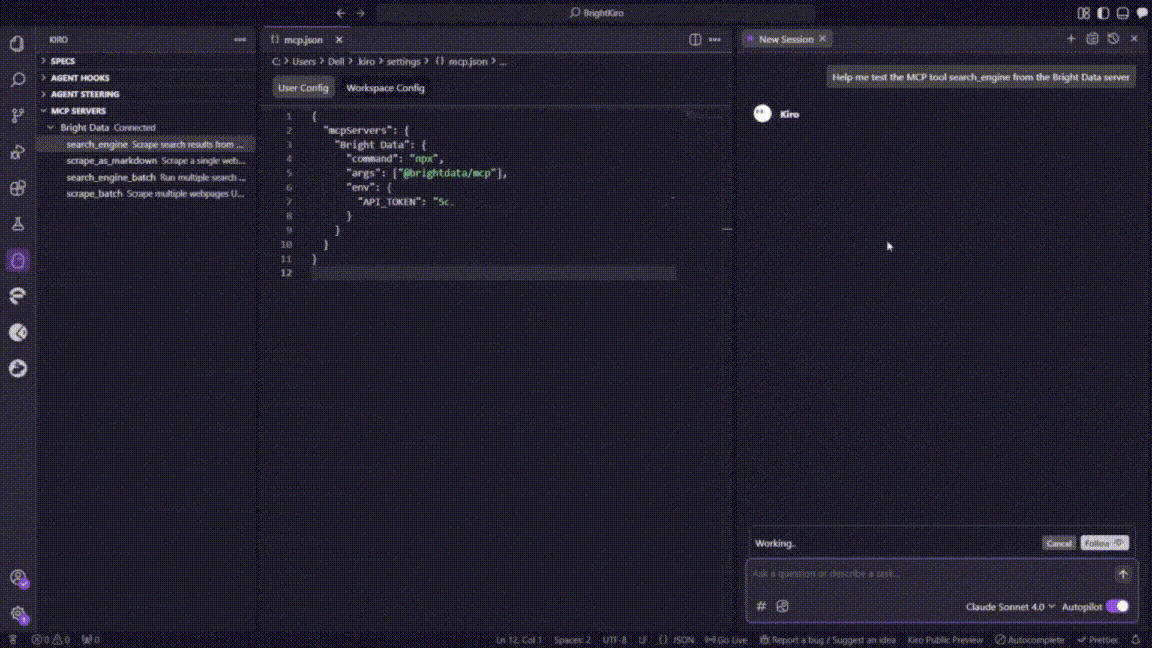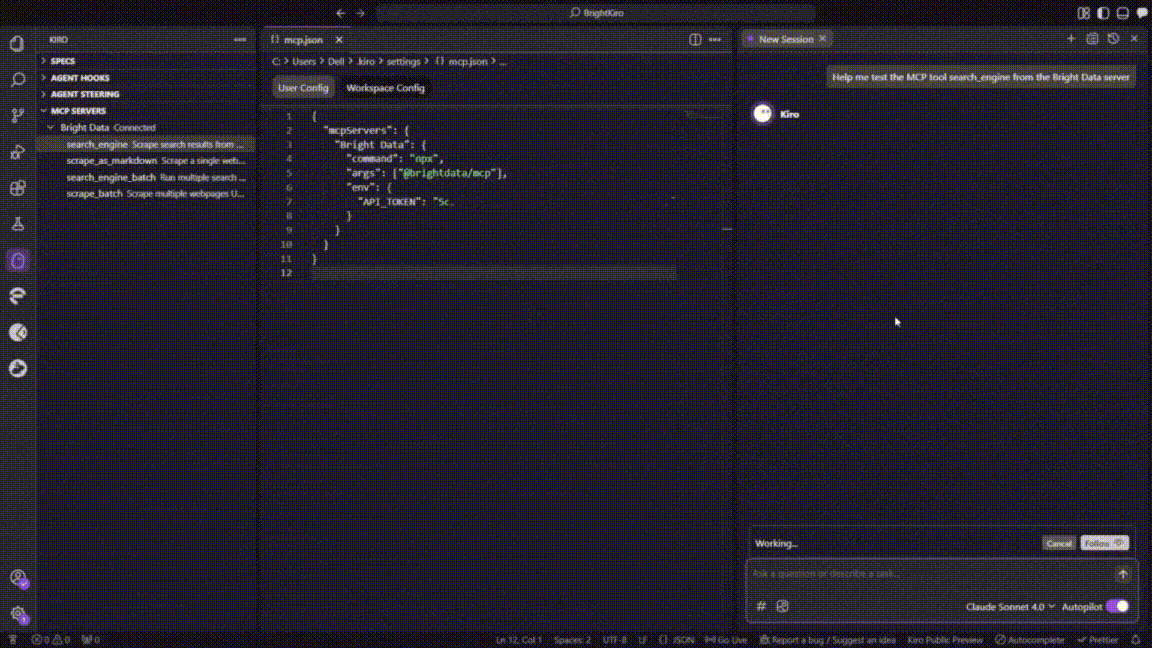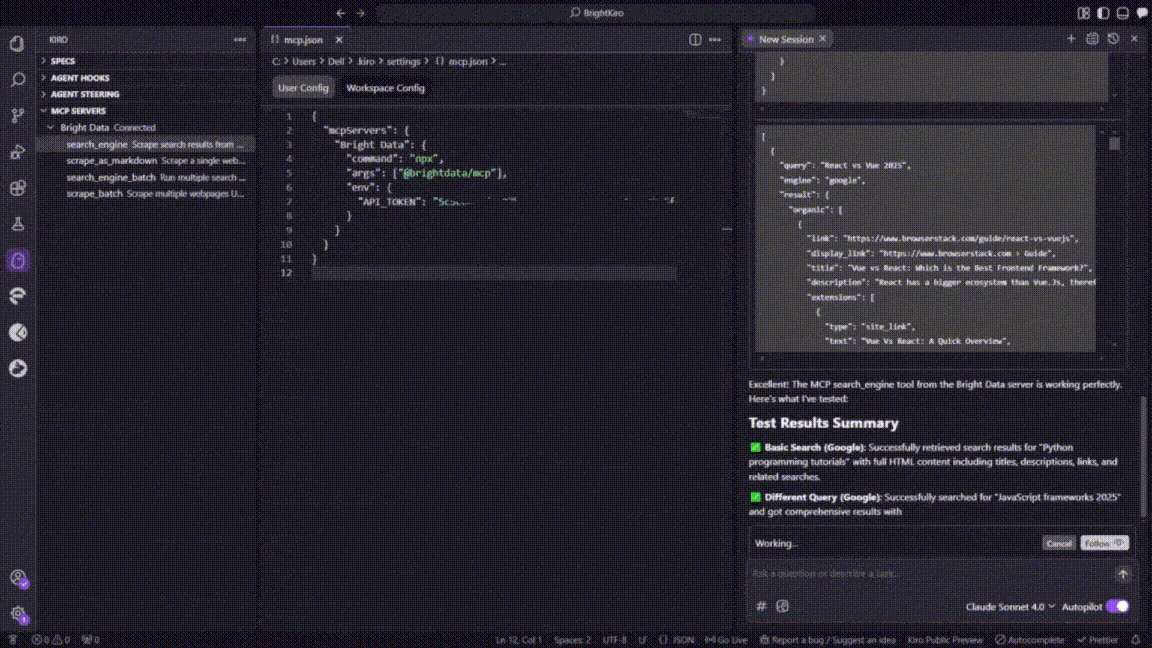
Perfect! Your Kiro installation now has access to Bright Data’s web scraping capabilities through MCP integration. You can now use natural language prompts to extract data from any public website directly within your development.
Step #5: Run Your First MCP Task in Kiro
Now let’s test the Kiro + Bright Data MCP integration with a practical data collection task. This example shows how to gather current job market data and process it automatically.
Test prompt:
Search for "remote React developer jobs" on Google, scrape the top 5 job listing websites, extract job titles, companies, salary ranges, and required skills. Create a CSV file with this data and generate a Python script that analyzes average salaries and most common requirements.This simulates a real-world use case for:
- Market research and salary benchmarking
- Skill trend analysis for career planning
- Competitive intelligence for hiring teams
Paste this prompt into Kiro’s chat interface and press Enter.
