In this guide, you will learn:
- Why web scraping is an excellent method for enriching LLMs with real-world data
- The benefits and challenges of using scraped data in LangChain workflows
- A library for simplified scraping integration in LangChain
- How to create a complete LangChain web scraping integration in a step-by-step tutorial
Let’s dive in!
Using Web Scraping to Power Your LLM Applications
Web scraping involves retrieving data from the web pages. That data can then be used to fuel RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) applications by integrating it with LLMs (Large Language Models).
RAG systems require access to rich, fresh, real-time, domain-specific, or expansive data that are not readily available in static datasets you can buy or download online. Web scraping bridges that gap by providing both structured information extracted from various sources such as news articles, product listings, and social media.
Learn more in our article on collecting LLM training data.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Scraped Data in LangChain
LangChain is a powerful framework for building AI-driven workflows, enabling simplified integration of LLMs with diverse data sources. It excels at data analysis, summarization, and question-answering by combining LLMs with real-time, domain-specific knowledge. However, acquiring high-quality data is always a problem.
Web scraping can tackle that problem, but it comes with several challenges, including anti-bot measures, CAPTCHAs, and dynamic websites. Maintaining compliant and efficient scrapers can also be time-consuming and technically complex. For more details, check out our guide on anti-scraping measures.
These hurdles can slow the development of AI-powered applications that depend on real-time data. The solution? Bright Data’s Web Scraper API—a ready-to-use tool offering scraping endpoints for hundreds of websites.
With advanced features like IP rotation, CAPTCHA solving, and JavaScript rendering, Bright Data automates data extraction for you. That ensures reliable, efficient, and hassle-free data collection, all accessible through simple API calls.
LangChain Bright Data Tools
Now, while you could integrate Bright Data’s Web Scraper API and other scraping tools directly into your LangChain workflow, doing so would require custom logic and boilerplate code. To save time and effort, you should prefer the official LangChain Bright Data integration package langchain-brightdata.
This package allows you to connect to Bright Data’s services within LangChain workflows. In particular, it exposes the following classes:
BrightDataSERP: Integrates with Bright Data’s SERP API to perform search engine queries with geo-targeting.BrightDataUnblocker: Works with Bright Data’s Web Unlocker to access websites that may be geo-restricted or protected by anti-bot systems.BrightDataWebScraperAPI: Interfaces with Bright Data’s Web Scraper API to extract structured data from various domains.
In this tutorial, we will focus on using the BrightDataWebScraperAPI class. Time to see how!
LangChain Web Scraping Powered By Bright Data: Step-by-Step Guide
In this section, you will learn how to build a LangChain web scraping workflow. The goal is to utilize LangChain to retrieve content from a LinkedIn profile using Bright Data’s Web Scraper API and then use OpenAI to evaluate whether the candidate is a good match for a specific job position.
We will use my public LinkedIn profile page as the reference, but any other LinkedIn profile will work as well:

Note: What we are building here is just an example. The code you are about to write is easily adaptable to different scenarios. That means it can also be extended with additional features from LangChain. For instance, you could even create a RAG chatbot based on SERP data.
Follow the steps below to get started!
Prerequisites
To get through this tutorial, you will need the following:
- Python 3+ installed on your machine
- An OpenAI API key
- A Bright Data account
Do not worry if you are missing any of these. We will guide you through the entire process, from installing Python to obtaining your OpenAI and Bright Data credentials.
Step #1: Project Setup
First of all, check if Python 3 is installed on your machine. If not, download and install it.
Run this command in the terminal to create a folder for your project:
mkdir langchain-scrapinglangchain-scraping will contain your Python LangChain scraping project.
Then, navigate to the project folder and initialize a Python virtual environment inside it:
cd langchain-scraping
python3 -m venv venvNote: On Windows, use python instead of python3.
Now, open the project directory in your favorite Python IDE. PyCharm Community Edition or Visual Studio Code with the Python extension will do.
Inside langchain-scraping, add a script.py file. This is an empty Python script, but it will soon contain your LangChain web scraping logic.
In the IDE’s terminal, on Linux or macOS, activate the virtual environment with the command below:
source venv/bin/activateOr, on Windows, run:
venv/Scripts/activateAwesome! You are now fully set up.
Step #2: Install the Required Libraries
The Python LangChain scraping project relies on the following libraries:
python-dotenv: To load environment environment variables from a.envfile. It will be used to manage the Bright Data and OpenAI API keys.langchain-openai: LangChain integrations for OpenAI through itsopenaiSDK.langchain-brightdata: LangChain integration with Bright Data scraping services.
In an activated virtual environment, install all the dependencies with this command:
pip install python-dotenv langchain-openai langchain-brightdataAmazing! You are ready to write some scraping logic.
Step #3: Prepare Your Project
In script.py, add the following import:
from dotenv import load_dotenvThen, create a .env file in your project folder to store all your credentials. Here is what your current project file structure should look like:

Instruct python-dotenv to load the environment variables from .env with this line in script.py:
load_dotenv()Cool! Time to configure Bright Data’s Web Scraper API solution.
Step #4: Configure Web Scraper API
As mentioned at the beginning of this article, web scraping comes with several challenges. Fortunately, it becomes significantly easier with an all-in-one solution like Bright Data’s Web Scraper APIs. These APIs allow you to retrieve parsed content from over 120 websites effortlessly.
To set up the Web Scraper API in LangChain using langchain_brightdata, follow the instructions below. For a general introduction to Bright Data’s scraping solution, refer to the official documentation.
If you have not already, create a Bright Data account. After logging in, you will be directed to your account dashboard. From here, click the “Account settings” button located at the bottom left:

On the “Account Settings” page, If you have already created a Bright Data API token, click on the “…” and then select the “Copy token” option:

Otherwise, click the “Add token” button:

The following modal will show up. Configure your Bright DAta API token and press the “Save” button:

You will receive your new API token:

Copy the value of your Bright Data API key.
In your .env file, store this information as a BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY environment variable:
BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY="<YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY>"Replace <YOUR_BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY> with the value you copied from the modal/table.
Now, in script.py, import langchain_brightdata:
from langchain_brightdata import BrightDataWebScraperAPINo further action is required, as langchain_brightdata automatically attempts to read the Bright Data API key from the BRIGHT_DATA_API_KEY environment variable.
Here we go! Your can now use Web Scraper API in LangChain.
Step #5: Use Bright Data for Web Scraping
langchain_brightdata supports integration with Bright Data’s Web Scraper API through the BrightDataWebScraperAPI class.
Below is an overview of how that class works:
- It makes a synchronous request to the configured Web Scraper API, accepting the URL of the page to scrape.
- A cloud-based scraping task is launched to retrieve and parse data from the specified URL.
- The library waits for the scraping task to terminate, then it returns the scraped data in JSON format.
To integrate web scraping into your LangChain workflow, define a reusable function with the following code:
def get_scraped_data(url, dataset_type):
# Initialize the LangChain Bright Data Scraper API integration class
web_scraper_api = BrightDataWebScraperAPI()
# Retrieve the data of interest by connecting to Web Scraper API
results = web_scraper_api.invoke({
"url": url,
"dataset_type": dataset_type
})
return resultsThe function accepts the following arguments:
url: The URL of the page to retrieve data from.dataset_type: Specifies the type of Web Scraper API to use for extracting data from the page. For example,"linkedin_person_profile"instructs the Web Scraper API to scrape data from the public LinkedIn profile URL provided.
In this example, call it as follows:
url = "https://linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini"
scraped_data = get_scraped_data(url, "linkedin_person_profile")scraped_data will contain data like this:
{
"input": {
"url": "https://linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini"
},
"id": "antonello-zanini",
"name": "Antonello Zanini",
# Omitted for brevity...
"about": "I'm a freelance software engineer, technical editor, and technical writer with hundreds...",
"current_company": {
"name": "Freelance"
},
"current_company_name": "Freelance",
# Omitted for brevity...
"languages": [
{
"title": "Italian",
"subtitle": "Native or bilingual proficiency"
},
{
"title": "English",
"subtitle": "Full professional proficiency"
},
{
"title": "Spanish",
"subtitle": "Full professional proficiency"
}
],
"recommendations_count": 32,
"recommendations": [
# Omitted for brevity...
],
"posts": [
# Omitted for brevity...
],
"activity": [
# Omitted for brevity...
],
# Omitted for brevity...
}In detail, it stores all the information available on the public version of the target LinkedIn profile page—but structured in JSON format. To get that data, Web Scraper API bypassed any anti-bot or anti-scraping mechanisms for you.