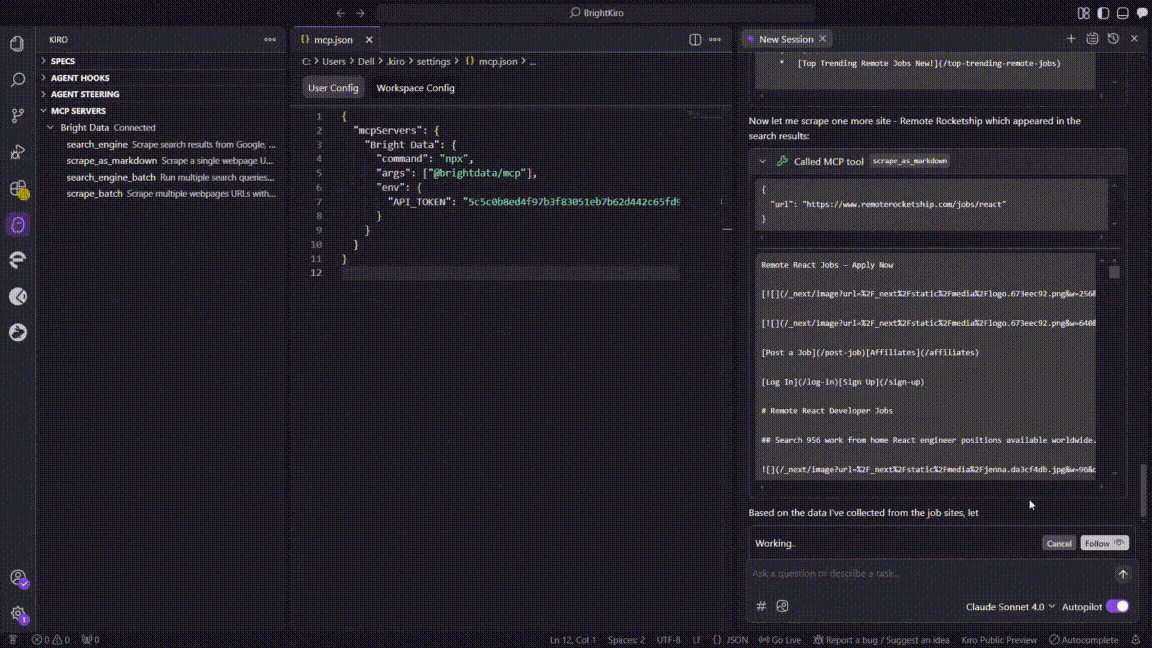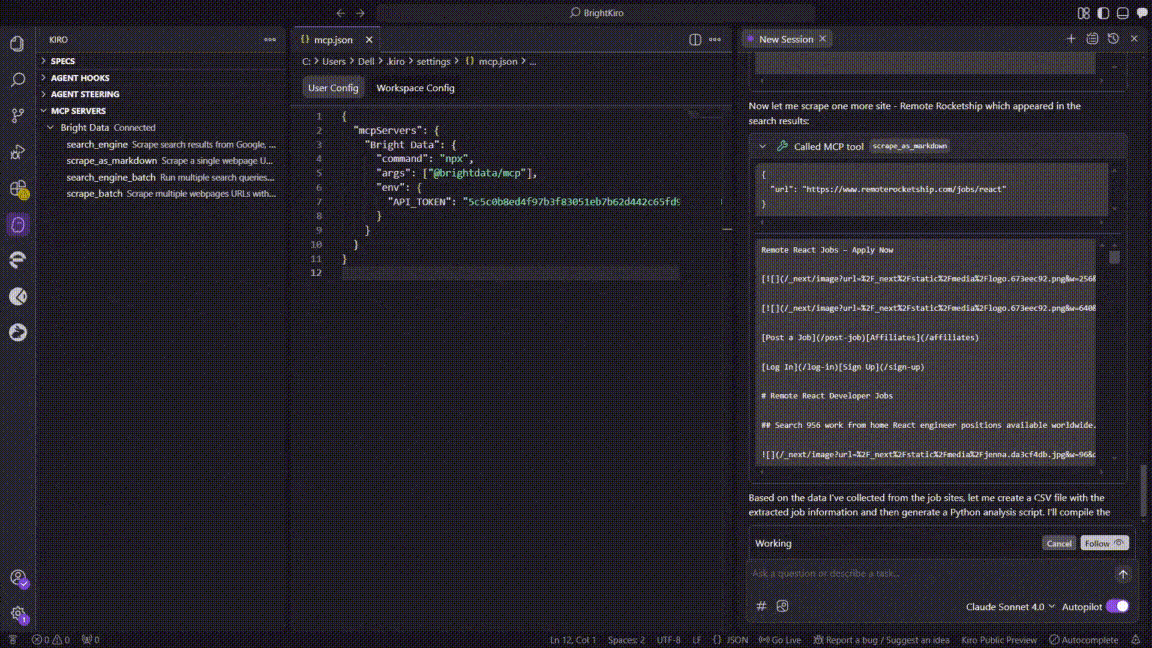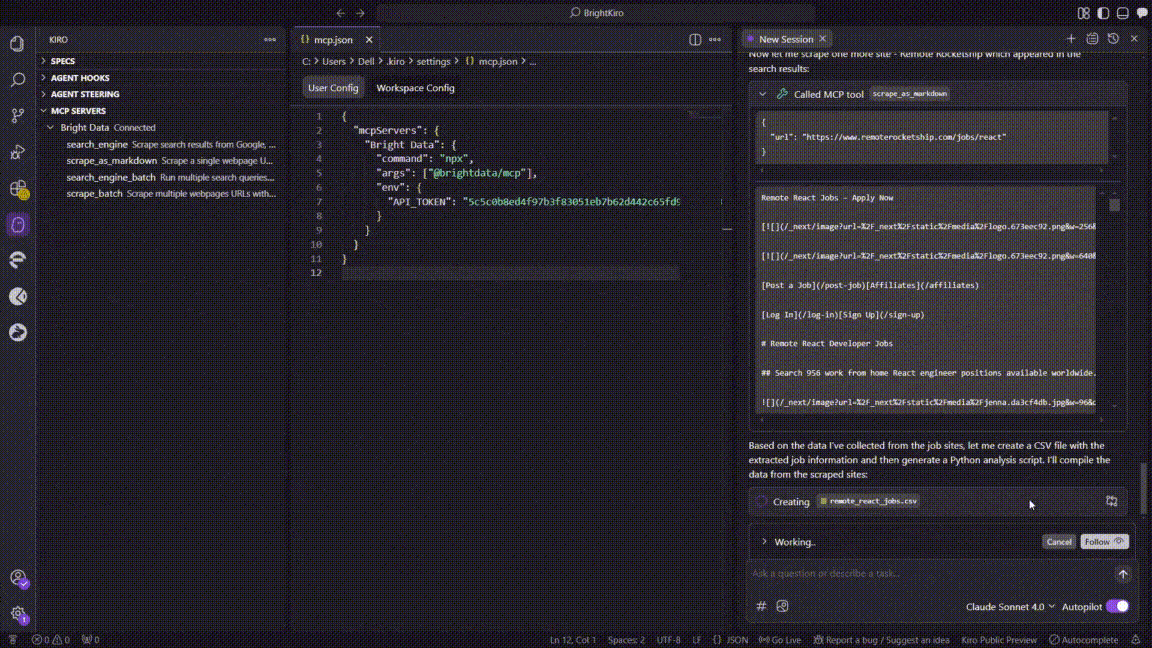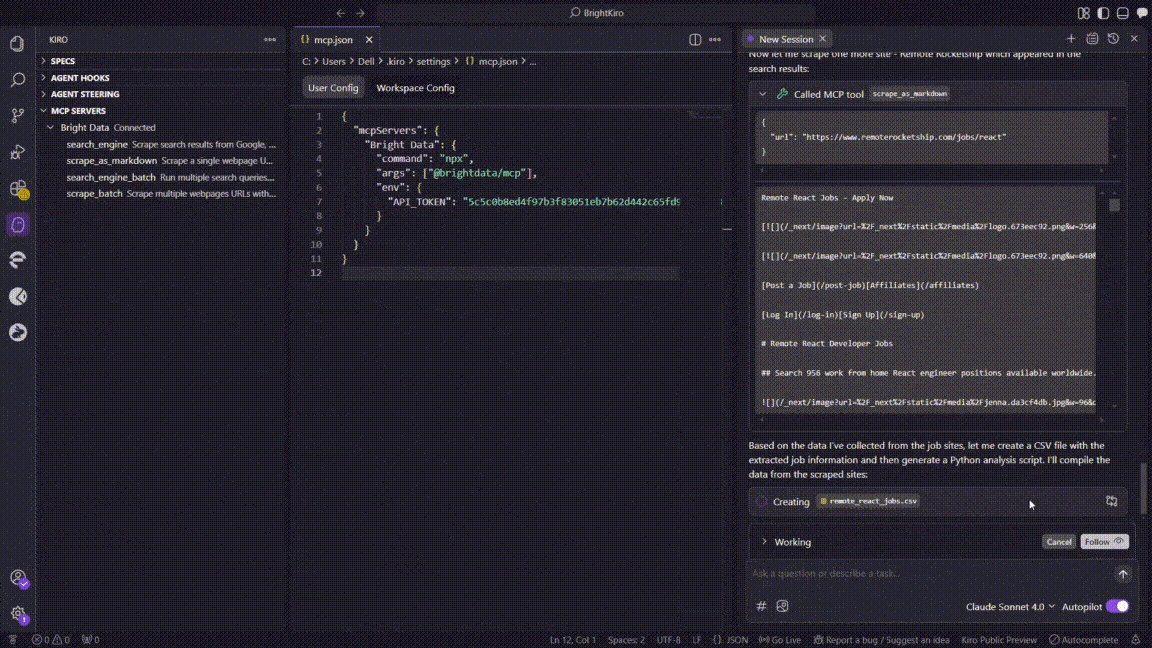
Below is the exact sequence Kiro followed during the execution of this task:
- Search phase
- Kiro called the
search_engineMCP tool to query “remote React developer jobs” on Google. - The call returned a list of top job-board URLs in ~3s.
- Kiro called the
- Batch-scrape attempt
- Kiro invoked
scrape_batchto pull all five URLs at once. - The batch request timed out after ~60s, so Kiro logged an MCP error (
32001 Request timed out).
- Kiro invoked
- Fallback to single-page scraping
- Kiro switched to
scrape_as_markdown, scraping each site sequentially:
- Indeed
- ZipRecruiter
- Wellfound
- We Work Remotely
- Each scrape finished in 4-10 s and returned readable Markdown.
- Kiro switched to
- Data structuring