Incredible! You just learned how to use Bright Data Web’s Scraper API for web scraping in LangChain.
Step #6: Get Ready to Use OpenAI Models
This example relies on OpenAI models for LLM integration within LangChain. To use those models, you must configure an OpenAI API key in your environment variables.
Thus, add the following line to your .env file:
OPENAI_API_KEY="<YOUR_OPEN_API_KEY>"Replace <YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY> with the value of your OpenAI API key. If you do not know how to get one, follow the official guide.
Now, in script.py, import langchain_openai like this:
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAIYou do not need to do anything else. langchain_openai will automatically look for your OpenAI API key in the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable.
Great! Time to use OpenAI models in your LangChain scraping script.
Step #7: Generate the LLM Prompt
Define an f-string variable that takes the scraped data and generates a prompt for the LLM. In this case, the prompt includes your HR request and embeds the scraped candidate data:
prompt = f"""
"Do you think this candidate is a good fit for a remote Software Engineer position? Why?
Answer in no more than 150 words.
CANDIDATE:
'{scraped_data}'
"""In this example, you are building an HR advisor AI workflow using LangChain. Thanks to the flexibility of Web Scraper API (which supports over 120 domains) combined with LLMs, you can easily adapt this approach to power a wide range of other LangChain workflows.
💡 Idea: For even greater flexibility, consider reading the prompt from the .env file.
In the current example, the complete prompt will be:
Do you think this candidate is a good fit for a remote Software Engineer position? Why?
Answer in no more than 150 words.
CANDIDATE:
'{
"input": {
"url": "https://linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini"
},
"id": "antonello-zanini",
"name": "Antonello Zanini",
// omitted for brevity...
"about": "I'm a freelance software engineer, technical editor, and technical writer with hundreds...",
},
[ommitted for brevity...]'If you pass it to ChatGPT, you should get the desired result:
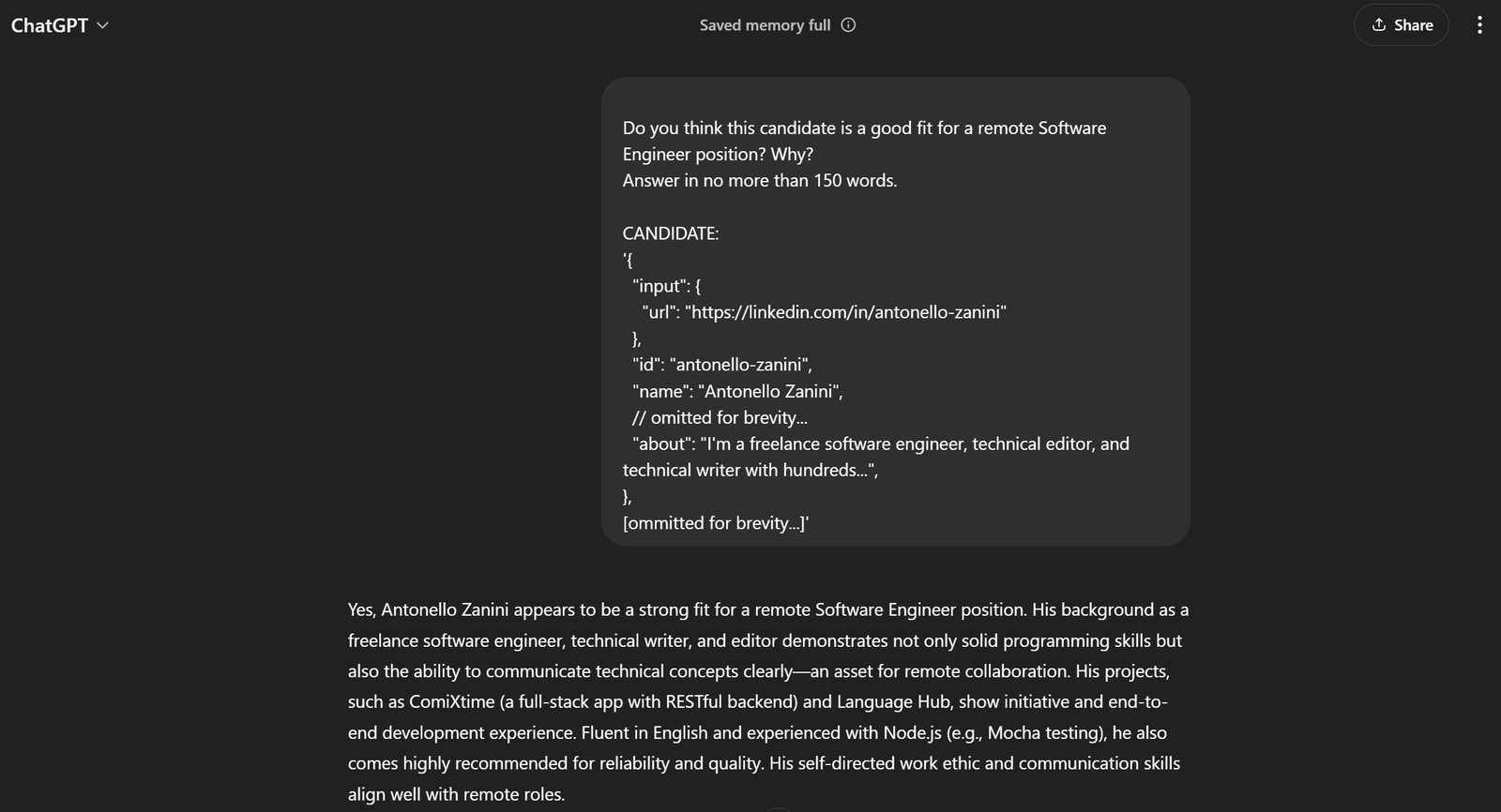
This is enough to tell that the prompt works like a charm!
Step #8: Integrate OpenAI