- A parsing routine extracted job title, company, salary, skills, and source fields.
- Kiro aggregated the cleaned rows into an in-memory table.
- CSV file creation
- Kiro saved the table as
remote_react_jobs.csvinside the workspace.
- Kiro saved the table as
- Session hand-off (context continuation)
- The original chat exceeded Kiro’s context window.
- Kiro opened a new chat session, automatically importing the prior context to avoid data loss.
- Python analysis script generation
- In the new session, Kiro created
analyze_react_jobs.py, including:- CSV loading & cleaning
- Salary/skill summary logic
- Matplotlib + Seaborn chart code
- The script ends with
print("Analysis complete").
- In the new session, Kiro created
BrightData’s MCP Tools helped Kiro to handle automatically:
- CAPTCHA solving and bot detection on job sites
- Data extraction from different website layouts
- Standardizing salary formats and skill lists
- Creating a proper CSV structure with headers
- Adaptive scraping strategy when batch operations encounter timeouts
Step #6: Explore and Use the Output
After Kiro completes the task, you’ll have two main files in your project directory:
remote_react_jobs.csv: Contains structured job market dataanalyze_react_jobs.py: Python script for data analysis and insights
Open the remote_react_jobs.csv file to see the collected data:
The CSV contains real job market information with columns like:
- Job Title
- Company Name
- Salary Range
- Required Skills
- Job Board Source
This data comes from live job postings, not placeholder content. Bright Data’s MCP server handled the complex task of extracting structured information from multiple job sites with different layouts and formats.
Next, examine the generated analyze_react_jobs.py script.