Pass the prompt you generated earlier to a ChatOpenAI LangChain object configured on the GPT-4o mini AI model:
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
response = model.invoke(prompt)At the end of the AI processing, response.content should contain a result similar to the evaluation generated by ChatGPT in the previous step. Access that text response with:
evaluation = response.contentWow! The LangChain web scraping logic is complete.
Step #9: Export the AI-Processed Data
Now, you just need to export the data generated by the selected AI model via LangChain to a human-readable format, such as a JSON file.
First, nitialize a dictionary with the data you want. Then, export and then save it as a JSON file, as shown below:
export_data = {
"url": url,
"evaluation": evaluation
}
file_name = "analysis.json"
with open(file_name, "w") as file:
json.dump(export_data, file, indent=4)Import json from the Python Standard Library:
import jsonCongrats! Your script is ready.
Step #10: Add Some Logs
The scraping process using Web Scraping AI and ChatGPT analysis may take some time. This is normal due to the overhead involved in scraping and processing data from third-party services. Therefore, it is a good practice to include logging to track the script’s progress.
Achieve that by adding print statements at key steps in the script, as follows:
url = "https://linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini"
print(f"Scraping data with Web Scraper API from {url}...")
scraped_data = get_scraped_data(url, "linkedin_person_profile")
print("Data successfully scrapedn")
print("Creating the AI prompt...")
prompt = f"""
"Do you think this candidate is a good fit for a remote Software Engineer position? Why?
Answer in no more than 150 words.
CANDIDATE:
'{scraped_data}'
"""
print("Prompt createdn")
print("Sending prompt to ChatGPT...")
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
response = model.invoke(prompt)
evaluation = response.content
print("Received response from ChatGPTn")
print("Exporting data to JSON"...)
export_data = {
"url": url,
"evaluation": evaluation
}
file_name = "analysis.json"
with open(file_name, "w") as file:
json.dump(export_data, file, indent=4)
print(f"Data exported to '{file_name}'")Note that each step of the LangChain web scraping workflow is clearly logged. The execution in the terminal will now be much easier to follow.
Step #11: Put It All Together
Your final script.py file should contain:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from langchain_brightdata import BrightDataWebScraperAPI
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
import json
# Load the environment variables from the .env file
load_dotenv()
def get_scraped_data(url, dataset_type):
# Initialize the LangChain Bright Data Scraper API integration class
web_scraper_api = BrightDataWebScraperAPI()
# Retrieve the data of interest by connecting to Web Scraper API
results = web_scraper_api.invoke({
"url": url,
"dataset_type": dataset_type
})
return results
# Retrieve the content from the given web page
url = "https://linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini"
print(f"Scraping data with Web Scraper API from {url}...")
# Use Web Scraper API to get the scraped data
scraped_data = get_scraped_data(url, "linkedin_person_profile")
print("Data successfully scrapedn")
print("Creating the AI prompt...")
# Define the prompt using the scraped data as context
prompt = f"""
"Do you think this candidate is a good fit for a remote Software Engineer position? Why?
Answer in no more than 150 words.
CANDIDATE:
'{scraped_data}'
"""
print("Prompt createdn")
# Ask ChatGPT to perform the task specified in the prompt
print("Sending prompt to ChatGPT...")
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
response = model.invoke(prompt)
# Get the AI result
evaluation = response.content
print("Received response from ChatGPTn")
print("Exporting data to JSON...")
# Export the produced data to JSON
export_data = {
"url": url,
"evaluation": evaluation
}
# Write the output dictionary to JSON file
file_name = "analysis.json"
with open(file_name, "w") as file:
json.dump(export_data, file, indent=4)
print(f"Data exported to '{file_name}'")Can you believe it? In around 50 lines of code, you just build an AI-based LangChain web scraping script.
Verify that it works with this command:
python3 script.pyOr, on Windows:
python script.pyThe output in the terminal should be:
Scraping data with Web Scraper API from https://linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini...
Data successfully scraped
Creating the AI prompt...
Prompt created
Sending prompt to ChatGPT...
Received response from ChatGPT
Exporting data to JSON...
Data exported to 'analysis.json'Open the analysis.json file that appeared in the project’s directory and you should see something like this:
{
"url": "https://linkedin.com/in/antonello-zanini",
"evaluation": "Antonello Zanini appears to be a strong candidate for a remote Software Engineer position. His experience as a freelance software engineer indicates adaptability and self-motivation, crucial for remote work. His technical writing and editorial background suggest strong communication skills, essential for collaborating with remote teams. Additionally, his diverse programming knowledge, evidenced by posts on unit testing and JavaScript bundlers, reinforces his technical expertise.nnHe has garnered significant positive feedback from clients, emphasizing his reliability and clarity in deliverables, which are critical traits for effective remote collaboration. Moreover, his multilingual abilities in Italian, English, and Spanish can enhance communication in diverse international teams. Overall, Antonello's combination of technical proficiency, communication skills, and positive recommendations makes him an excellent fit for a remote position."
}Et voilà! The HR LangChain workflow, enriched with live data, is now complete.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you discovered why web scraping is an effective method for gathering data for your AI workflows and how to analyze that data using LangChain.
Specifically, you created a Python-based LangChain web scraping script to extract data from a LinkedIn profile page and process it using OpenAI APIs. While this LangChain workflow is ideal for supporting HR tasks, the code shown can easily be extended to other workflows and scenarios.
The main challenges with web scraping in LangChain are:
- Online sites often change their page structures.
- Many sites implement advanced anti-bot measures.
- Retrieving large volumes of data simultaneously can be complex and expensive.
Bright Data’s Web Scraper API represents an effective solution for extracting data from major websites, easily overcoming these challenges. Thanks to its smooth integration with LangChain, it is an invaluable tool for supporting RAG applications and other LangChain-powered solutions.
Be also sure to explore our additional offerings for AI and LLM.
Sign up now to discover which of Bright Data’s proxy services or scraping products best suit your needs. Start with a free trial!