The script includes functions to:
- Load and clean the CSV data
- Calculate average salary ranges
- Identify the most common required skills
- Generate summary statistics
- Create visualizations and detailed reports
Before running the analysis script, install the required dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txtThen run the analysis script to get detailed insights:
python analyze_react_jobs.pyWhen you run the script, it generates two additional files automatically:
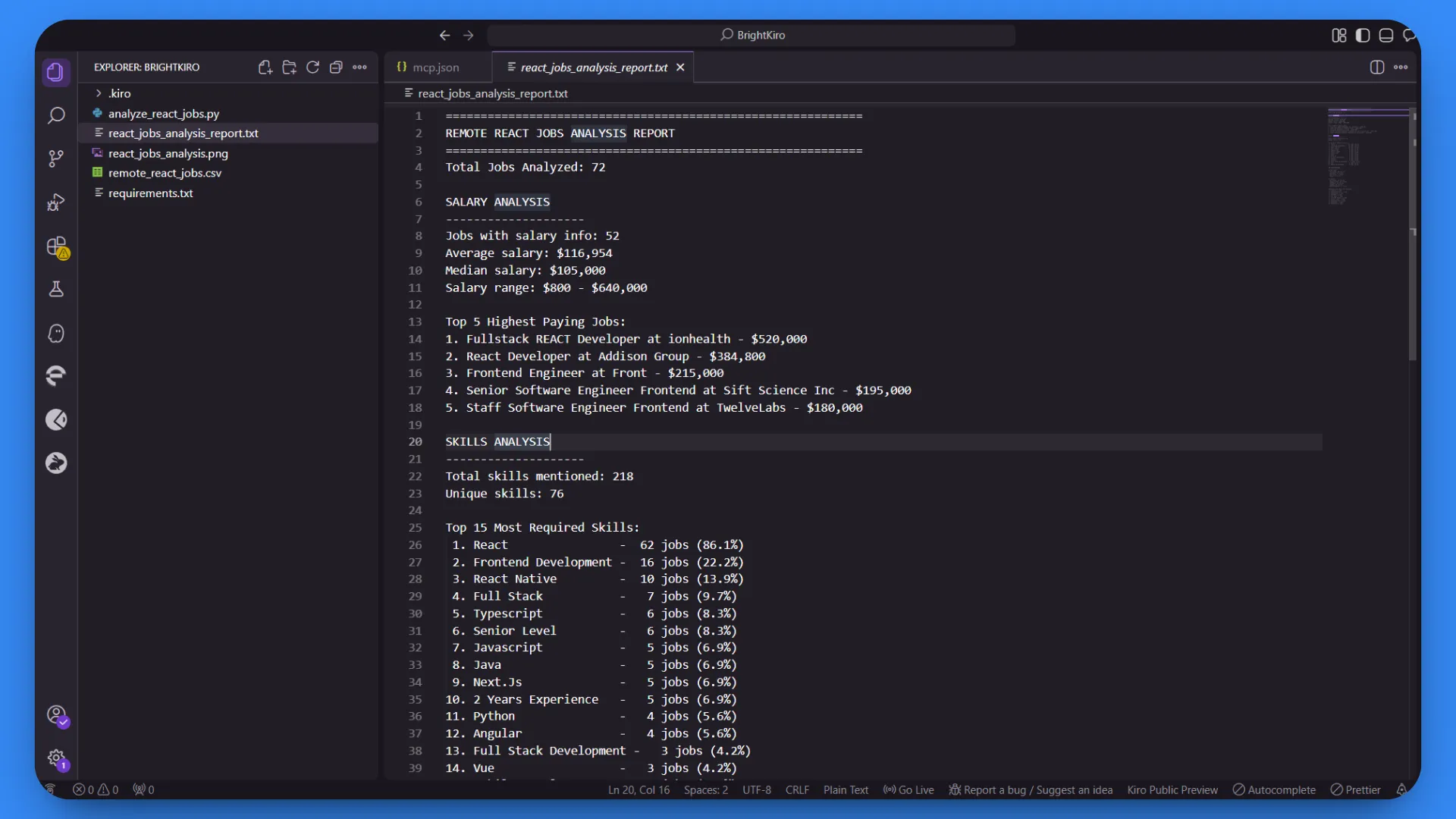
1. Detailed Text Report (react_jobs_analysis_report.txt):
2. Visual Analytics Chart (react_jobs_analysis.png):
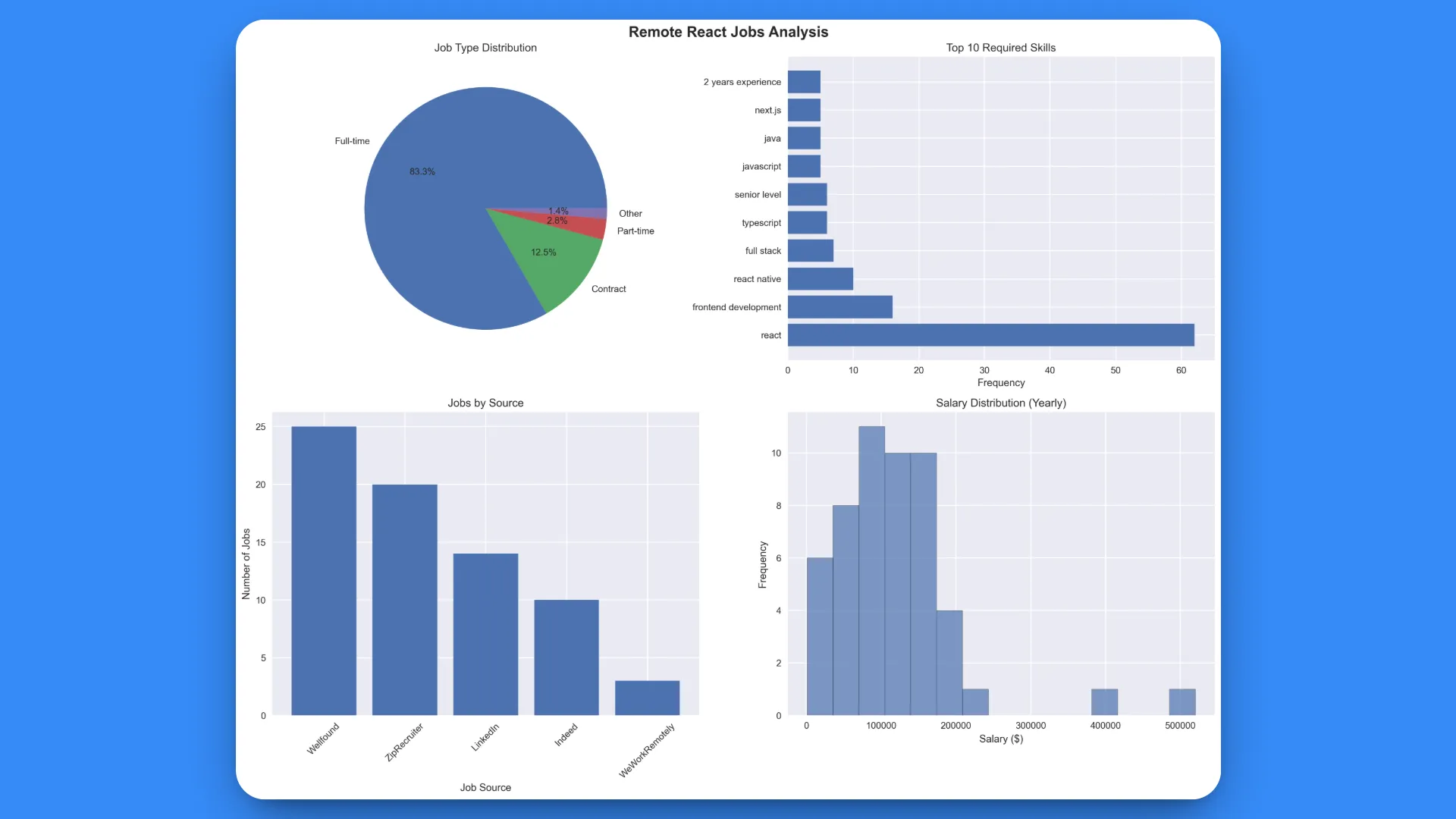
The comprehensive analysis was based on 72 jobs successfully collected.
The generated visualization provides four key insights:
- Job Type Distribution: Clear breakdown of full-time vs contract vs part-time roles
- Top 10 Required Skills: Visual representation of skill demand frequency
- Jobs by Source: Platform-specific job posting volumes
- Salary Distribution: Histogram showing salary ranges across all positions
This shows how Kiro turns a simple request in natural language into a full data collection and analysis process. The integration automatically deals with web scraping problems, like adjusting when batch operations time out, while creating ready-to-use code, detailed reports, and professional visuals for ongoing market research.
Conclusion
That’s it for this tutorial. In this blog, you learned how to make Kiro better by connecting it with Bright Data’s Web MCP servers. This lets you scrape live web data and process real-time information right in your AI development setup.
We showed this with a practical example of scraping, cleaning, analyzing, and visualizing remote React developer jobs from different sources. This complete automation demonstrates the strength of combining Kiro’s AI with Bright Data’s top-notch scraping tools.
By using this integration, developers can go beyond static code generation to fully automated, data-driven workflows that speed up product development and improve accuracy.
Create your Bright Data account today and start using real-time web intelligence to power your AI agents.